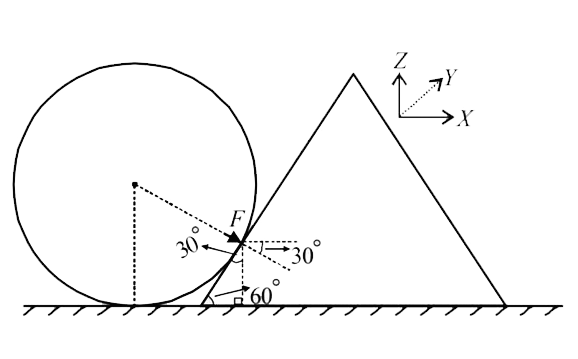
Resolving the force F acting on the wadge
`F_x = F cos 30^@, F_y = F sin 30^@`
The collison is elastic and since the spher is fixed,
the wadge will return back with the same velocity
(in magnitude).
The force responsible to change the velocity of the wedge
in X-direction is `Fx`
`F_x xx Delta t = mv - (-mv)`
(impulse) = (Change in momentum)
`:. F_x =(2mv)/(Delta t) rArr F cos 30^@ = (2mv)/(Deltat) rArr F = (4mv)/(sqrt3 Delta t)`
In vector terms
`vecF = F_x hati + F_y(-hatk) = F cos 30^@hati + F sin 30^@ (-hatk)`
`=Fxx(sqrt3)/(2)hati+Fxx(1)/(2) (-hatk)`
`rArr vecF = (F)/(2)(sqrt3 hati - hatk) = (2mv)/(sqrt3 Delta t) (sqrt3 hati - hatk)`
Taking equilibrium of force in Z-direction(acting on wadge)
we get
`F_y + mg = n`
`rArr N = (F)/(2) + mg = (2mv)/(sqrt3Delta t) + mg`
`N = ((2mv)/(sqrt3Delta t )+mg))hatk`
(b) Taking torques on wedge about the c.m. of lthe wedge.
Fxxh - Torque due to N+mgxx0 = 0
rArr Torque due to N = Fxxh = (4mv)/(sqrt3 Delta t) xxh`
