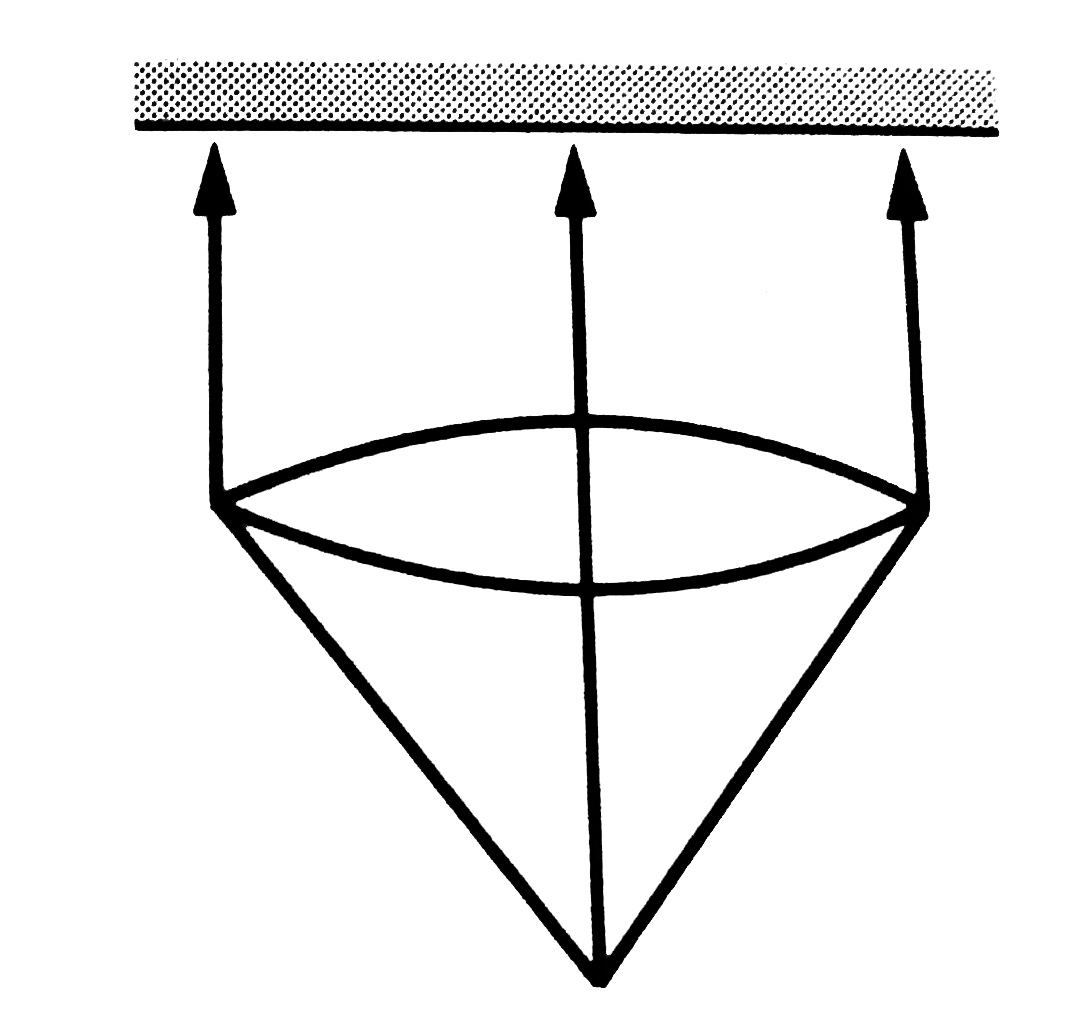
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
HC VERMA-PHOTO ELECTRIC EFFECT AND WAVE PARTICLE DUALITY-Exercises
- A parallel beam of monochromatic light of wavelength 663 nm is incide...
Text Solution
|
- A beam of white light is incident normally on a plane surface absorbin...
Text Solution
|
- A totally reflecting, small plane mirror placed horizontally faces a p...
Text Solution
|
- A 100 W light bulb is placed at the centre of a spherical chamber of r...
Text Solution
|
- A sphere of radius 1.00 cm is placed in the path of a parallel beam of...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the situation described in the previous problem. Show that th...
Text Solution
|
- It is not possible for a photon to be completely absorbed by a free el...
Text Solution
|
- Two neutral particles are kept 1m apart. Suppose by some mechanism som...
Text Solution
|
- Find the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons ejected when lig...
Text Solution
|
- The work function of a photoelectric material is 4.0 e V. (a) What i...
Text Solution
|
- Find the maximum magnitude of the linear momentum of a photoelectron e...
Text Solution
|
- When a metal plate is exposed to a monochromatic beam of light of wave...
Text Solution
|
- In an experiment on photoelectric effect, the stopping potential is me...
Text Solution
|
- The electric field associated with a monochromataic beam of light beco...
Text Solution
|
- The electric field associated with a light wave is given by E= E0 sin...
Text Solution
|
- The electric field at a point associated with a light wave is E=(100Vm...
Text Solution
|
- A monochromatic light source of intensity 5 m W emits (8xx10^15) photo...
Text Solution
|
- A photographic film is coated with a silver bromide layer. When light ...
Text Solution
|
- In an experiment on photoelectric effect light of wavelength 400 nm is...
Text Solution
|
- A silver ball of radius 4.8 cn is suspended by a thread in a cacuum ch...
Text Solution
|