Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
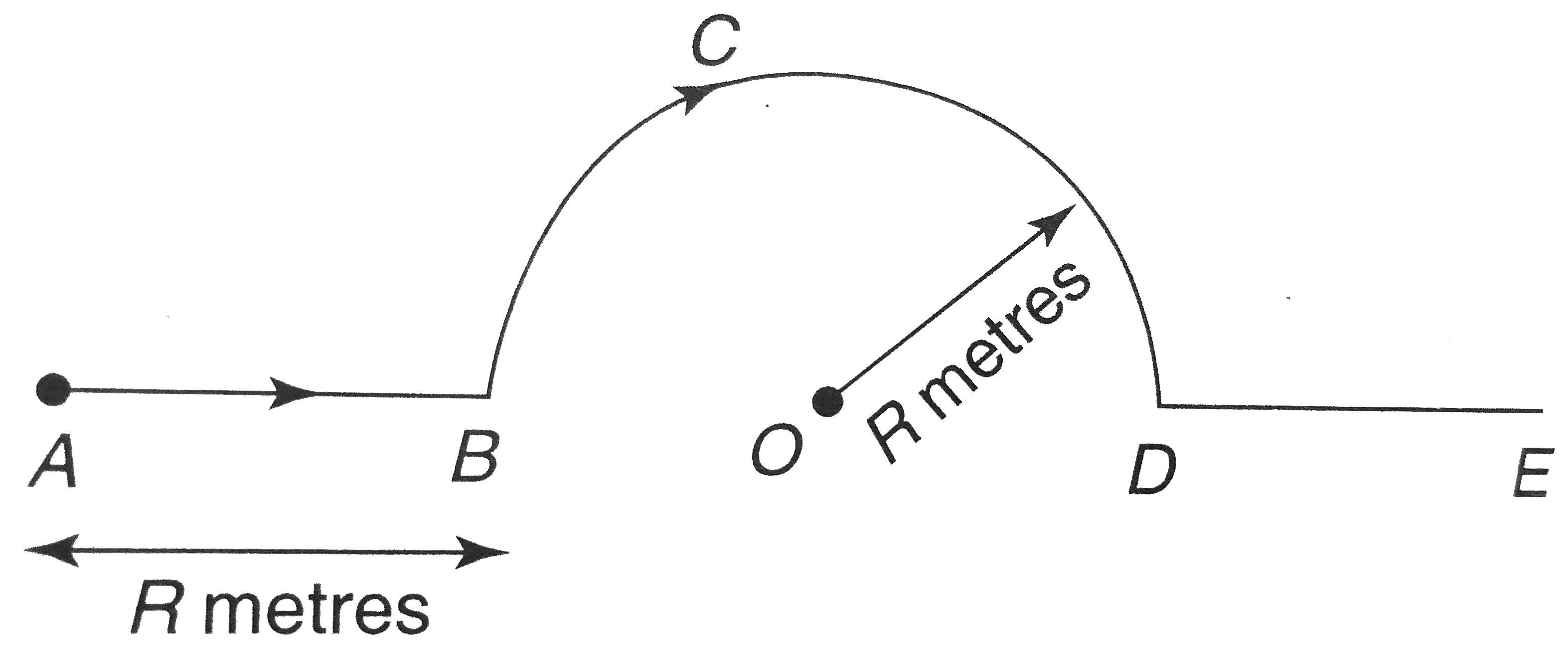
- A particle at t = 0 second is at point A and moves along the shown pat...
Text Solution
|
- A particle moves along a straight line and its velocity depends on tim...
Text Solution
|
- A particle at t = 0 second is at point A and moves along the shown pat...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is moving along a circle of radius R with a uniform speed v...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows the velocity time graph of a particle moving along straig...
Text Solution
|
- A bus moves with uniform velocity along a straigth line path. If the a...
Text Solution
|
- [" A particle is moving along "],[" a straight line with non- "],[" un...
Text Solution
|
- [" A particle is moving along "],[" a straight line with non- "],[" un...
Text Solution
|
- A particle move with a velocity v=alpha t^(3) along a straight line.Th...
Text Solution
|