One mole of a substance is cooled at the rate of `0.4 kJ min^(-1)` as shown in the graph. Curve `AB`, points `B` and `C` and curve `CD` represent respectively, the cooling of the liquid, start of freezing, completion of freezing and cooling of the solid based on this data. The entropy of fusion in `J molK^(-1)` is :
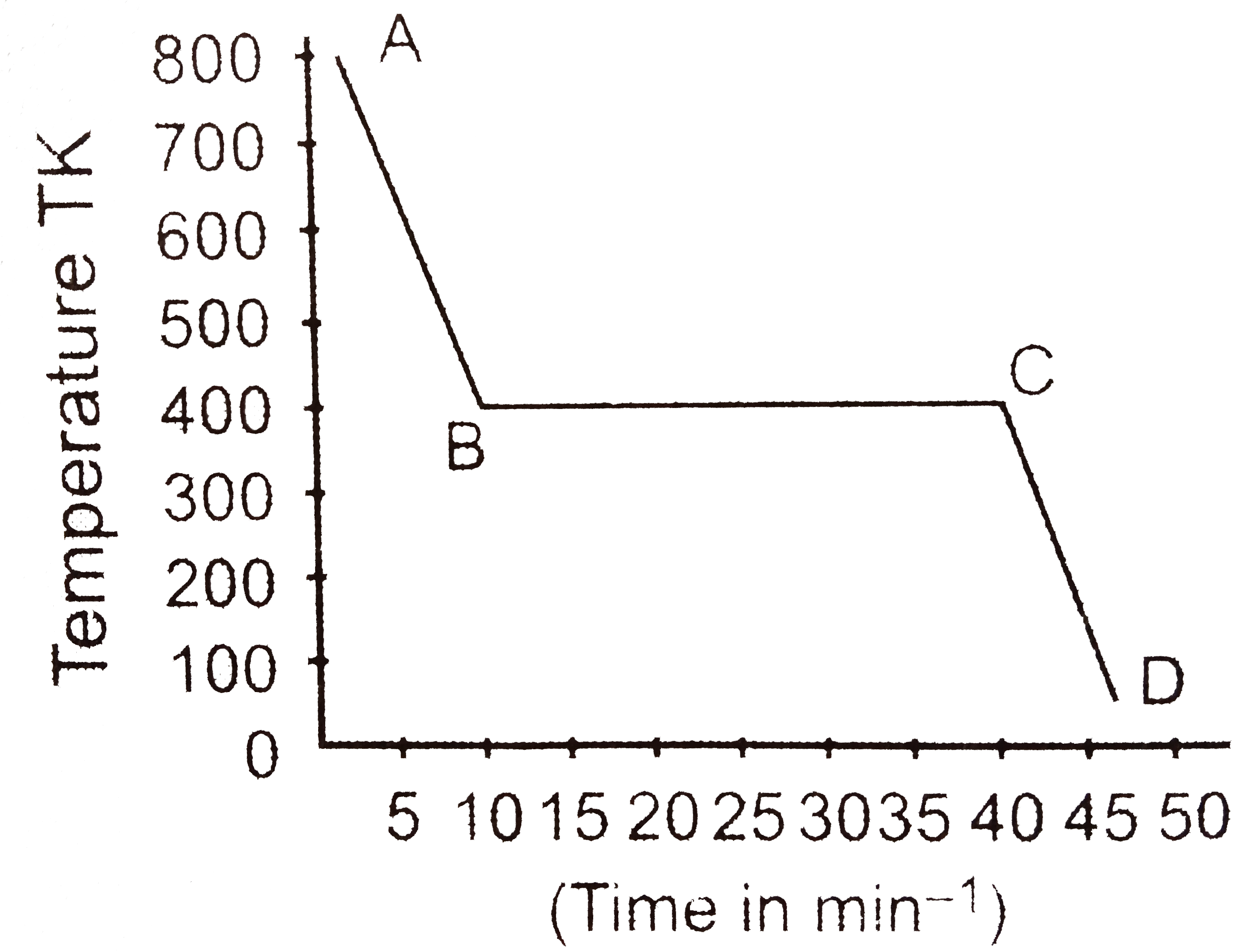
One mole of a substance is cooled at the rate of `0.4 kJ min^(-1)` as shown in the graph. Curve `AB`, points `B` and `C` and curve `CD` represent respectively, the cooling of the liquid, start of freezing, completion of freezing and cooling of the solid based on this data. The entropy of fusion in `J molK^(-1)` is :
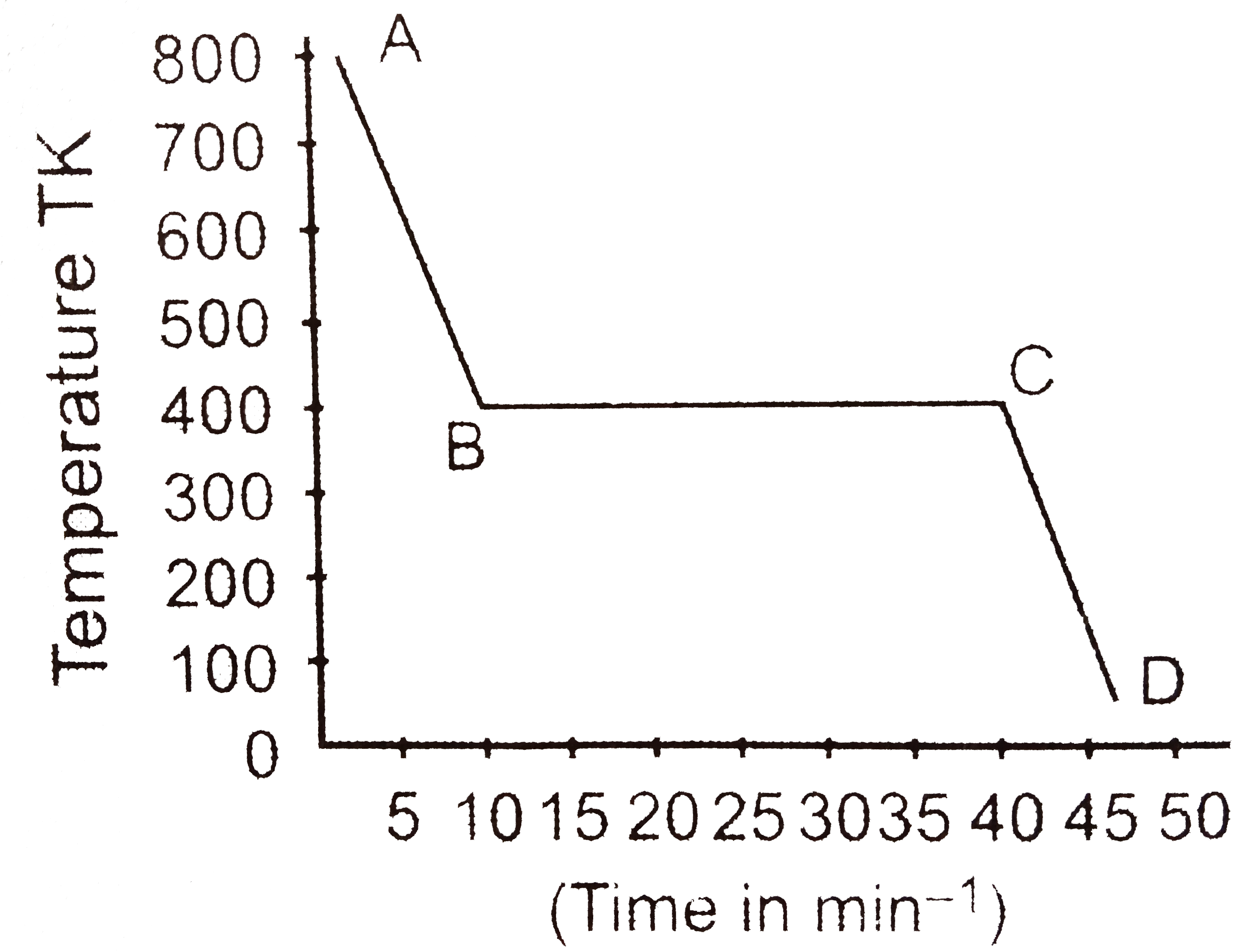
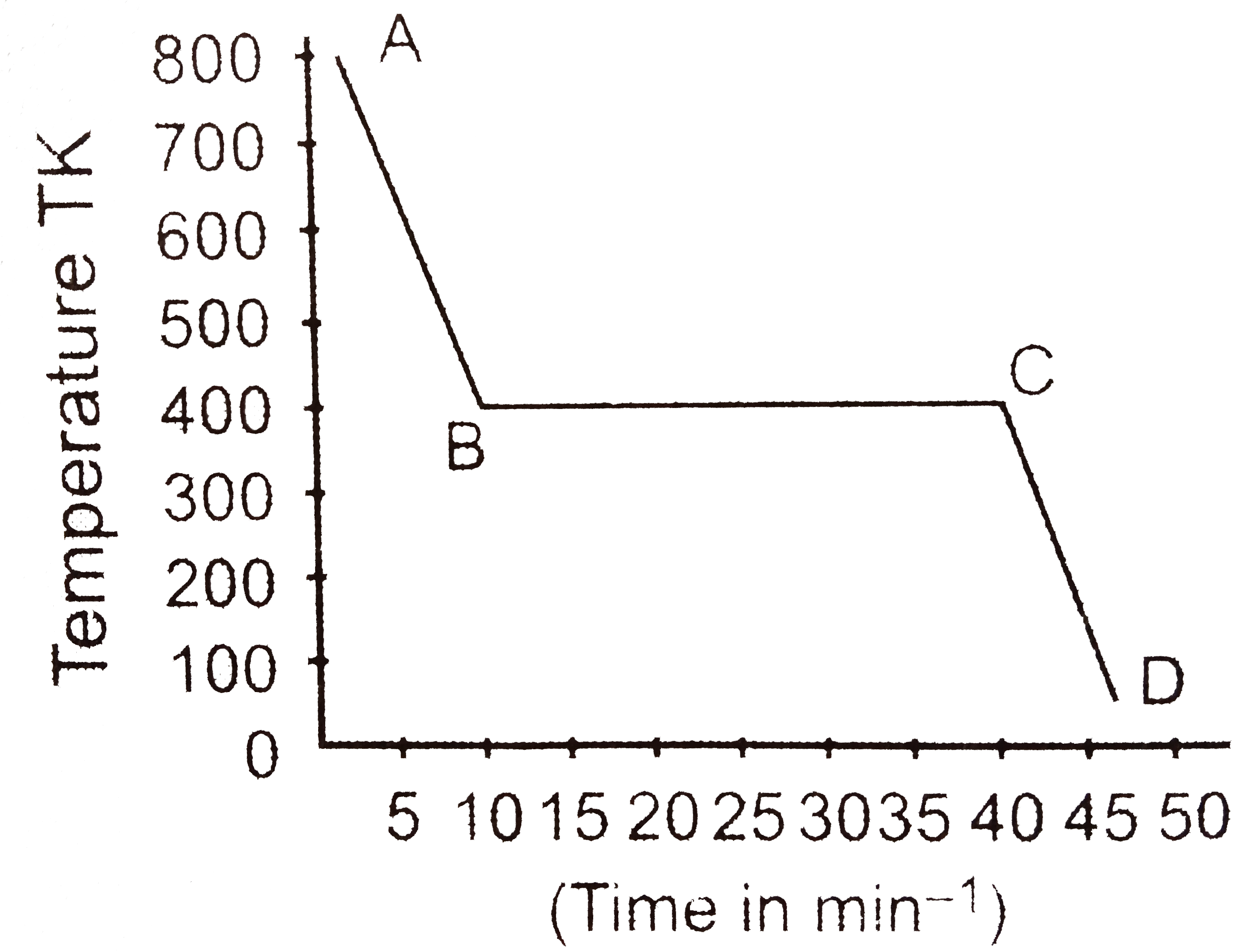
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
The curve shown results when a liquid is cooled. What temperature is closest to the freezing point of the liquid ?
A solution containing 0.1 mole of naphthalenen and 0.9 mole of benzenen is cooled out until some benzene freezes out. The solution is then decanted off from the solid and warmed upto 353K where its vapour pressure was found to be 670 torr. The freezing point and and boiling point of benzene are 278.5K and 353K respectively and its enthalpy of fusion is 10.67 Lk "mol"^(-1) . Calculate the temperature to which the solution was cooled originally and the amount of benzene that must have frozen out. Assume ideal behavious.
A solution containing 0.1 mol of naphthalene and 0.9 mol of benzene is cooled out until some benzene freezes out. The solution is then decanted off from the solid and warmed upto 353 K where its vapour pressure was found to be 670 mm . The freezing point and boiling point of benzene are 278.5 K and 353 K respectively, and its enthalpy of fusion is 10.67 KJ "mol"^(-1) . Calculate the temperature to which the solution was cooled originally and the amount of benzene that must have frozen out. Assume ideal behaviour.
A solution containing 0.1 mol of naphthalene and 0.9 mol of benzene is cooled out until some benzene freezes out. The solution is then decanted off from the solid and warmed upto 353 K where its vapour pressure was found to be 670 mm . The freezing point and boiling point of benzene are 278.5 K and 353 K respectively, and its enthalpy of fusion is 10.67 KJ "mol"^(-1) . Calculate the temperature to which the solution was cooled originally and the amount of benzene that must have frozen out. Assume ideal behaviour.
A solution containing 0.1 mol of naphthalene and 0.9 mol of benzene is cooled out until some benzene freezes out. The solution is then decanted off from the solid and warmed upto 353 K where its vapour pressure was found to be 670 mm . The freezing point and boiling point of benzene are 278.5 K and 353 K respectively, and its enthalpy of fusion is 10.67 KJ "mol"^(-1) . Calculate the temperature to which the solution was cooled originally and the amount of benzene that must have frozen out. Assume ideal behaviour.
The given graph represents the cooling curve of substance X. Which of the following statements are incorrect? I. Process I represents cooling of liquid state of X while process III involves cooling of the solid state. II. The freezing point of substance X is 25^(@)C . III. At 35^(@)C , the substance exists in solid state. IV. Substance X exists both in gaseous and liquid form along the curve QR.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions: Boiling point or freezing point of liquid solution would be affected by the dissolved solids in the liquid phase. A soluble solid in solution has the effect of raising its boiling point and depressing its freezing point. The addition of non-volatile substances to a solvent decreases the vapor pressure and the added solute particles affect the formation of pure solvent crystals. According to many researches the decrease in freezing point directly correlated to the concentration of solutes dissolved in the solvent. This phenomenon is expressed as freezing point depression and it is useful for several applications such as freeze concentration of liquid food and to find the molar mass of an unknown solute in the solution. Freeze concentration is a high quality liquid food concentration method where water is removed by forming ice crystals. This is done by cooling the liquid food below the freezing point of the solution. The freezing point depression is referred as a colligative property and it is proportional to the molar concentration of the solution (m), along with vapor pressure lowering, boiling point elevation, and osmotic pressure. These are physical characteristics of solutions that depend only on the identity of the solvent and the concentration of the solute. The characters are not depending on the solute’s identity. (Jayawardena, J. A. E. C., Vanniarachchi, M. P. G., & Wansapala, M. A. J. (2017). Freezing point depression of different Sucrose solutions and coconut water.) When a non volatile solid is added to pure water it will:
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions: Boiling point or freezing point of liquid solution would be affected by the dissolved solids in the liquid phase. A soluble solid in solution has the effect of raising its boiling point and depressing its freezing point. The addition of non-volatile substances to a solvent decreases the vapor pressure and the added solute particles affect the formation of pure solvent crystals. According to many researches the decrease in freezing point directly correlated to the concentration of solutes dissolved in the solvent. This phenomenon is expressed as freezing point depression and it is useful for several applications such as freeze concentration of liquid food and to find the molar mass of an unknown solute in the solution. Freeze concentration is a high quality liquid food concentration method where water is removed by forming ice crystals. This is done by cooling the liquid food below the freezing point of the solution. The freezing point depression is referred as a colligative property and it is proportional to the molar concentration of the solution (m), along with vapor pressure lowering, boiling point elevation, and osmotic pressure. These are physical characteristics of solutions that depend only on the identity of the solvent and the concentration of the solute. The characters are not depending on the solute’s identity. (Jayawardena, J. A. E. C., Vanniarachchi, M. P. G., & Wansapala, M. A. J. (2017). Freezing point depression of different Sucrose solutions and coconut water.) Colligative properties are:
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions: Boiling point or freezing point of liquid solution would be affected by the dissolved solids in the liquid phase. A soluble solid in solution has the effect of raising its boiling point and depressing its freezing point. The addition of non-volatile substances to a solvent decreases the vapor pressure and the added solute particles affect the formation of pure solvent crystals. According to many researches the decrease in freezing point directly correlated to the concentration of solutes dissolved in the solvent. This phenomenon is expressed as freezing point depression and it is useful for several applications such as freeze concentration of liquid food and to find the molar mass of an unknown solute in the solution. Freeze concentration is a high quality liquid food concentration method where water is removed by forming ice crystals. This is done by cooling the liquid food below the freezing point of the solution. The freezing point depression is referred as a colligative property and it is proportional to the molar concentration of the solution (m), along with vapor pressure lowering, boiling point elevation, and osmotic pressure. These are physical characteristics of solutions that depend only on the identity of the solvent and the concentration of the solute. The characters are not depending on the solute’s identity. (Jayawardena, J. A. E. C., Vanniarachchi, M. P. G., & Wansapala, M. A. J. (2017). Freezing point depression of different Sucrose solutions and coconut water.) Identify which of the following is a colligative property :
Recommended Questions
- One mole of a substance is cooled at the rate of 0.4 kJ min^(-1) as sh...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of a substance is cooled at the rate of 0.4 kJ min^(-1) as sh...
Text Solution
|
- Cooling curves are drawn for three liquids a,b,c, shown in fig. for wh...
Text Solution
|
- A hot liquid is kept in a bog room. Accoding to Newton's law of coolin...
Text Solution
|
- The curve shown results when a liquid is cooled. What temperature is c...
Text Solution
|
- Cooling curves for amorophous and crystalline substances represented a...
Text Solution
|
- When 1 mole of super cooled water freezes, its temperature suddenly ri...
Text Solution
|
- A solution containing 0.1 mole of naphthalene and 0.9 mole of benzene ...
Text Solution
|
- शीतलन वक्र क्या है ?
Text Solution
|