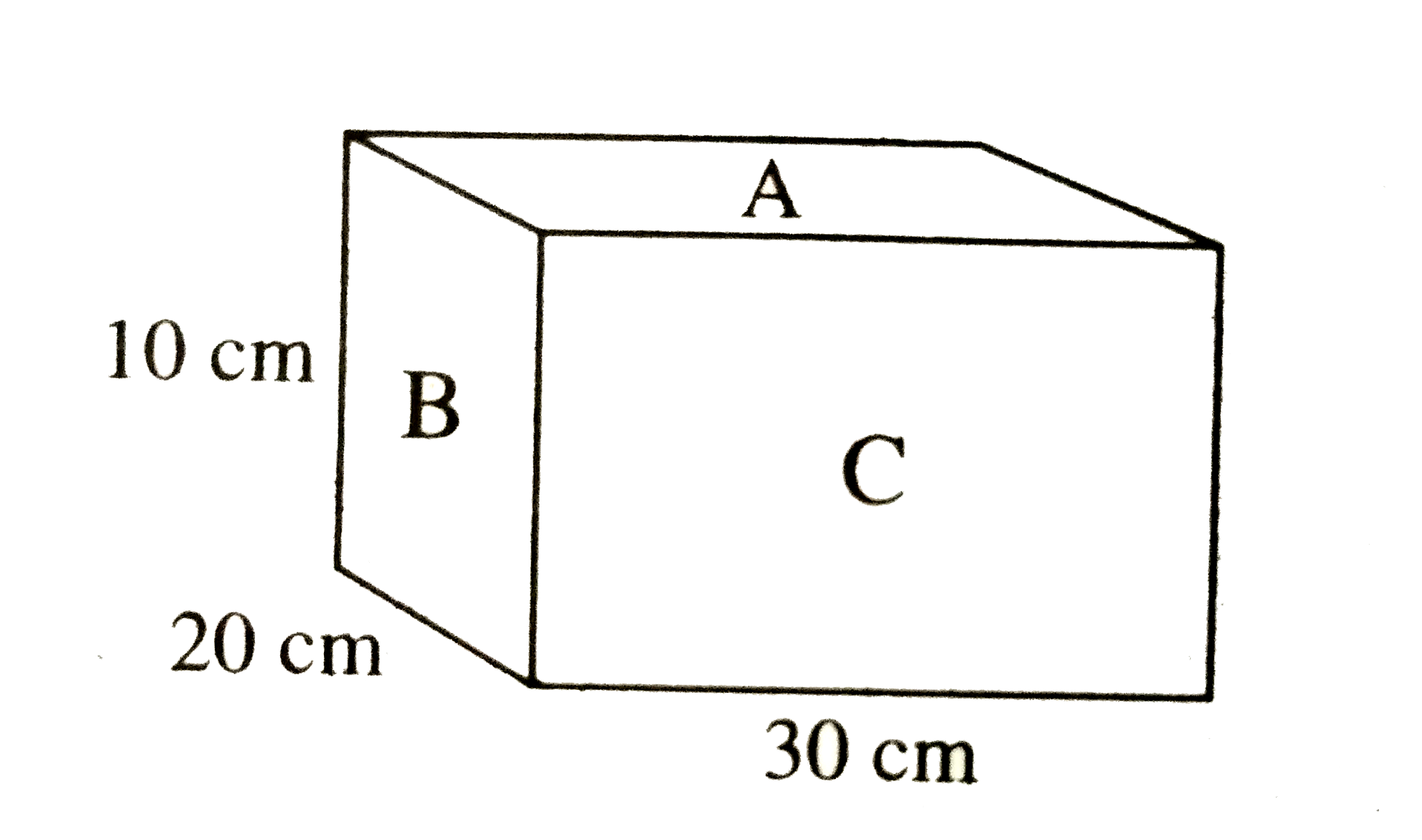
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
NAVNEET PUBLICATION - MAHARASHTRA BOARD|Exercise Surface Tension|6 VideosMULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
NAVNEET PUBLICATION - MAHARASHTRA BOARD|Exercise Wave Motion|6 VideosMULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
NAVNEET PUBLICATION - MAHARASHTRA BOARD|Exercise Oscillations|5 VideosMODEL QUESTION PAPER FOR PRACTICE
NAVNEET PUBLICATION - MAHARASHTRA BOARD|Exercise SECTION-D|5 VideosQUESTION BANK 2021
NAVNEET PUBLICATION - MAHARASHTRA BOARD|Exercise Semiconductors Devices (Long Answer ( LA) ( 4 marks Each) )|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NAVNEET PUBLICATION - MAHARASHTRA BOARD-MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS-Elasticity
- A block, resting on the ground, has the dimensions as shown in the dia...
Text Solution
|
- For a constant hydraulic stress on an object, the fractional change in...
Text Solution
|
- A decrease in temperature of 40^(@)C produces a 0.1 % strain in a wire...
Text Solution
|
- The sag delta of a centrally loaded rectangular beam supported at its ...
Text Solution
|
- The area of cross section of a steel rope used for lifting should be g...
Text Solution
|