Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
HC VERMA-FRICTION-Worked Out Examples
- The coefficient of static friction between a block of mass m and an in...
Text Solution
|
- A horizontal force of 20 N i sapplied to a block of mass 4 kg resting ...
Text Solution
|
- The coefficient of static friction between the block of 2 kg and the ...
Text Solution
|
- The coefficient of static friction between the two blocks shown in fig...
Text Solution
|
- A block slide down an inckline of angle 30^@ with an acceleration g//4...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 2.5 mg is kept on a rough horizontal surface. It is fo...
Text Solution
|
- A block placed on a horizotnal surface is being pushed by a force F ma...
Text Solution
|
- Find the maximum value of M//m in the situation shown in figure so tha...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the situation shown in figure. The horizontal surface below t...
Text Solution
|
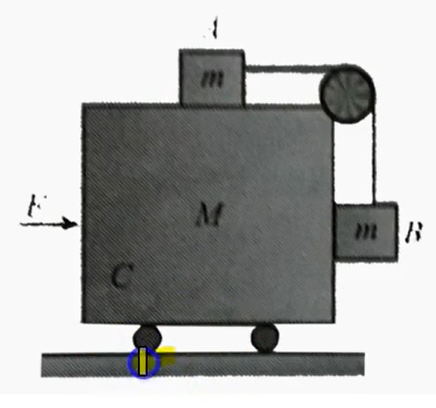
- figure shows two blocks connected by a light string placed on the two ...
Text Solution
|
 ,
,