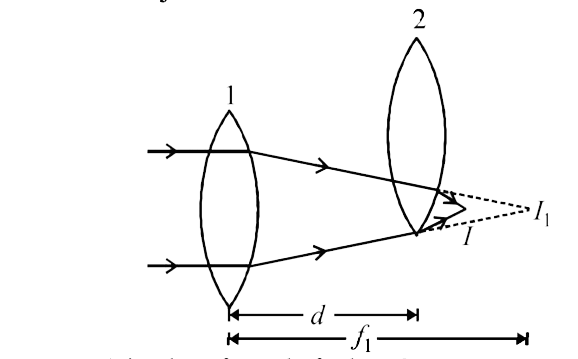
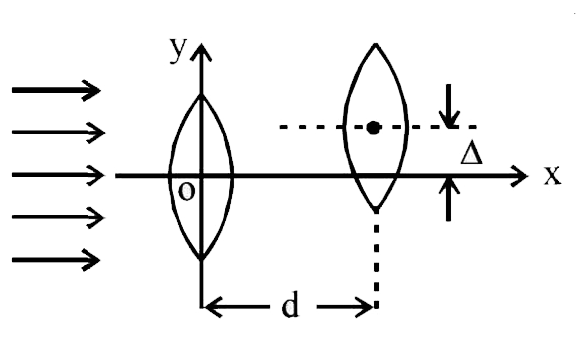A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
SUNIL BATRA (41 YEARS IITJEE PHYSICS)-RAY AND WAVE OPTICS-JEE Main And Advanced
- A thin prism P(1) with angle 4degree and made from glass of refractive...
Text Solution
|
- A planet is observed by astronomical refracting telescope having an ob...
Text Solution
|
- Two thin convex lenses of focal lengths f(1) and f(2) are separated by...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following form(s) a virtual and erect image for all posit...
Text Solution
|
- A real image of a distant object is formed by a plano-convex lens of i...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light travelling in a transparant medium falls on a surface s...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel monochromatic beam of light is incident normally on a narro...
Text Solution
|
- A concave mirror is placed on a horizontal table, with its axis direct...
Text Solution
|
- A spherical surface of radius of curvature R separates air (refractive...
Text Solution
|
- In a Young's double slit experiment, the separation between the two sl...
Text Solution
|
- A student performed the experiment of determination of focal length of...
Text Solution
|
- A ray OP of monochromatic light is incident on the face AB of prism AB...
Text Solution
|
- A transparent thin film of uniform thickness and refractive index n(1)...
Text Solution
|
- A light source, which emits two wavelength lamda(1)=400nm and lamda(2)...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical glass rods S(1) and S(2) (refractive index=1.5) have one...
Text Solution
|
- A plano-covex lens is made of a material of refractive index n. When a...
Text Solution
|
- A transparent slab of thickness d has a refractive index n(z) that inc...
Text Solution
|
- While conduction the Young's double slit experiment, a student replace...
Text Solution
|
- A pin is placed 10cm in front of a convex lens of focal length 20cm, m...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light is incident at an angle of 60^@ on the face of a prism ...
Text Solution
|