Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
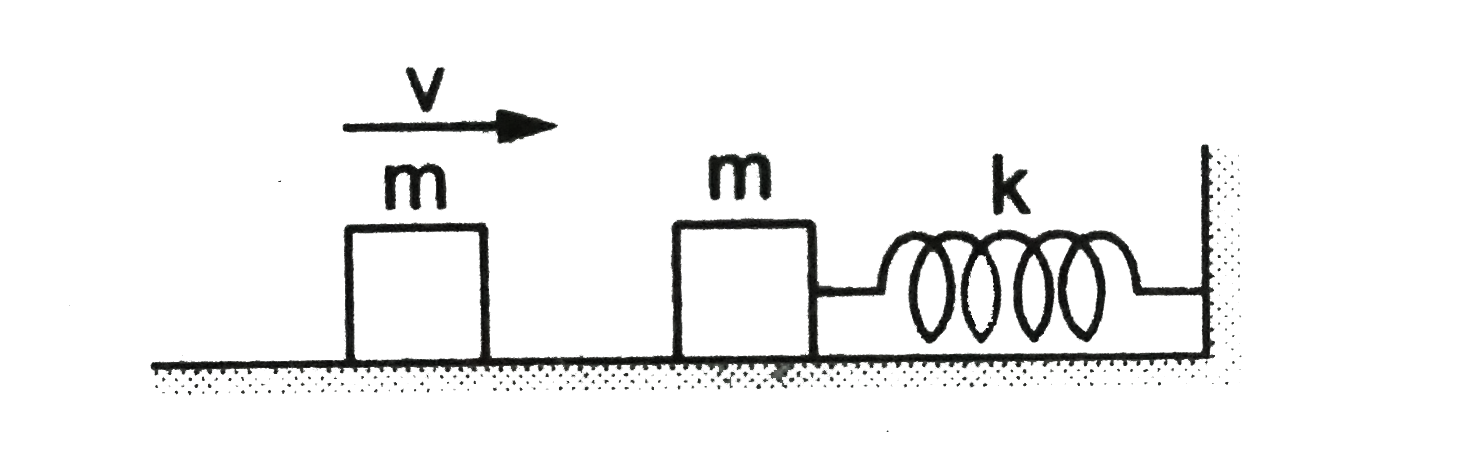
- The left block in filgure collides inelastically with the right block ...
Text Solution
|
- The left block in filgure collides inelastically with the right block ...
Text Solution
|
- A 1kg block is executing simple harmonic motion of amplitude 0.1m on a...
Text Solution
|
- A block is resting on a piston which is moving vertically with simple ...
Text Solution
|
- (a) The right block collides with left block and sticks to it. Find am...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 'm' collides perfectly inelastically with another iden...
Text Solution
|
- A block is resting on a piston which is moving vertically with simple ...
Text Solution
|
- The left block in figure collides inelastically with the right block a...
Text Solution
|
- चित्र 21.W5 में बायी और का ब्लॉक दाहिनी और के ब्लॉक से अप्रत्यास्थ टक्...
Text Solution
|