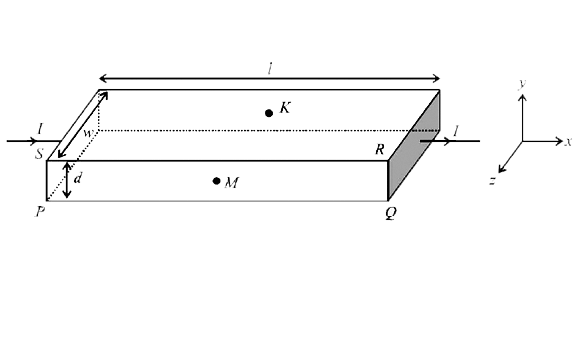
In a thin rectangular metallic strip a constant current `I` flows along the positive `x-direction , as shown in the figure. The length , width and thickness of the strip are `l, w and d`, respectively.
A uniform magnetic field `vec(B)` is applied on the strip along the positive `y- direction` . Due to this, the charge carriers experience a net deflection along the `z- direction` . This results in accumulation of charge carriers on the surface `PQRS` ansd apperance of equal and opposite charges on the face opposite to `PQRS`. A potential difference along the `z-direction` is thus developed. Charge accumulation contiues untill the magnetic force is balanced by the electric force. The current is assumed to be uniformly distributed on the cross- section of the strip and carried by electrons.
Consider two different metallic strips `(1 and 2)` of the same material . Their lengths are the same,widths are `w_(1) and w_(2)` and thickness are `d_(1) and d_(2)` respectively. Two points `K and M` are symmetrically located on the opposite faces parallel to the ` x-y` plane ( see figure) . `V_(1) and V_(2)` are the potential differences between `K and M` in strips ` 1 and 2`, respectively . Then, for a given current `I` flowing through them in a given magnetic field strength `B`, the correct statement(s) is (are)