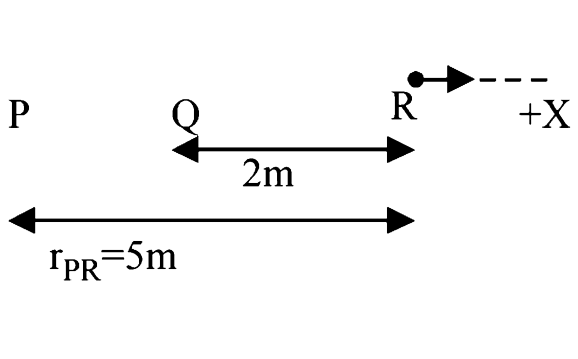
(i) The magnetic field (due to current in wire `P`) at `R`
` = (mu_(0))/( 4 pi ) xx(2I_(p))/(r_(PR)) = ( mu_(0))/( 4 pi)xx( 2xx2.5)/(5)`` = (mu_(0))/(4 pi)`
` = (mu_(0))/(4 pi) [ in the plane of paper downwards]`
Similarly , the magnetic field ( due to current is wire `Q`) ar `R`
`(mu_(0))/( 4 pi)xx( 2xxI)/(2) = (mu_(0))/( 4 pi)I`
`[ in the plane of paper downwards]`
The total magnetic field at `R [ due to `P and Q`]`
` B = (mu_(0))/( 4 pi )+(mu_(0))/( 4 pi)I = ( mu_(0))/( 4 pi) (1 + I)`
`[ in the plane of paper downwards ]`
The force experienced by the electron
` F = qvB sin theta`
` = evB sin 90^(@) = 1.6xx10^(-19)xx4xx10^(5)xx(mu_(0))/( 4 pi) ( 1+I)`
But ` F = 3.2xx10^(-20) N (Given)
:. `3.2xx10^(-20) = 1.6xx10^(-19)xx4xx10^(5)xx10^(-7)(1+I)`
rArr `I = 4 amp`.
(ii) Let us consider a position between ` Q and R` . The magnetic field produced should be equal to ` 5xx10^(-7)T` in the plane of paper acting upwards.
For this let the wire having current `2.5 amp` be placed at a distance `r` from ` R` and current flowing outwards the plane of paper. ltbr gt :. ` 5xx10^(-7) = (mu_(0))/(4 pi) xx( 2xx2.5)/(r) or r = 1 m`
Let us consider another position beyond ` R` collinear with `P, Q and R`. Let it be placed at a distance `r'' from `R' , having current in the plane of paper.
:. ` 5xx10^(-7) = (mu_(0))/(4 pi)xx( 2xx2.5)/(r') or r' = 1 m`