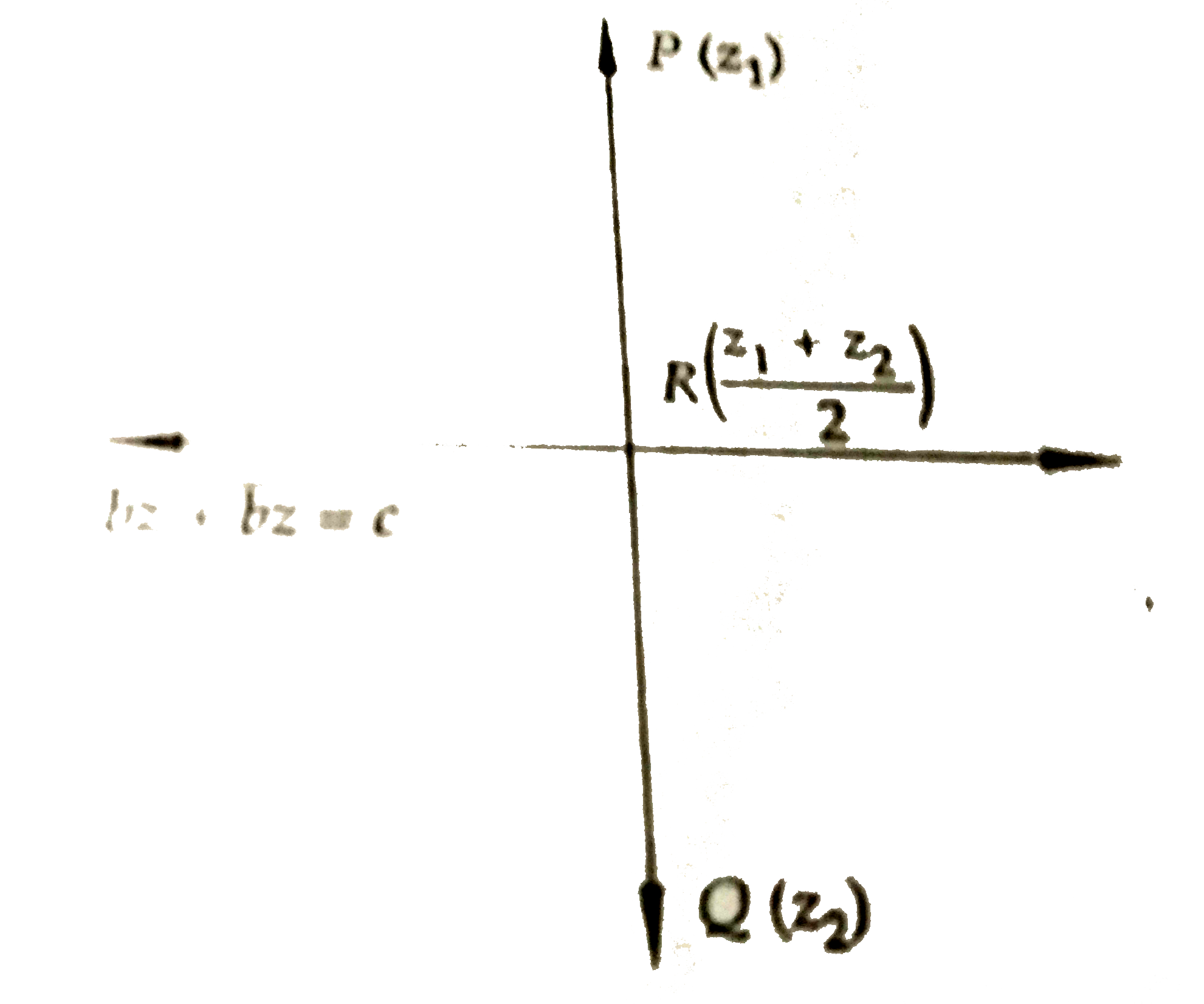A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
COMPLEX NUMBERS
OBJECTIVE RD SHARMA|Exercise Section II - Assertion Reason Type|15 VideosCOMPLEX NUMBERS
OBJECTIVE RD SHARMA|Exercise Exercise|131 VideosCOMPLEX NUMBERS
OBJECTIVE RD SHARMA|Exercise Chapter Test|59 VideosCIRCLES
OBJECTIVE RD SHARMA|Exercise Chapter Test|55 VideosCONTINUITY AND DIFFERENTIABILITY
OBJECTIVE RD SHARMA|Exercise Exercise|86 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
OBJECTIVE RD SHARMA-COMPLEX NUMBERS -Section I - Solved Mcqs
- If|z| = 2 and the locus of 5z-1 is the circle having radius 'a' and z...
Text Solution
|
- If |z+barz|+|z-barz|=8, then z lies on
Text Solution
|
- If a point z(1) is the reflection of a point z(2) through the line b b...
Text Solution
|
- If z is a complex number satisfying |z^(2)+1|=4|z|, then the minimum v...
Text Solution
|
- If z(1) and z(2) are two complex numbers satisying the equation. |(i...
Text Solution
|
- If alpha is an imaginary fifth root of unity, then log(2)|1+alpha+alph...
Text Solution
|
- The roots of the equation (1+isqrt(3))^(x)-2^(x)=0 form
Text Solution
|
- If |z|=1 and omega=(z-1)/(z+1) (where z in -1), then Re(omega) is
Text Solution
|
- Let z,w be complex numbers such that barz+ibarw=0 and arg (zw)=pi .The...
Text Solution
|
- Let OP.OQ=1 and let O,P and Q be three collinear points. If O and Q re...
Text Solution
|
- If |z|=1a n dz!=+-1, then all the values of z/(1-z^2) lie on a line no...
Text Solution
|
- Let A={z:"Im"(z) ge 1}, B={z:|z-2-i|=3}, C={z:"Re"{(1-i)z}=sqrt(2)} be...
Text Solution
|
- Let S=S1 cap S2 cap S3 where S1={z in C:|z| lt 4"}",S2={z in C: lm...
Text Solution
|
- In Q.no. 88, if z be any point in A frown B frown C and omega be any p...
Text Solution
|
- A particle P starts from the point z(0)=1+2i, where i=sqrt(-1). It mov...
Text Solution
|
- If w=alpha+ibeta where Beta 0 and z ne 1 satisfies the condition that...
Text Solution
|
- If z1 and bar z1 represent adjacent vertices of a regular polygon of n...
Text Solution
|
- I f|z|=max{|z-1|,|z+1|}, then
Text Solution
|
- The minimum value of |a+bomega+comega^(2)|, where a,b,c are all not eq...
Text Solution
|
- The shaded region, where P=(-1,0),Q=(-1+sqrt(2),sqrt(2))R=(-1+sqrt(2),...
Text Solution
|