Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
AAKASH INSTITUTE-DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS-Assignment Section - J (Aakash Challengers Questions)
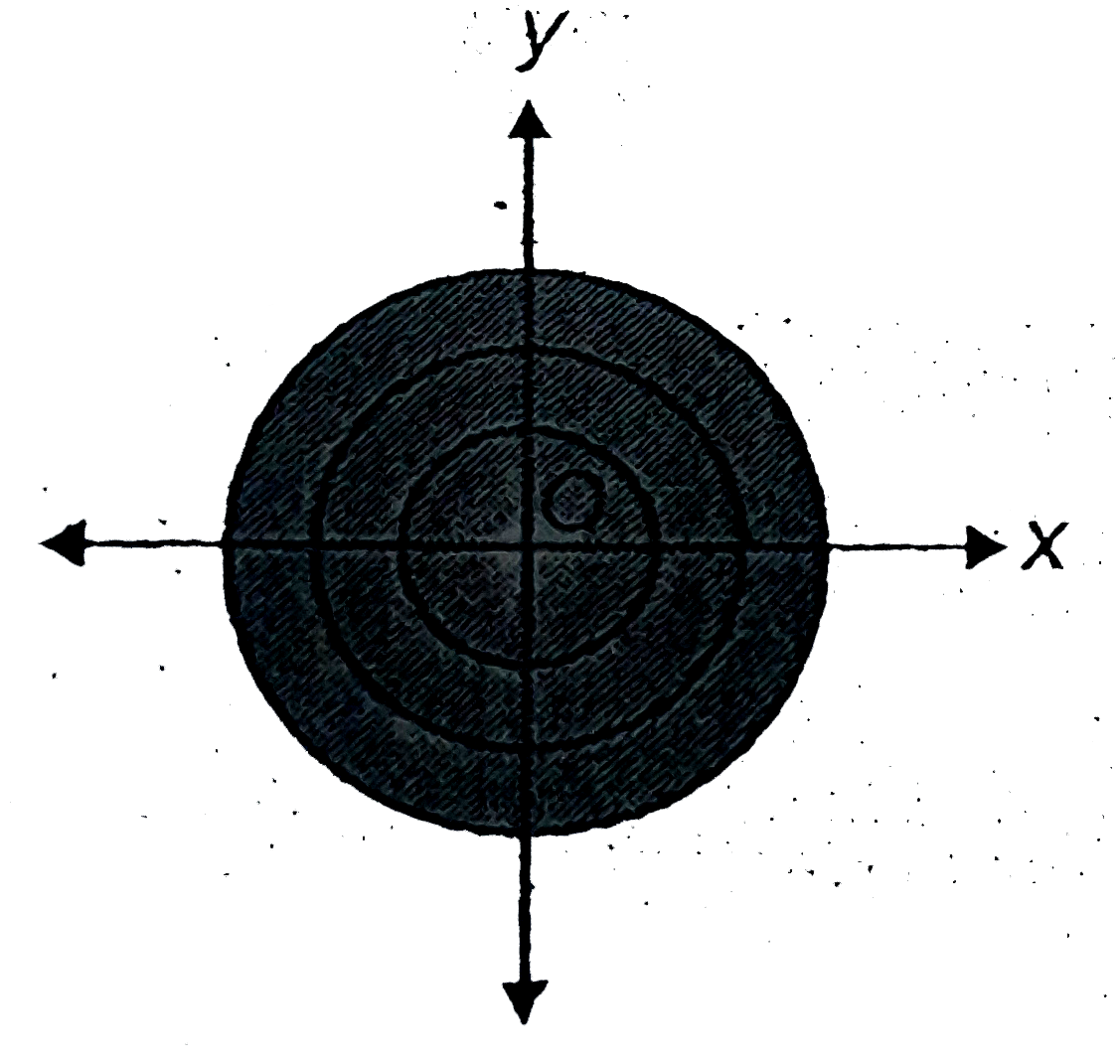
- Form the differential equation of all the circles whose centre is at o...
Text Solution
|
- Find the family of curves, the subtangent at any point of which is the...
Text Solution
|
- A line is drawn from a point P(x, y) on the curve y = f(x), making an ...
Text Solution
|
- A tangent and a normal to a curve at any point P meet the x and y axes...
Text Solution
|
- Given two curves y = f(x) passing through (0, 1) and y = int(-oo)^(x) ...
Text Solution
|