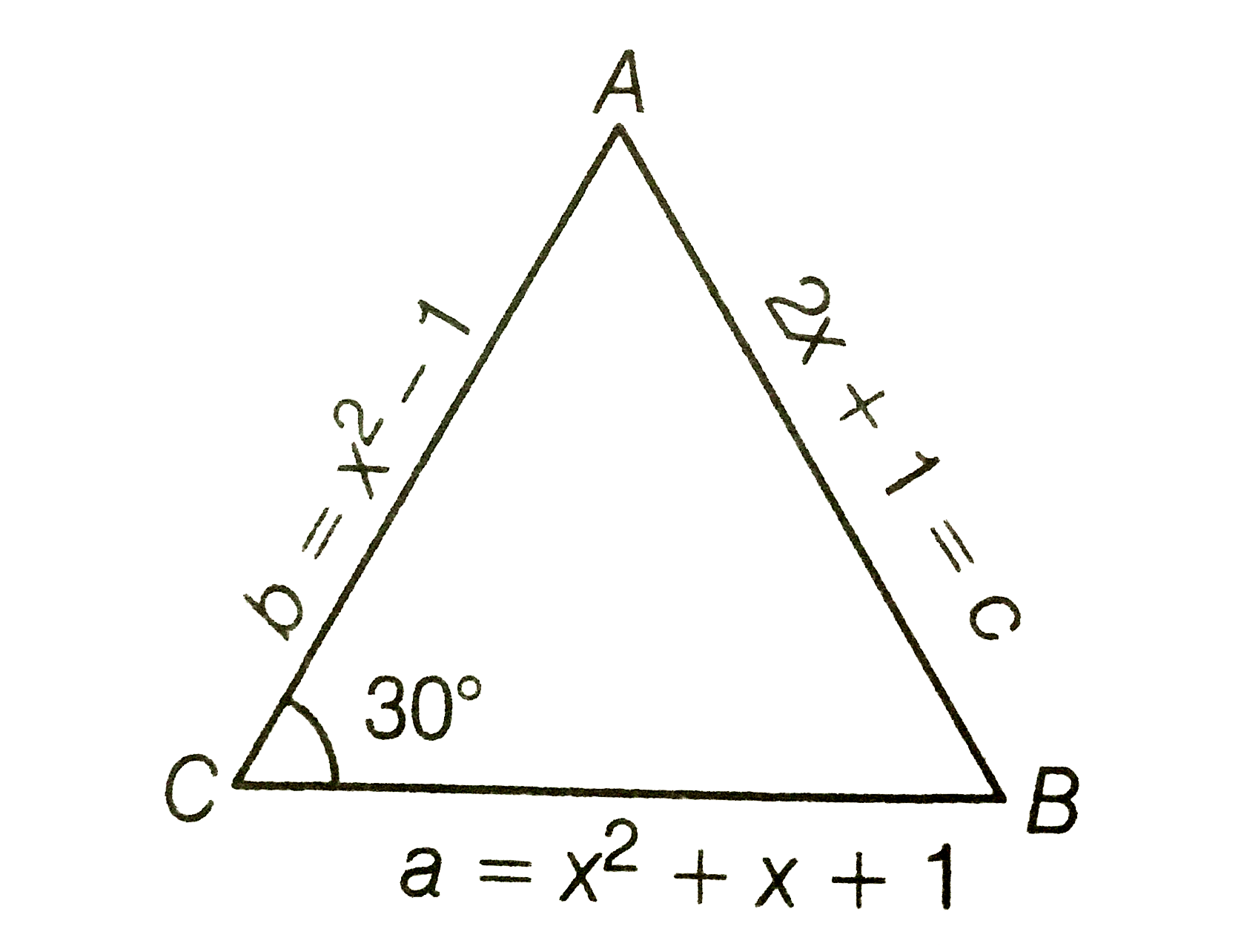
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Let A B C be a triangle such that /A C B=pi/6 and let a , ba n dc deno...
Text Solution
|
- Let ABC be a triangle such that angleACB=pi/6 and let a , b and c deno...
Text Solution
|
- Let ABC be a triangle such that /ACB=(pi)/(6) and let a,b and c denote...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a triangle A B C and let a , ba n dc denote the lengths of th...
Text Solution
|
- If the angle A ,Ba n dC of a triangle are in an arithmetic propression...
Text Solution
|
- If a ,b , a n dc are in G.P. and x ,y , respectively, are the arithmet...
Text Solution
|
- Let a , ba n dc be the three sides of a triangle, then prove that the ...
Text Solution
|
- If a ,b , a n dc are in G.P. and x ,y , respectively, are the arithmet...
Text Solution
|
- Let ABC be a triangle such that angleACB=pi/6 and let a , b and c deno...
Text Solution
|