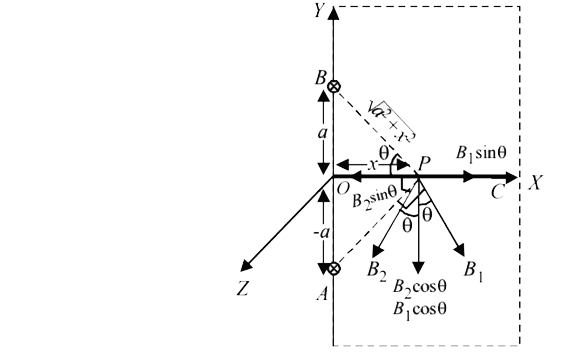
The magnetic field produced at different points on `OC` will be different. Let us consider an arbitrary point `P` on `OC` which is at a distance `x` from the origin. Let the magnetic field due to currents in `A and B` at `p` be ` B_(1) and B_(2)` respectively, both being in the ` X-Y` plane.
Let /_BPO = /_APO = theta`
`|vec(B)_(1)| = (mu_(0))/( 4 pi) (21)/(sqrt(a^(2) + x^(2))) = | vec(B)_(2)|`
On resolving `B_(1) and B_(2)` we get that the ` sin theta` components cancel out and the `cos theta` components add up. Therefore, the total magnetic field at `P` is
`B = 2B_(1) cos theta`
`= (2mu_(0))/( 4 pi) (2 I)/(sqrt(a^(2) + x^(2))) = ( mu_(0))/( 4 pi) ( 4 Ix)/( a^(2) + x^(2))`
`( towards - Y direction)`
Let us consider a small portion of wire `OC` at `P` of length ` dx`. The small amount of force acting on that small portion
`vec(d)F = I(vec(d)x xxvec(B)) :. dF = I dx B sin 90^(@)`
rArr dF = I dx xx (mu_(o))/( 4 pi) xx( 4 Ix)/(a^(2))+(x^(2))`
rArr `dF = (mu_(0))/( 4 pi) 4 I^(2) (xdx)/(( a^(2) + x^(2))`
The total force `F = (mu_(0))/( 4 pi )xx 4 I^(2) int _(0)^(L) ( xdx)/(a^(2) +x^(2))`
`= (mu_(0))/(4 pi)xx4 I^(2)[ 1/2 log_(e)(a^(2)+x^(2))]_(0)^(L)`
rArr `F = `= (mu_(0))/(4 pi)xx 2 I^(2)[ 1/2 log_(e)(a^(2)+ L^(2))/(a^(2))]`
To find the direction of force we can use Fleming's left hand rule. The direction of ` vec(F)` is towards ` -Z` direction .
When the current in wire `B` is reversed , the resultant magnetic field at any arbitrary point `P` on `OC` will be in the `x- direction`, therefore force acting will be zero ` (F = I l B sin theta and theta = 180^(@))`.