The figure shows the restriction enzyme cutting sites `(R1-R3)` in wild type (n) and mutant (n) gene.
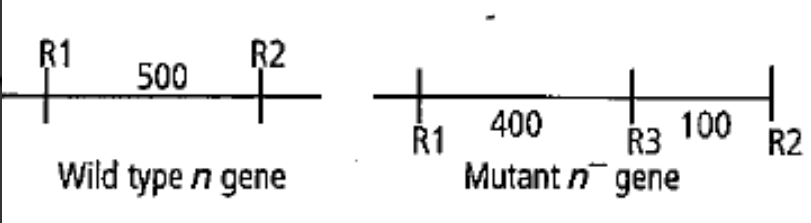
If a radioactively labelled probe (that hybridises at a sequence close to `R1)` is used for detecting the presence of DNA fragments after gel electrophoresis and Southern blotting, which of the following band patterns will yout expect ?
Note : L1 : wild type DNA, L2: mutant DNA
The figure shows the restriction enzyme cutting sites `(R1-R3)` in wild type (n) and mutant (n) gene.

If a radioactively labelled probe (that hybridises at a sequence close to `R1)` is used for detecting the presence of DNA fragments after gel electrophoresis and Southern blotting, which of the following band patterns will yout expect ?
Note : L1 : wild type DNA, L2: mutant DNA

If a radioactively labelled probe (that hybridises at a sequence close to `R1)` is used for detecting the presence of DNA fragments after gel electrophoresis and Southern blotting, which of the following band patterns will yout expect ?
Note : L1 : wild type DNA, L2: mutant DNA
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
_____ are the enzymes used for cutting the DNA molecule into fragments. An example for this type of enzyme is Eco RI. What does Eco, R and 1 stand for ?
Thin films, including soap bubbles and oil slicks, show patterns of alternating dark and bright regions resulting from interference among the reflected light waves. If two waves are in phase their crest and troughs will coincide. The interference will be constructive and the aplitude of the resultant wave will be greater than the amplitude of either constituent wave. if the two waves are out of phase, the crests of one wave will coincide with the troughs of the other wave. The interference will be destructive and the amplitude of the resultant wave will be less than that of either constituent wave. at the interface between two transparent media some light is reflected and some light is refracted. * When incident light, reaches the surface at point a, some of the light is reflected as ray R_(a) and and some is refracted following the path ab to the back of the film. *At point b some of the light is refracted out of the film and part is reflected back refracted out of the fiml as ray R_(c) . R_(a) and R_(c) are parallel. However, R_(c) has travelled the extra distance within the film of abc. if the angle of incidence is small then abc is approximately twice the film's thickness. if R_(a) and R_(c) are in phase they will undergo constructive interference and the region ac will be bright if R_(a) and R_(c) are out of phase, they will undergo destructive interference. * Refraction at an interface never changes the phase of the wave. * For reflection at the interface between two media 1 and 2, if n_(1)ltn_(2) the reflected wave will change phase by pi . if n_(1)gtn_(2) the reflected wave will not undergo a phase change. for reference n_(air)=1.00 * if the waves are in phase after refection at all interfaces, then the effects of path length in the film are Constructive interference occur when (n= refractive index) 2t=mlamda//n" "m=0,1,2,3... .. Destructive interference occurs when 2t=(m+1//2)lamda//n" "m=0,1,2,3... Q. A 600 nm light is perpendicularly incident on a soap film suspended in air. The film is 1.00 mum thick with n=1.35. Which statement most accurately describes the interference of the light reflected by the two surfaces of the film?
Thin films, including soap bubbles and oil slicks, show patterns of alternating dark and bright regions resulting from interference among the reflected light waves. If two waves are in phase their crest and troughs will coincide. The interference will be constructive and the aplitude of the resultant wave will be greater than the amplitude of either constituent wave. if the two waves are out of phase, the crests of one wave will coincide with the troughs of the other wave. The interference will be destructive and the amplitude of the resultant wave will be less than that of either constituent wave. at the interface between two transparent media some light is reflected and some light is refracted. * When incident light, reaches the surface at point a, some of the light is reflected as ray R_(a) and and some is refracted following the path ab to the back of the film. *At point b some of the light is refracted out of the film and part is reflected back refracted out of the fiml as ray R_(c) . R_(a) and R_(c) are parallel. However, R_(c) has travelled the extra distance within the film of abc. if the angle of incidence is small then abc is approximately twice the film's thickness. if R_(a) and R_(c) are in phase they will undergo constructive interference and the region ac will be bright if R_(a) and R_(c) are out of phase, they will undergo destructive interference. * Refraction at an interface never changes the phase of the wave. * For reflection at the interface between two media 1 and 2, if n_(1)ltn_(2) the reflected wave will change phase by pi . if n_(1)gtn_(2) the reflected wave will not undergo a phase change. for reference n_(air)=1.00 * if the waves are in phase after refection at all interfaces, then the effects of path length in the film are Constructive interference occur when (n= refractive index) 2t=mlamda//n" "m=0,1,2,3... .. Destructive interference occurs when 2t=(m+1//2)lamda//n" "m=0,1,2,3... Q. A 600 nm light is perpendicularly incident on a soap film suspended in air. The film is 1.00 mum thick with n=1.35. Which statement most accurately describes the interference of the light reflected by the two surfaces of the film?
In the figure below, the switches S_(1) and S_(2) are closed simultaneously at t =0 and a current starts to flow in the circuit. Both the batteries have the same magnitude of the electromotive force (emf) and the polarities are as indicated in the figure. Ignore mutual inductance between the inductors. The current ? in the middle wire reaches its maximum magnitude I_(max) at time t=tau . Which of the following statements is (are) true? A. I_("max")=(V)/(2R) B. I_("max")=(V)/(4R) C. tau=(L)/( R)""l n2 D. tau=(2L)/( R)" l n2
The Given question are based on the alphabetical series given below : C L R T B Q S M A P D I N F J K G Y X If CT is related to RQ and AI is related to DF in a certain way, to which of the following is SP related to, Given the same pattern? 1) MD 2) DN 3) AD 4) AI 5) DF
In this sectin each item consists of six sentences of a passage. The first and sixth sentences are given in the beginning as S1 and S6. The middle four sentences in each have been jumbled up and labelled as P, Q, R and S. You are required to find the proper sequence of the four sentences and mark your response accordingly on the Answer Sheet. S1 : Palaeontology is the study of the remains of dead organisms over enormous spans of time. S6 : Faunal analysis gives information about the animal people hunted and domesticated, the age of animal at death, and the diseases that afflicted them. P : Bones provide a great information. Q : The distribution of faunal remains (animal bones) at a site can indicate which areas were used for butchering, cooking, eating, bone tool making and refuse dumping. R : Within this discipline, molecular biology and DNA studies have been used to understant hominid evolution. S : Hominid evolution answers the questions about what ancient people looked like, and to plot patterns of migration. The correct sequence should be
Conductors allow the passage of electric current through them. Metallic and electrolytic are the two types of conductors. Current carriers in metallic and electrolytic conductors are free electrons and free ions respectively. Specific conductance or conductivity of the electrolyte solution is given by the following relation: K= cx (l)/(A) where, c=1/R is the conductance and 1/A is the cell constant, Molar conductance (^^_m) and equivalence conductance (^^_e) of an electrolyte solution are calculated using the following similar relations: ^^_m = K xx (1000)/(M) ^^_(e) = K xx (1000)/(N) where, M and N are the molarity and normality of the solution respectively. Molar conductance of strong electrolyte depends on concentration : ^^_m = ^^_m^(0) - b sqrt(C) ^^_m^(0) = molar conductance at infinite dilution C = concentration of the solution b = constant The degrees of dissociation of weak electrolytes are calculated as alpha = (^^_m)/(^^_m^(0)) = (^^_e)/(^^_e^(0)) Which of the following decreases on dilution of electrolytic solution?
Conductors allow the passage of electric current through them. Metallic and electrolytic are the two types of conductors. Current carriers in metallic and electrolytic conductors are free electrons and free ions respectively. Specific conductance or conductivity of the electrolyte solution is given by the following relation: K= cx (l)/(A) where, c=1/R is the conductance and 1/A is the cell constant, Molar conductance (^^_m) and equivalence conductance (^^_e) of an electrolyte solution are calculated using the following similar relations: ^^_m = K xx (1000)/(M) ^^_(e) = K xx (1000)/(N) where, M and N are the molarity and normality of the solution respectively. Molar conductance of strong electrolyte depends on concentration : ^^_m = ^^_m^(0) - b sqrt(C) ^^_m^(0) = molar conductance at infinite dilution C = concentration of the solution b = constant The degrees of dissociation of weak electrolytes are calculated as alpha = (^^_m)/(^^_m^(0)) = (^^_e)/(^^_e^(0)) Which of the following equality holds good for the strong electrolytes?
Recommended Questions
- The figure shows the restriction enzyme cutting sites (R1-R3) in wild ...
Text Solution
|
- The figure shows the restriction enzyme cutting sites (R1-R3) in wild ...
Text Solution
|
- Arrange the various steps of DNA fingerprinting technique in the corre...
Text Solution
|
- What is the correct sequence of DNA finger printing ? a-seperation o...
Text Solution
|
- Select the correct sequences of step in DNA finger printing involving ...
Text Solution
|
- The procedure, in which DNA fragments are separated by gel electrophor...
Text Solution
|
- The conversion of mutant type into wild type is called
Text Solution
|
- The following figure shows the cutting sites (RI-R3) for restriction e...
Text Solution
|
- The procedure in which DNA fragments are separated by gel electrophore...
Text Solution
|