Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
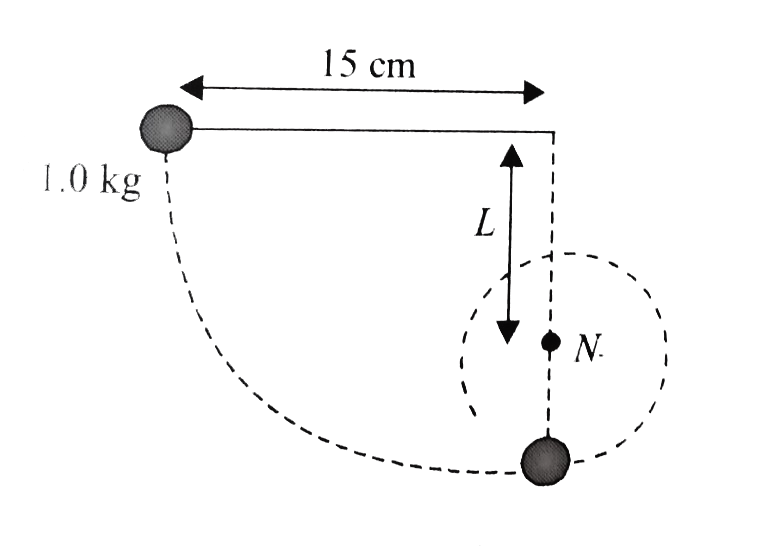
- A ball weighing 1.0 kg is tied to a string 15 cm long initially the ba...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass 1 kg is attached to an inextensible string. The ball is...
Text Solution
|
- A ball weighing 1.0 kg is tied to a string 15 cm long initially the ba...
Text Solution
|
- A small ball is attached to an end of a light string of length R. It i...
Text Solution
|
- A pendulum is made by attaching a ball at the end of a string (the oth...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure balls A&B are released simultaneously , when str...
Text Solution
|
- 0.3 किग्रा. द्रव्यमान की एक गेंद 0.8 मीटर लम्बी डोरी के एक सिरे से बाँ...
Text Solution
|
- एक गेंद, जिसका द्रव्यमान 0.1 किग्रा है, एक डोरी से लटकी हुयी है। उसे 6...
Text Solution
|
- A ball is held at rest in position A by two light strings. The horizo...
Text Solution
|