Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
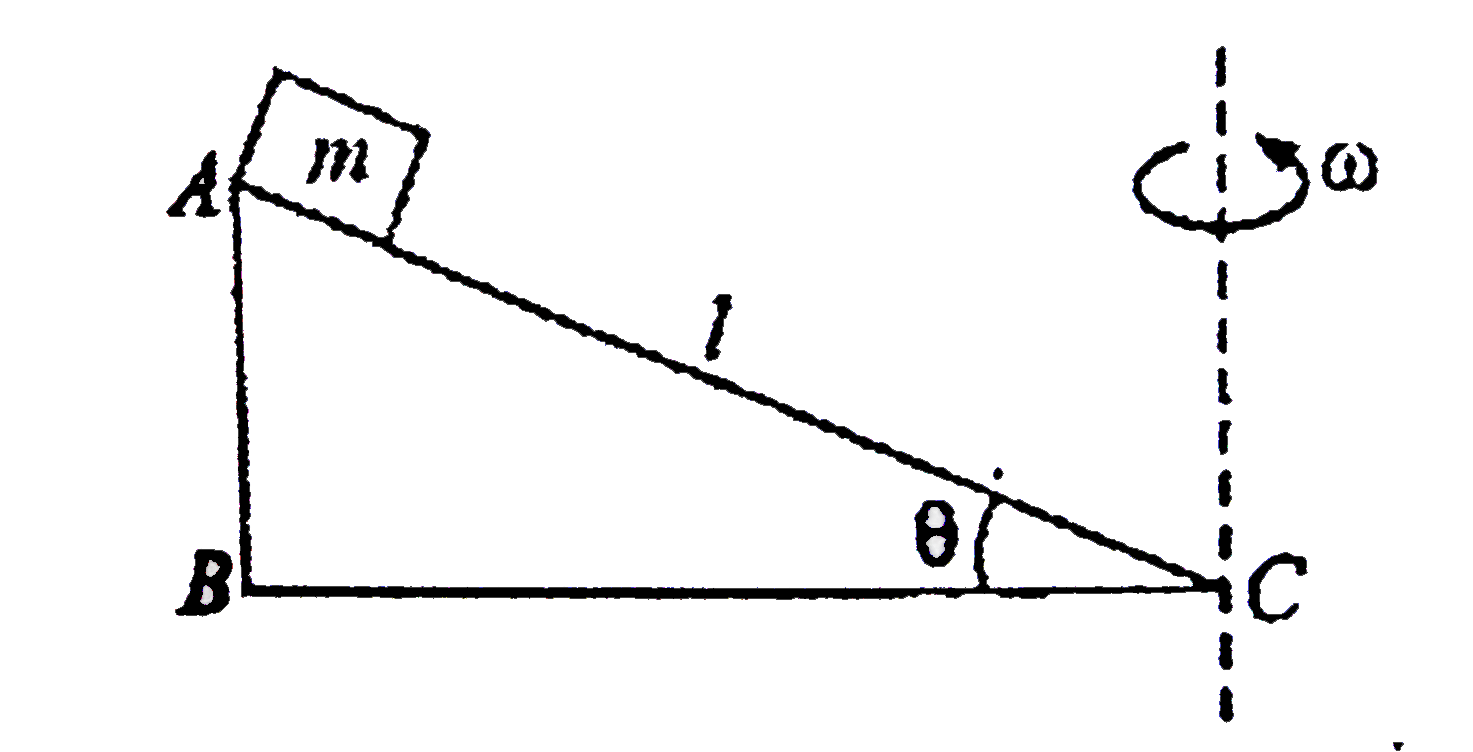
- A block of mass m is placed at the top of a smooth wedge ABC. The wedg...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is placed on a smooth wedge of incination theta. The...
Text Solution
|
- A small wedge whose base is horizontal is fixed to a vertical rod as s...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is placed on a smooth inclined wedge ABC of inclinat...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is placed on a smooth wedge of inclination. The whol...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is placed on a smooth wedge of inclination theta. T...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is placed on a smooth wedge of inclination theta & m...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is placed at the top of a smooth wedge ABC. The wedg...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is placed on a smooth wedge of wedge angle theta The...
Text Solution
|