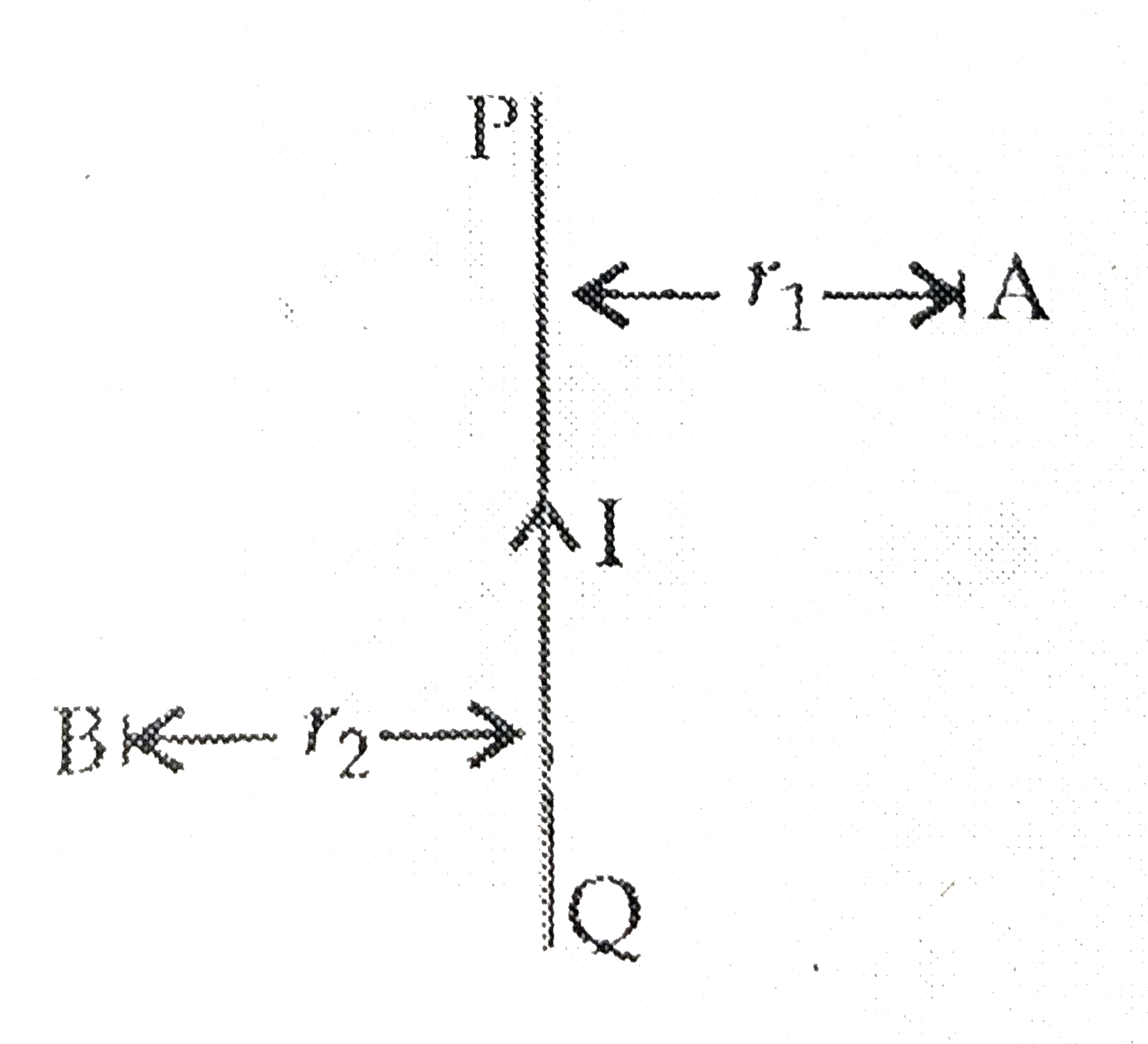Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- (i) State Maxwell's right-hand thumb rule. (ii) PQ is a current carr...
Text Solution
|
- AB is a current-carrying conductor in the plane of the paper as shown ...
Text Solution
|
- Find the direction of magnetic field at a point P due to two infinite ...
Text Solution
|
- (i) State Maxwell's right-hand thumb rule. (ii) PQ is a current carr...
Text Solution
|
- State Maxwell's right handed cork screw rule to find the direction of ...
Text Solution
|
- PQ is a current carrying conductor in the plane of the paper as shown ...
Text Solution
|
- Magnetic Field and Field Lines| Magnetic Field Due to Current Carrying...
Text Solution
|
- A current circular conducting loop exerts a magnetic field both inside...
Text Solution
|
- Assertion (A) : A straight wire carries current in the vertically upw...
Text Solution
|