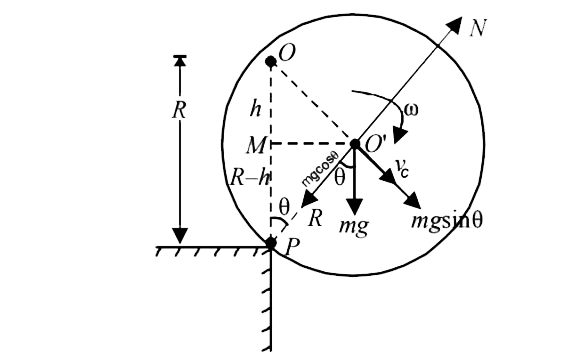
(a) Let the original position of centre of mass of the
cylinder be O. While rolling down off the edge, let the cylinder
be at such a position that its centre of mass is at a position
`O.let /_NPO be theta`. As the cylinder is rolling the c.m. rotates
in a circular path. The centripetal force required for the
circular motion is given by the equation.
`mgcos theta -N = (mv_c^2)/(R )`
Where N is the normal reaction
and m is mass of cylinder.
The conditon for the cylinder
leaving the edge is N = 0
`mg cos theta = (mv_c^2)/(R ) rArr cos theta = (v_c^2)/(Rg) ...(i)`
Applying energy conservation from O ot O.
Loss of potential energy of cylinder
=Gain in translation K.E.+Gain in rotational K.E.
`mgh = (1)/(2)mv_c^2 + (1)/(2)Iomega^2 ......(ii)`
Where i is the momentu of inertia of the cylinder about O, its
axis of rotation `omega` is the angular speed `V_c` is the velocity of
centre of mass.
Also for rolling, `v_c = omegaR`
`rArr omega = (v_c)/(R ) .....(iii)`
`I = (1)/(2)MR^2 ...(iv)`
From (ii), (iii) and (iv), we get
`mgh = (1)/(2)mv_c^2 +(1)/(4)v_c^2 = (3)/(4)v_c^2 rArr v_c^2 = (4gh)/(3)`
in `Delta O'MP, cos theta)`
`:. v_c^2 = (4g)/(3)R(1-cos theta) ...(v)`
From (i) and (v) we get
`costheta = (4gr)/(3Rg) (1-cos theta)`
`rArr 3cos theta = 4-4 cos theta rArr cos theta = (4)/(7)`
(b) From (v) speed of C.M. of cylinder before leaving
contact with edge.
`v_c^2 = (4gR)/(3) ((1-(4)/(7)) = (4gR)/(7) rArr v_c = sqrt((4gR)/(7))`
(c ) Before the cylinder's c.m. reaches the horizontal line of
the edge, it leaves contact with the edge as
`theta =cos^(-1)(4)/(7) = 55.15^@`
Therefore the rotational K.E., which the cylinder gains at
the time of leaving contact with the edge remains the same
in its further motion. Thereafter the cylinder gains
translational K.E.
Again applying energy conservation from O to the point
where c.m. is in horizontal line with edge
`mgR = (1)/(2)l omega^2 + (1)/(2)m(v'_c)^2`
`mgR = (1)/(2)xx(1)/(2)mR^2xx((sqrt((4g)/(7R)))^2 +(1)/(2)m(v'_c)^2`
`:. omega = (v_c)/(R ) = sqrt((4gR//7)/(R ))`
`rArr mgR - (mgR)/(7) = Translational K.E. = (6mgR)/(7)`
Also, Rotational K.e. = (1)/(2) Iomega^2 = (mgR)/(7)`
`:. (Translational K.E.)/(Rotational K.E.) = 6`