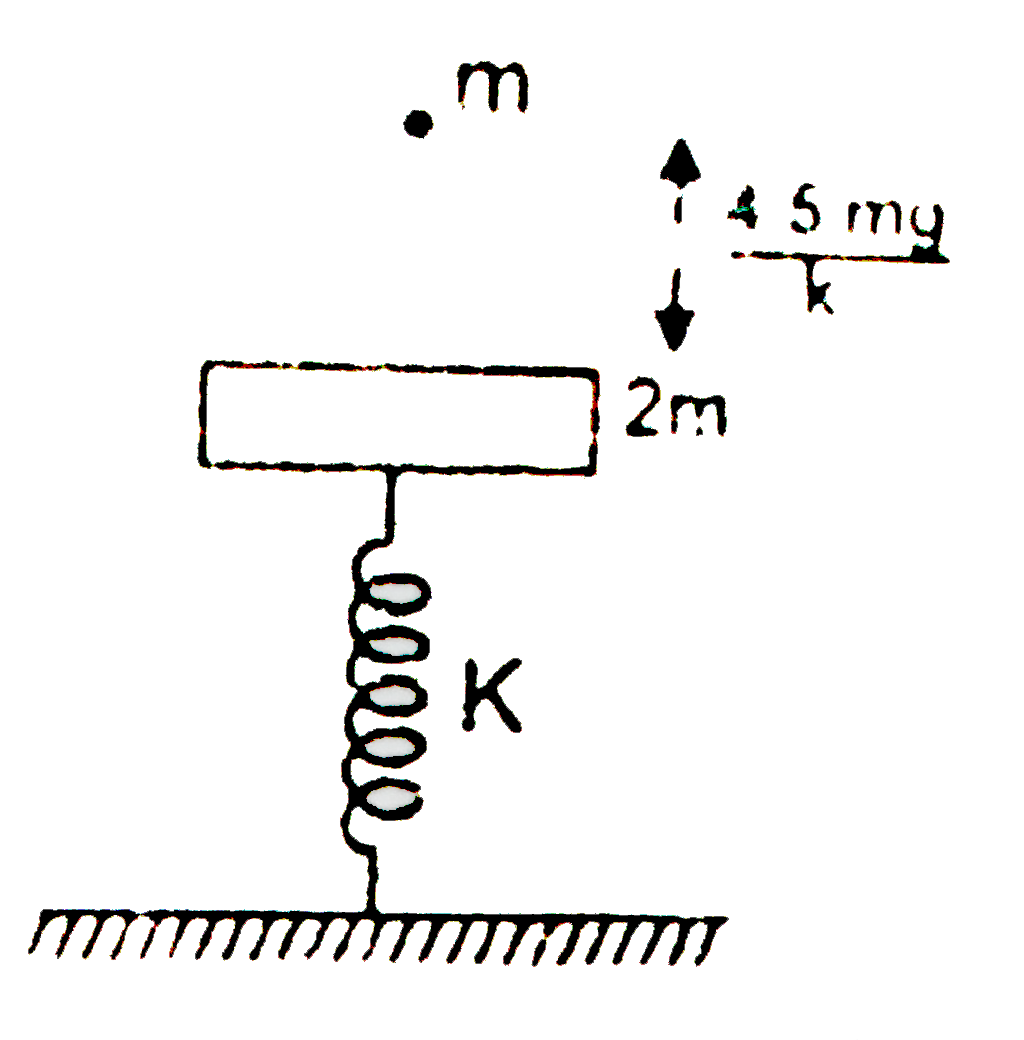Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- In the figure shown mass 2m is at rest and in equilibrium. A particle ...
Text Solution
|
- In an ideal pulley particle system, mass m2 is connected with a vertic...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown, mass 2m connected with a spring of force constant...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m collides elastically with the pan of mass (M = 2m...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of mass M and 2M are connected to the two ends of a light, ...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown mass 2m is at rest and in equilibrium. A particle ...
Text Solution
|
- द्रव्यमान m का एक कण वेग v से चलता हुआ एक स्थिर द्रव्यमान 2m के एक अ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m moving with velocity v strikes a particle of mass...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 200 g is suspended by a vertical spring. The spring is...
Text Solution
|