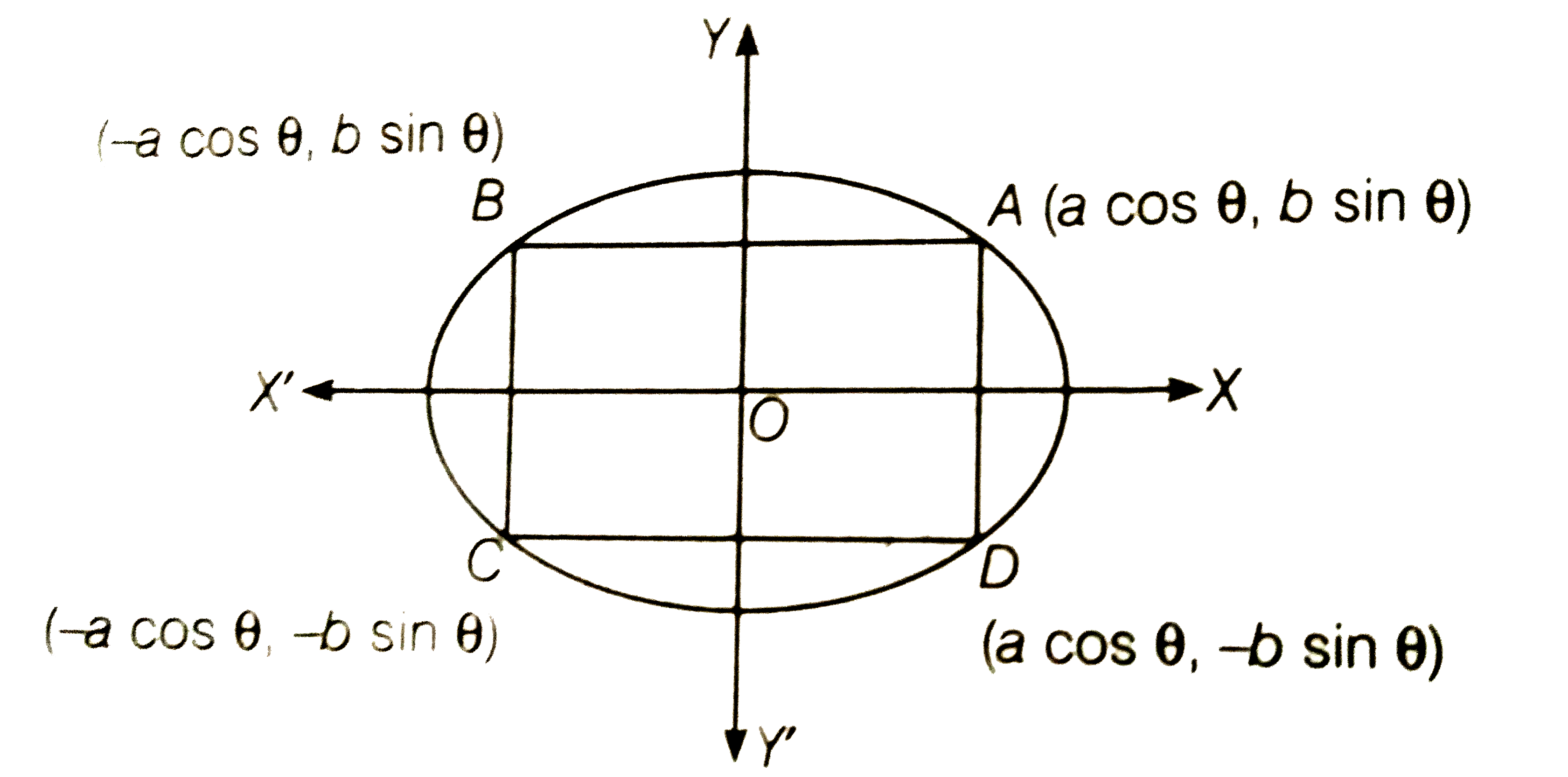
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
APPLICATIONS OF DERIVATIVES
MHTCET PREVIOUS YEAR PAPERS AND PRACTICE PAPERS|Exercise MHT CET CORNER|21 VideosAPPLICATIONS OF DERIVATIVES
MHTCET PREVIOUS YEAR PAPERS AND PRACTICE PAPERS|Exercise MHT CET CORNER|21 VideosAPPLICATIONS OF DEFINITE INTEGRALS
MHTCET PREVIOUS YEAR PAPERS AND PRACTICE PAPERS|Exercise MHT CET Corner|6 VideosBINOMIAL DISTRIBUTION
MHTCET PREVIOUS YEAR PAPERS AND PRACTICE PAPERS|Exercise MHT CET Corner|6 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MHTCET PREVIOUS YEAR PAPERS AND PRACTICE PAPERS-APPLICATIONS OF DERIVATIVES-MISCELLANEOUS PROBLEMS
- A stone, vertically thrown upward is moving in a line. Its equation of...
Text Solution
|
- A triangular park is enclosed on two sides by a fence and on the third...
Text Solution
|
- Find the area of the greatest rectangle that can be inscribed in th...
Text Solution
|
- The function f defined by f(x)=4x^(4)-2x+1 is increasing for
Text Solution
|
- The radius of a cylinder is increasing at the rate 2cm/sec. and its...
Text Solution
|
- The function f(x)=(x-1)^(2) has a minimum at x is equal to
Text Solution
|
- एक स्थिर झील में एक पत्थर डाला जाता है ओर तरंगों व्रतों में 5 cm /s क...
Text Solution
|
- If the line a x+b y+c=0 is a normal to the curve x y=1, then a >0,b >...
Text Solution
|
- If the function f(x)=2x^3-9a x^2+12 x^2x+1,w h e r ea >0, attains its ...
Text Solution
|
- For the curve y^(n)=a^(n-1)x if the subnormal at any point is a consta...
Text Solution
|
- The maximum value of logx is
Text Solution
|
- The length of subtangent to the curve x^2 + xy + y^2=7 at the point (1...
Text Solution
|
- The displacement s of a particle at time t is given by s=alpha sin ome...
Text Solution
|
- Find the point on the curve y = 2x^(2) - 6x - 4 at which the tangent i...
Text Solution
|
- The distance s travelled by a particle moving on a straight line in ti...
Text Solution
|
- The tangent and the normal drawn to the curve y=x^(2)=x+4 at P(1,4) cu...
Text Solution
|
- The approximate surface area of a sphere of radius 4.01 cm is
Text Solution
|
- The perimeter of a sector is a constant. If its area is to be maximum,...
Text Solution
|
- If x=t^(2) and y=2t then equation of the normal at t=1 is
Text Solution
|
- The equation of the tangent to the curve y=(1+x)^(y)+sin^(-1)(sin^(2)x...
Text Solution
|