Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
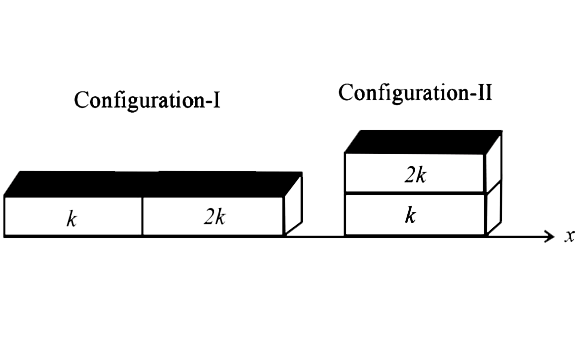
- Two rectangular blocks, having identical dimensions, an be arranged ei...
Text Solution
|
- Two rectangular blocks, having identical dimensions, an be arranged ei...
Text Solution
|
- Two rods with the same dimensions have thermal conductivities in the r...
Text Solution
|
- एथेन के दो छोरवाले संरूपण ……………... और ……………... कहलाते है।
Text Solution
|
- Electronic configuration of is block of elements is
Text Solution
|
- संरूपण और विन्यास में अन्तर समझाइये।
Text Solution
|
- दो समरूपी आयताकार गुटकों को दर्शाये चित्रानुसार दो विन्यासों I और II म...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following electronic configuration does not be belongs to...
Text Solution
|
- Give the general electronic configurations of (i) p-block " " (ii)...
Text Solution
|