Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
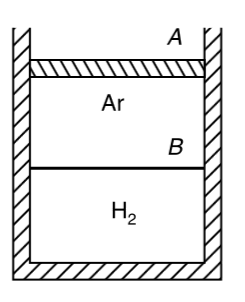
- A cylinder contains equal volumes of Ar and H(2), separated by a freel...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of a gas is put under a weightless piston of a vertical cylin...
Text Solution
|
- A closed and isolated cylinder contains ideal gas. An adiabatic separa...
Text Solution
|
- In a cylindrical container two pistons enclose gas in two compartments...
Text Solution
|
- A freely sliding massive piston is supported by a spring inside a vert...
Text Solution
|
- A cylinder contains equal volumes of Ar and H(2), separated by a freel...
Text Solution
|
- Two cylinder A and B having piston conneted by massless rod (as shown ...
Text Solution
|
- An adiabatic piston of mass m equally divides an insulated container o...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas enclosed in a vertical cylindrical container supports a f...
Text Solution
|