Text Solution
Verified by Experts
HC VERMA-SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITIES OF GASES-Exercises
- The volume of an ideal gas (gamma 1.5 ) is changed adiabatically from ...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas at pressure 2.5 xx 10^(5) pa and temperture 300k occupies...
Text Solution
|
- Air (gamma = 1.4 ) is pumped at 20atm pressure in a motor tyre at 20^@...
Text Solution
|
- A gas is enclosed in a cylindrical can fitted with a piston. The walls...
Text Solution
|
- The initial pressure and volume of a given mass of a gas (Cp / Cv = ga...
Text Solution
|
- Conider a given sample of an ideal gas (Cp / Cv = gamma ) having initi...
Text Solution
|
- A given sample of an ideal gas (gamma = 1.5 ) is compressed adiabatica...
Text Solution
|
- Three samples A, B and C of the same gas (gamma = 1.5) have equal volu...
Text Solution
|
- Two samples A and B of the same gas have equal volumes and pressures ....
Text Solution
|
- 1 liter of an ideal gas (gamma =1.5) at 300k is suddenly compressed to...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a cylindridcal tube with a adibatic walls and fitted with...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows two rigid vessels A and B, each of volume 200 cm ^(3) con...
Text Solution
|
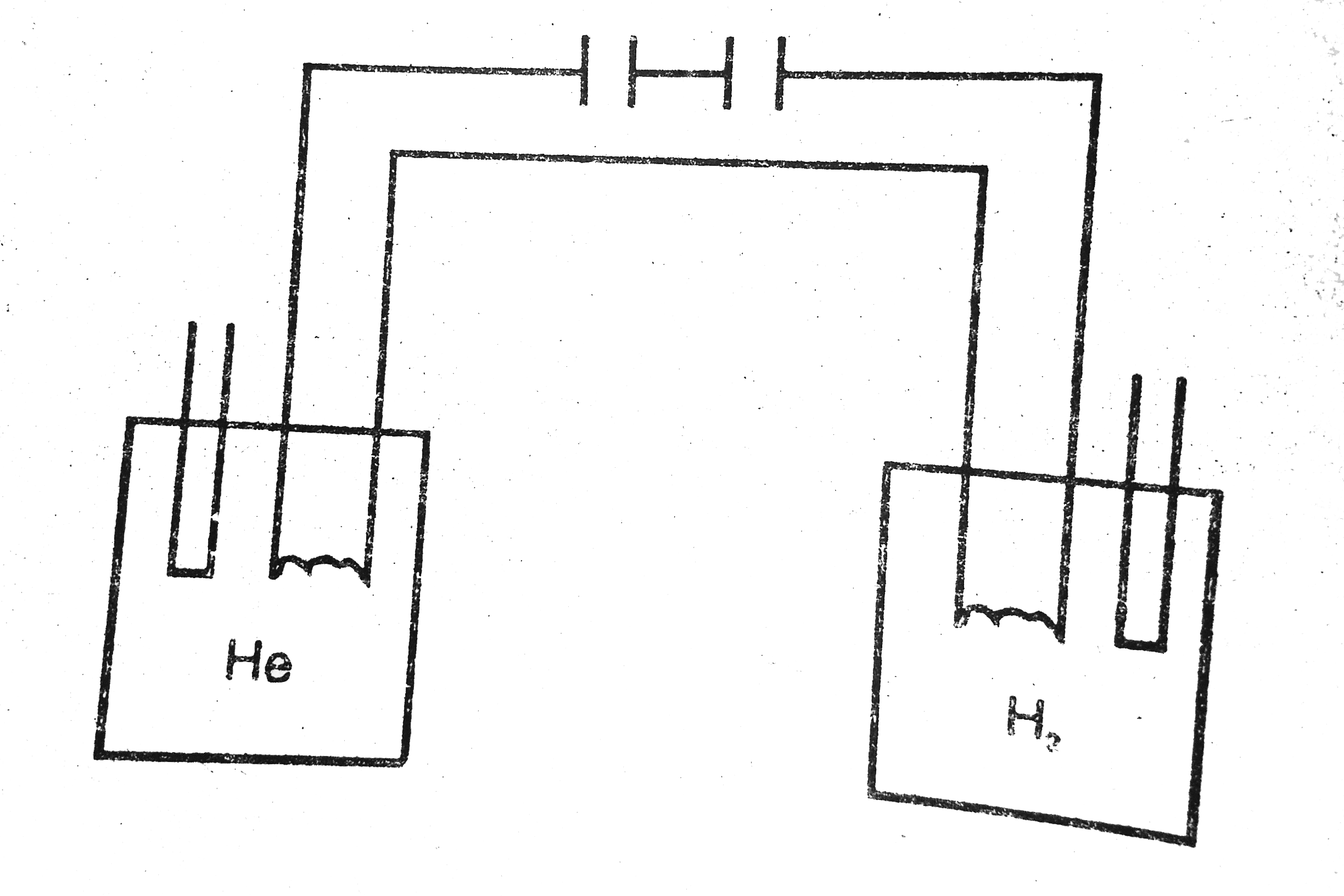
- Figure shows two vessels with adiabatic walls, one containing 0.1 g of...
Text Solution
|
- Two vessels A and B of equal volume (V0) are connected by a narrow tub...
Text Solution
|
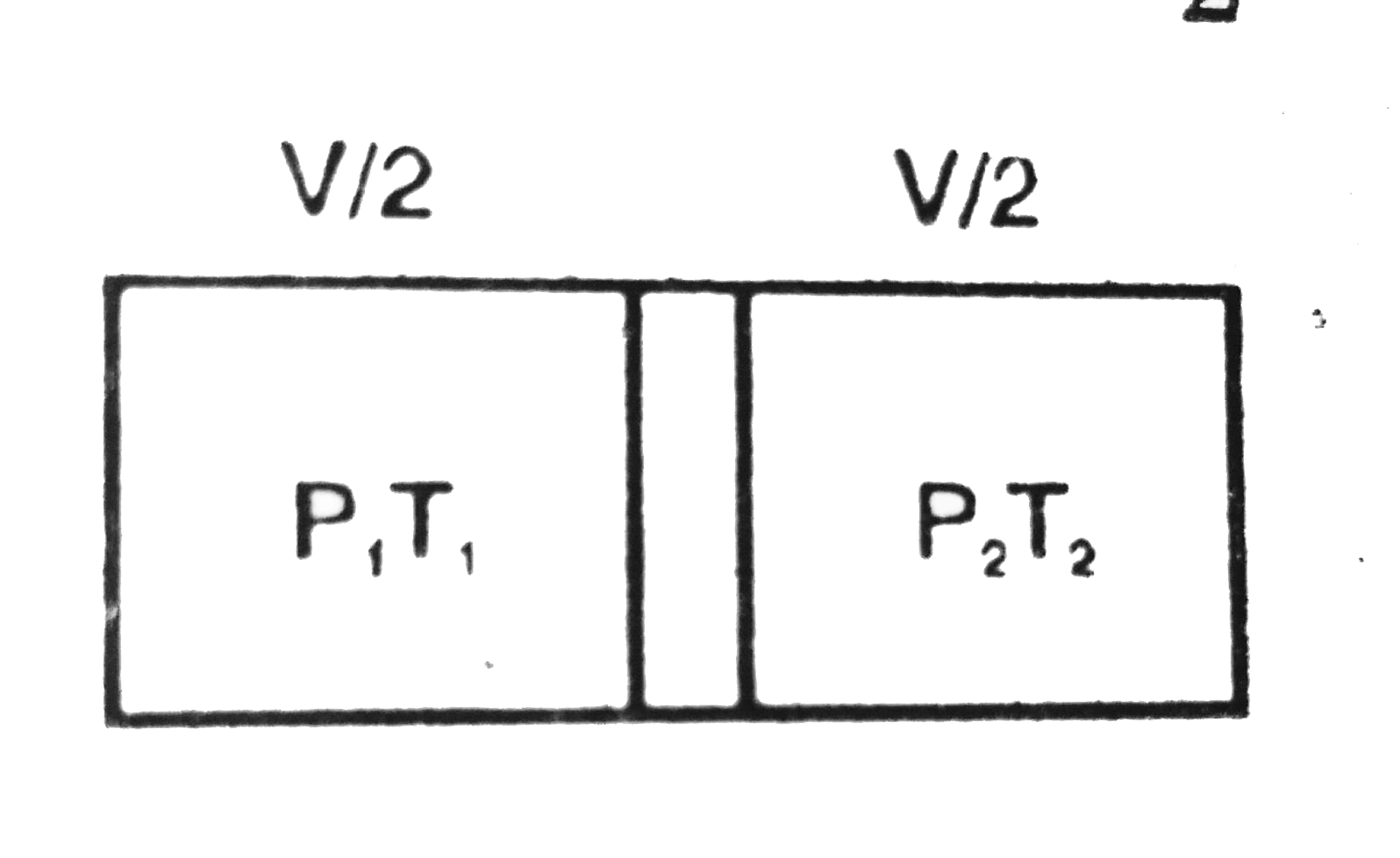
- Figure shows an adiabatic cylindrical tube of volume (V0) divided in t...
Text Solution
|
- An adibatic cylindrical tube of cross-sectional area 1 cm^(2) is close...
Text Solution
|
- The speed of sound in hydrogen at 0^@c is 1280 m s^(-1). The density o...
Text Solution
|
- 4.0 g of helium occupies 22400 cm^(3) at STP. The specific heat capaci...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal gas having density 1.7 xx 10^(-3) g cm ^(-3) at a preesure 1....
Text Solution
|
- Standing waves of frequency 5.0 kHz are produced in a tube filled with...
Text Solution
|