Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
JEE MAINS PREVIOUS YEAR-JEE MAIN-All Questions
- On a photosensitive metal of area1 cm^(2) and work function 2eV, light...
Text Solution
|
- A carnot engine operates between two reservoirs of temperature 900K an...
Text Solution
|
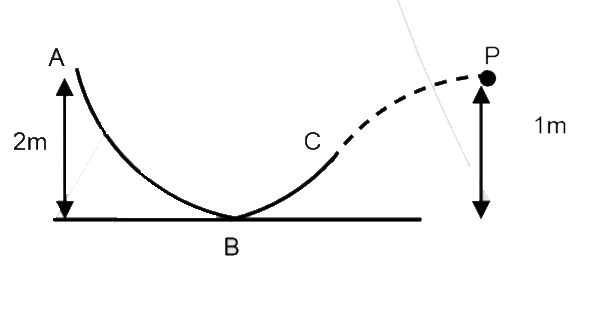
- A particle is released at point A. Find Kinetic energy at point P Give...
Text Solution
|
- Focal length of convex lens in air is 16 cm (muglass = 1.5). Now the l...
Text Solution
|
- The hysteresis curve for a material is shown in the figure. Then for t...
Text Solution
|
- A ring is rotated about diametric axis in a uniform magnetic field per...
Text Solution
|
- In YDSE, separation between slits is 0.15 mm, distance between slits a...
Text Solution
|
- A mass of 10 kg is suspended vertically by a rope from the roof. When ...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal fluid is flowing in a pipe in streamline flow. Pipe has maxim...
Text Solution
|
- Two Carnot engines A and B are operated in series. The engine A receiv...
Text Solution
|
- Under an adiabatic process, the volume of an ideal gas gets doubled. C...
Text Solution
|
- If weight of an object at pole is 196 N then weight at equator is [g =...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of charge q and mass m starts moving from the origin under ...
Text Solution
|
- An inductor of inductance 10 mH and a resistance of 5 is connected to...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure, potential difference between A and B is
Text Solution
|
- A stationary observer receives sound from two indentical tuning forks,...
Text Solution
|
- Electric field in space is given by vec(E(t) = E0 (i+j)/sqrt2 cos(omeg...
Text Solution
|
- In a house 15 Bulbs of 45 W, 15 bulbs of 100 W, 15 bulbs of 10 W and T...
Text Solution
|
- The surface density (mass/area) of a circular disc of radius a depends...
Text Solution
|
- An electron & a photon have same energy E. Find the ratio of de Brogli...
Text Solution
|