Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
SUNIL BATRA (41 YEARS IITJEE PHYSICS)-RAY AND WAVE OPTICS-JEE Main And Advanced
- A plano-convex lens has thickness 4cm. When places on a horizontal tab...
Text Solution
|
- A beam of light consisting of two wavelengths 650 nm and 520 nm is use...
Text Solution
|
- A monochromatic light is incident on the plane interface AB between tw...
Text Solution
|
- A right angled prism is to be made by selecting a proper material and ...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel bean of light travelling in water (refractie index =4/3) is...
Text Solution
|
- In a modified Young's double-slit experiment, a monochromatic uniform ...
Text Solution
|
- A narrow monochromatic beam of light of intensity 1 is incident on a g...
Text Solution
|
- Two parallel beams of light P and Q (separation d) containing radiatio...
Text Solution
|
- Light is incident at an angle alpha on one planar end of a transparent...
Text Solution
|
- In figure S is a monochromatic point source emitting light of waveleng...
Text Solution
|
- An image Y is formed of a point object x by a lens whose optic axis is...
Text Solution
|
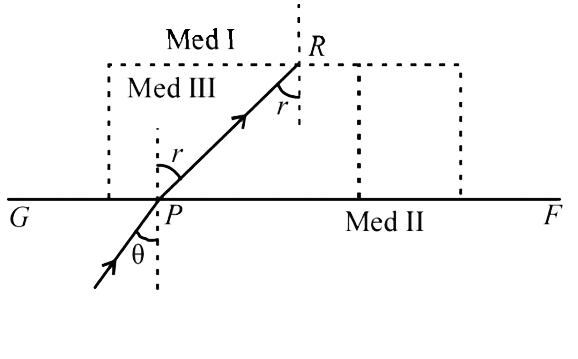
- A ray of light travelling in air is incident at grazing angle (incide...
Text Solution
|
- A right angles prism (45^(@),90^(@), 45^(@)) of refractive index n ha...
Text Solution
|
- A double slit apparatus is immersed in a liquid of refractive index 1....
Text Solution
|
- A thin plano-convex lens of focal length f is split into two halves. O...
Text Solution
|
- In Young's experiment the upper slit is covered by a thin glass plate ...
Text Solution
|
- A prism of refractive index n(1) & another prism of reactive index n(2...
Text Solution
|
- A coherent parallel beam of microwaves of wavelength lambda = 0.5 mm f...
Text Solution
|
- The young's double slit experiment is done in a medium of refractive i...
Text Solution
|
- The XY plane is the boundary between two tranparednt media. Medium 1 w...
Text Solution
|