Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
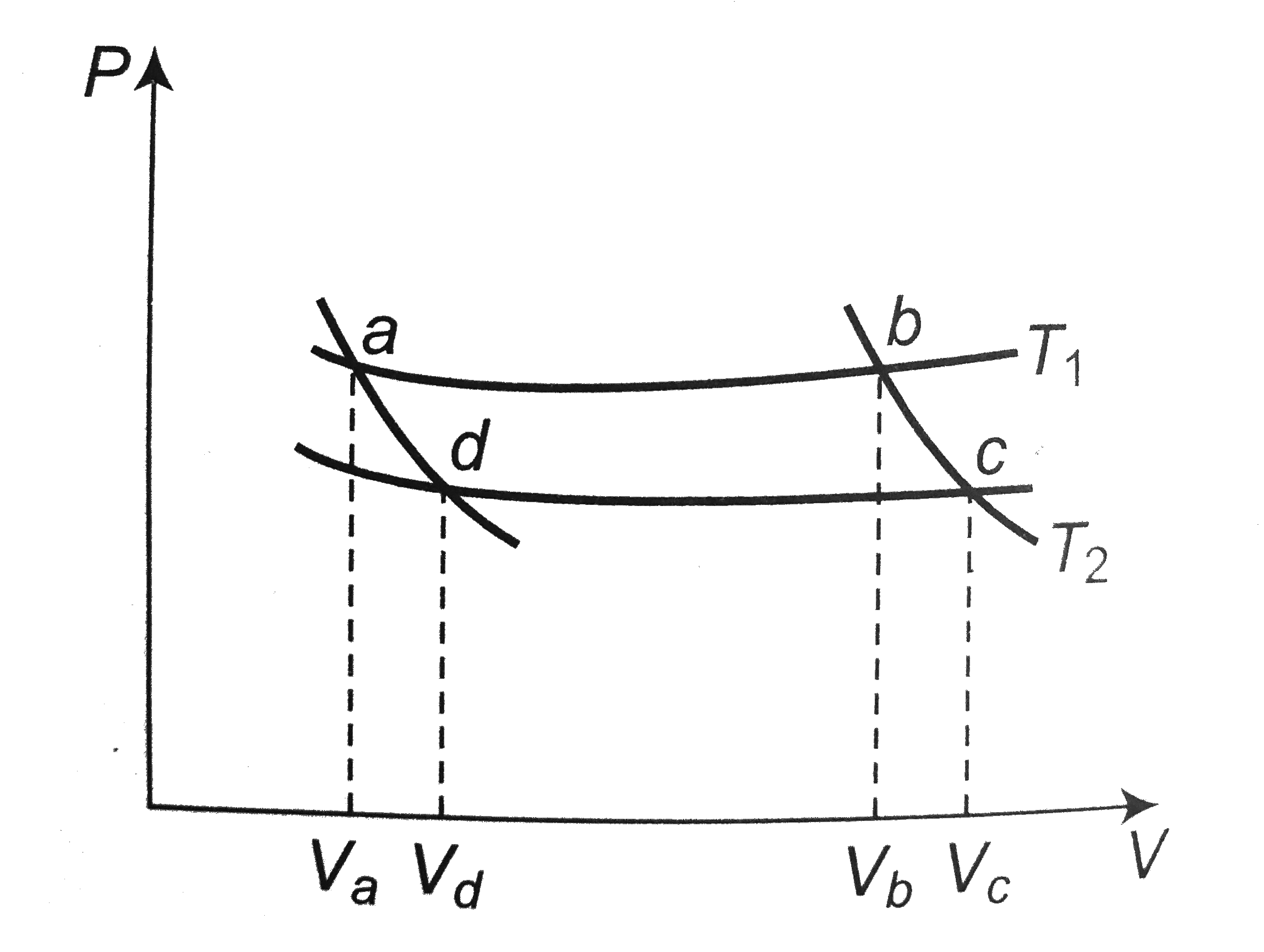
- In the following P-V diagram two adiabatics cut two isothermals at tem...
Text Solution
|
- In the following P-V diagram two adiabatics cut two isothermals at tem...
Text Solution
|
- Two different adiabatic curves for the same gas intersect two isotherm...
Text Solution
|
- Letvec(V) =v(x)hat(i)+v(y)hat(j)+v(z)hat(k), then int(t(1))^(t(2)) V(y...
Text Solution
|
- For any arbitrary motion in space, which of the following relations ar...
Text Solution
|
- Two different adiabatic parts for the same gas intersect two isotherma...
Text Solution
|
- यदि वस्तु समय t(1) तक वेग v(1) से तथा समय t(2) तक वेग v(2) से चले तो...
Text Solution
|
- Two curves are given at temperatures T(1) and T(2) in an isothermal pr...
Text Solution
|
- एक समान त्वरण के साथ गतिमान एक कण के औसत वेग, v एवं क्रमिक समयान्तरालो...
Text Solution
|