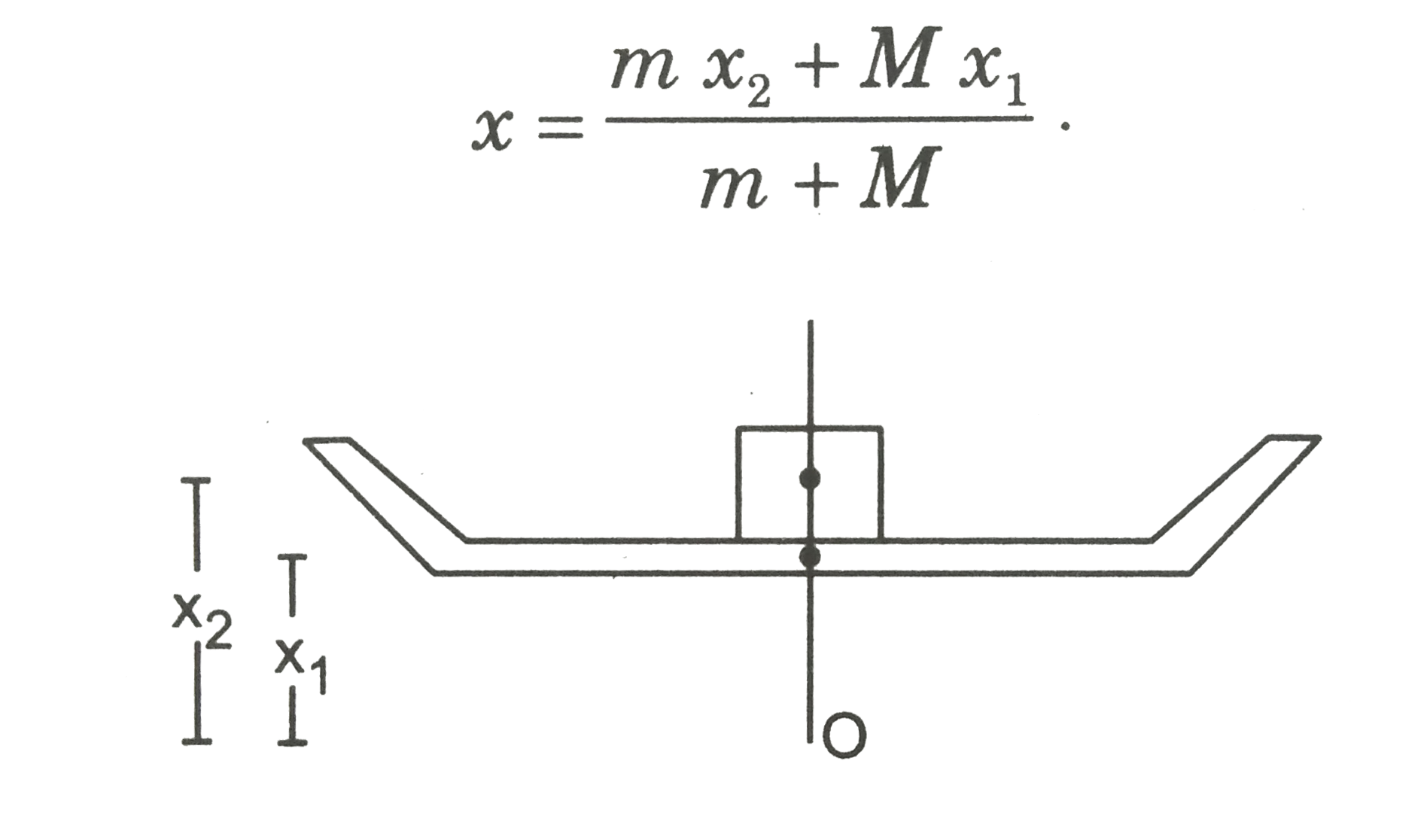Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A cubical block of ice of mass m and edge L is placed in a large tray ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a gravity free hall in which a tray of mas M, carrying a cubi...
Text Solution
|
- 80 g of water at 30^@C are poured on a large block of ice at 0^@C. The...
Text Solution
|
- A cubical ice block of side length 'a' is floating in water in a beake...
Text Solution
|
- A block of ice with mass m falls into a lake. After impact, a mass of ...
Text Solution
|
- 30^(@)C के 80 ग्राम जल को 0^(@)C के बर्फ की एक बड़ी सिल्ली पर डाला जाता...
Text Solution
|
- द्रव्यमान M वाली एक बड़ी-सी ट्रे के ठीक बीच में बीफ का एक छोटा-सा धनाका...
Text Solution
|
- पृथ्वी से दूर किसी स्थान पर एक हॉल में गुरुत्वाकर्षण बल नगण्य है | इस ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a gravity free hall in which a tray of mas M, carrying a cubi...
Text Solution
|