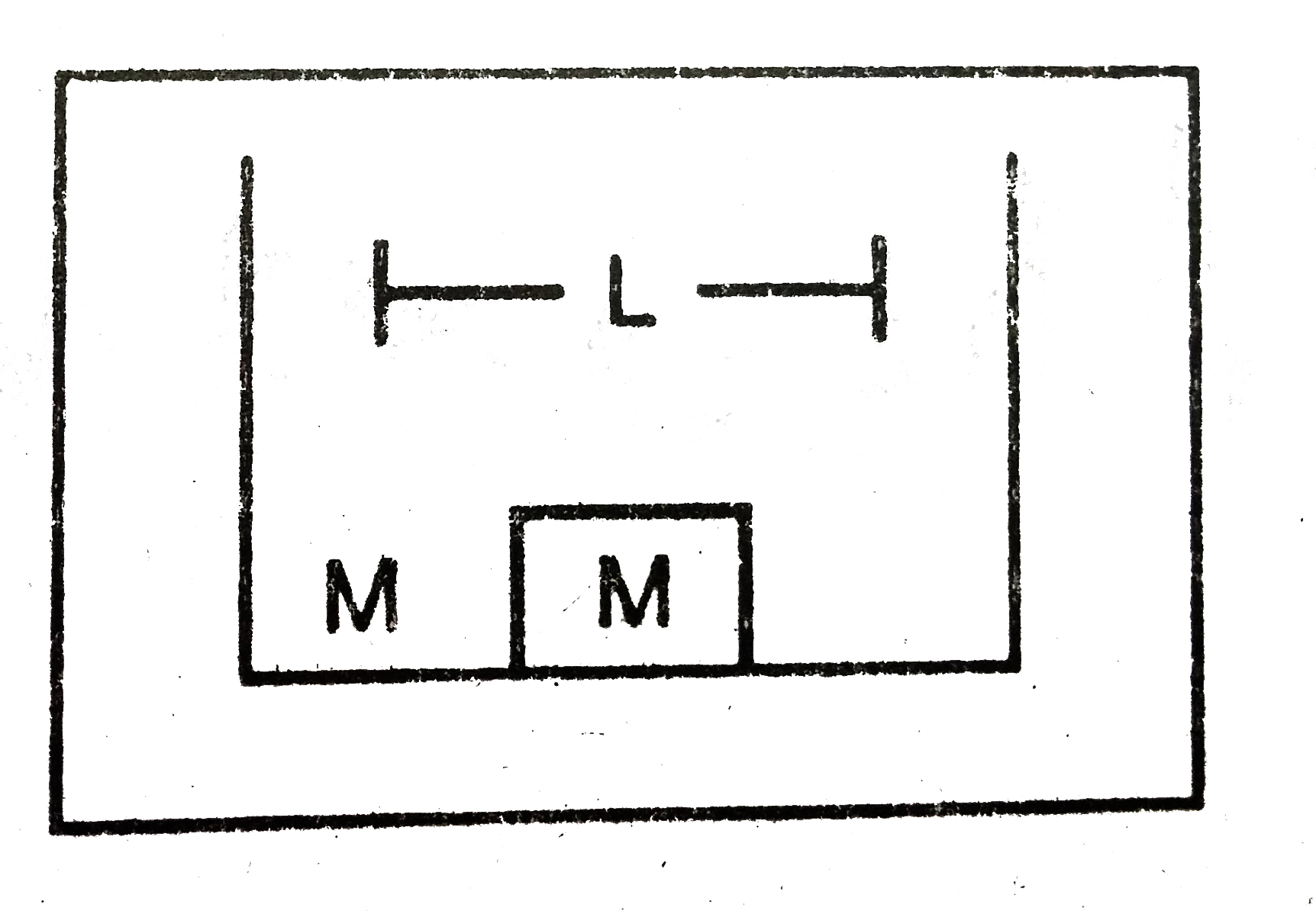Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
HC VERMA-CENTRE OF MASS, LINEAR MOMENTUM, COLLISION-Exercises
- Two bocks of masses 10 g and 20 kg are placed on the X-axis. The first...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of masses 10 kg and 30 kg are placed along a vertical line...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a gravity free hall in which a tray of mas M, carrying a cubi...
Text Solution
|
- Find the centre of mass of a uniform plate having semicircular inner a...
Text Solution
|
- Mr. Verma (50kg) and Mr. Mathur (60kg) are sitting at the two extremes...
Text Solution
|
- A cart of mas M is at rest on a frictionless horizontal surface and a ...
Text Solution
|
- The ballon the light rope and the monkey shown in figure are at rest ...
Text Solution
|
- Find the ratio of the linear omenta of two particles of masses 1.0 kg ...
Text Solution
|
- A uranium 238 nucleus, initially at rest emits n alpha particle with a...
Text Solution
|
- A man of mass 50 kg starts moving on the earth and acquires speed of 1...
Text Solution
|
- A neutron initially at rest, decays into a proton, an electron and an ...
Text Solution
|
- A man of mass m having a bag ofmas m slips from the roof of atall bui...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass 50 g moving at a speed of 2.0 m/s strikes a placne surf...
Text Solution
|
- Light in certain cases may be considered as a stream of paerticles cal...
Text Solution
|
- A block at rest explodes into three equal parts. Two parts start movin...
Text Solution
|
- Two fat astronauts each of mass 120 kg are travelling in a closed spac...
Text Solution
|
- Dureing a heavy rain hailstones of average size 1.0 cm in diameter fal...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass m is dropped onto a floor from a certain height. The co...
Text Solution
|
- A railroad car of mass M is at rest on frictionless rails when a man o...
Text Solution
|
- A gun is monted on a railroad car. The mass of the car, the gun, the s...
Text Solution
|