Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Recommended Questions
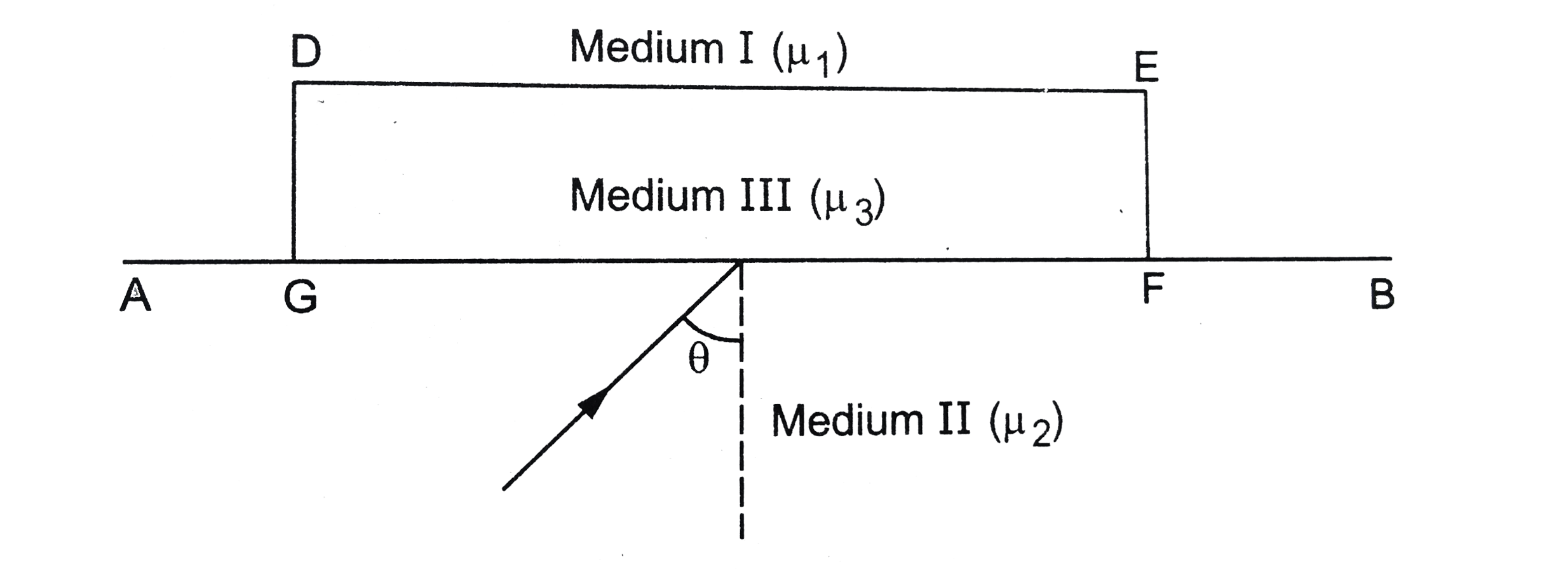
- Monochramatic light is incident on the pane interface AB between two m...
Text Solution
|
- Two refracting media are separated by a spherical interfaces as shown ...
Text Solution
|
- AB and CD are surfaces ot two slabs as shown in Figure . The medium be...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure (a) the light is incident at an angle theta (slightly gr...
Text Solution
|
- A ray is incident on interface of two media at critical angle as shown...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light refracts from medium 1 into a thin layer of medium 2, c...
Text Solution
|
- In total internal reflection when the angle of incidence is equal to t...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light refracts from medium 1 into a thin layer of medium 2, c...
Text Solution
|
- In total internal reflection when the angle of incidence is equal to t...
Text Solution
|