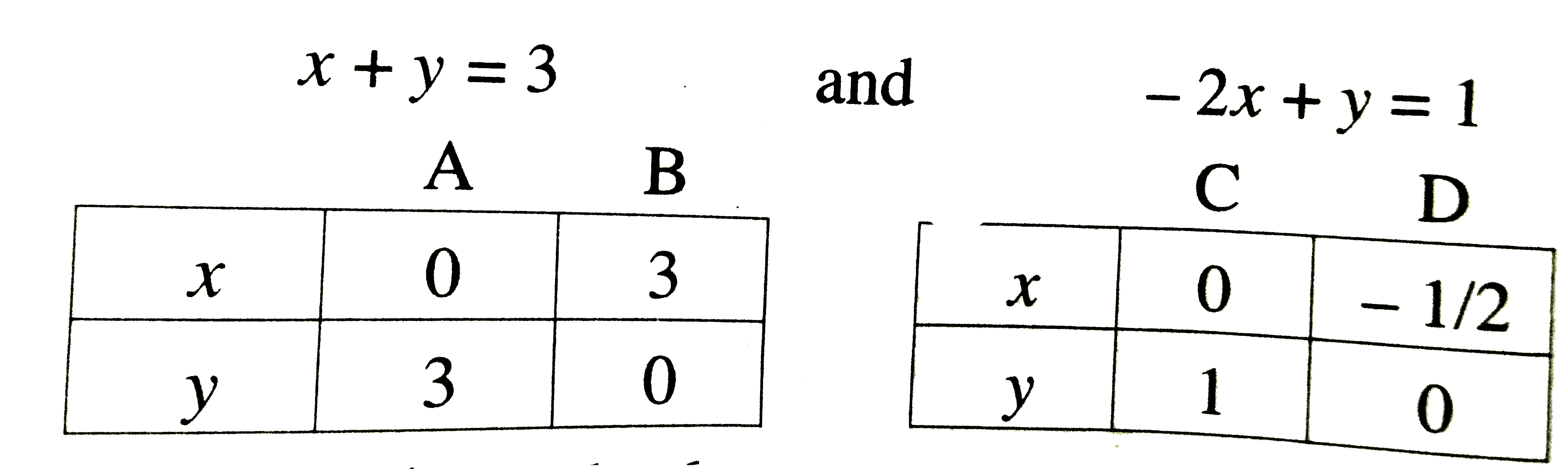
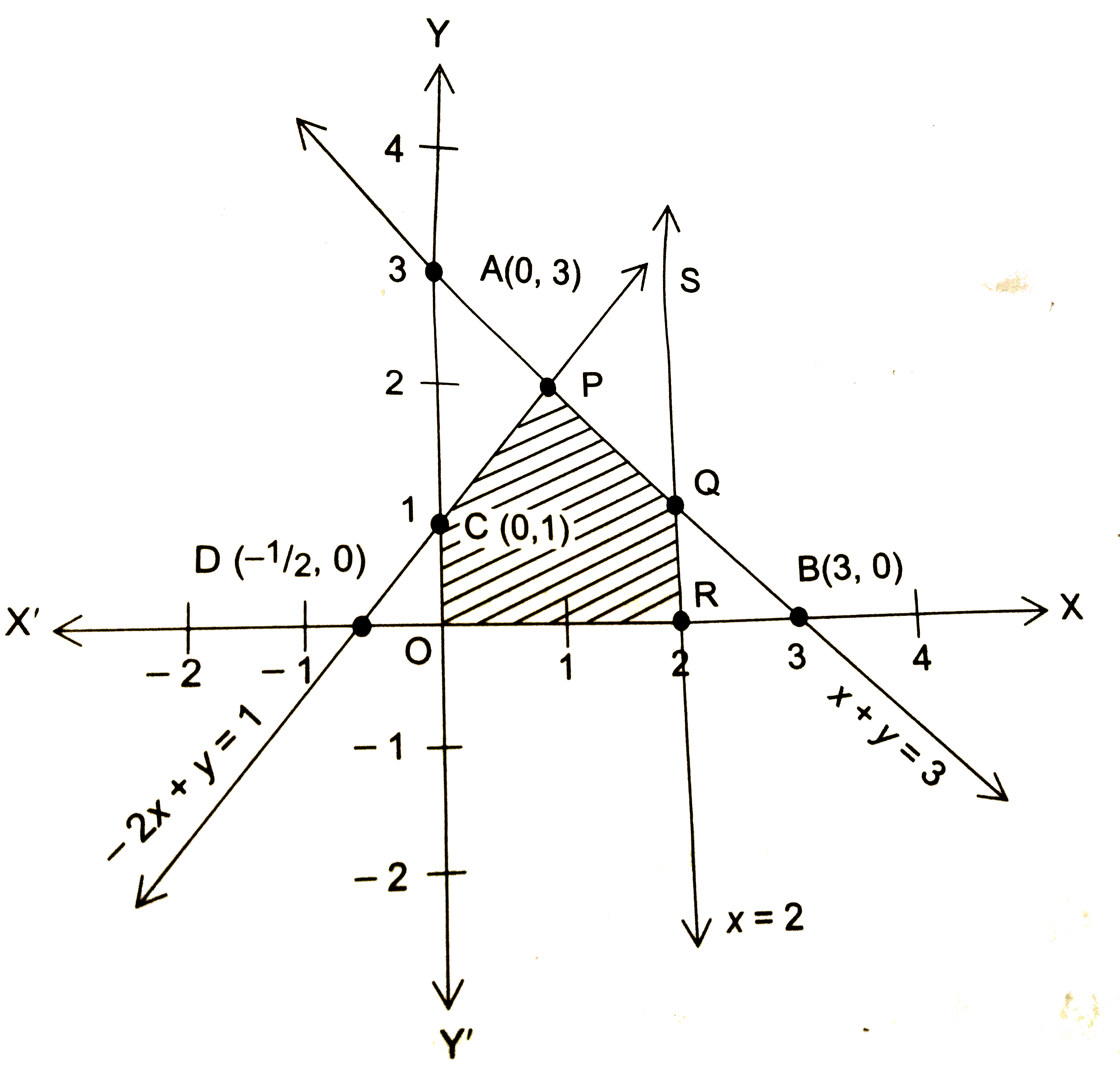
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
GURUKUL PUBLICATION - MAHARASHTRA PREVIOUS YEAR PAPERS- OCTOBER 2014-SECTION - II
- Solve the following LPP by using graphical method. Maximize : Z=6x+4...
Text Solution
|
- If X is the a random variable with probability mass function P(x) =...
Text Solution
|
- If sec((x+y)/(x-y))=a^(2),"then "(d^(2)y)/(dx^(2))=......
Text Solution
|
- If y=sin^(-1)(3x)+sec^(-1)((1)/(3x)), find (dy)/(dx).
Text Solution
|
- Evaluate : intx log x dx
Text Solution
|
- if int0^k (dx)/(2+8x^2)=pi/16 then find the value of k
Text Solution
|
- The probability that a certain kind of component will survive a check ...
Text Solution
|
- Find the area of the region bounded by the curve y = sinx , ...
Text Solution
|
- Examine the continuity of the following function at given point : f(...
Text Solution
|
- If x=phi(t) is a differentiable function of 't', then prove that int...
Text Solution
|
- 3e^(x) tan y dx + (1+e^(x)) sec^(2) dy =0 , " when" x = 0 and y = pi
Text Solution
|
- A point source of light is hung 30 feet directly above a straight hori...
Text Solution
|
- Evaluate the following integrals: int(logx)/((1+logx)^(2))dx
Text Solution
|
- If x=f(t), y=g(t) are differentiable functions of parameter 't' then p...
Text Solution
|
- Show that the function defined by f(x) = | cos x |is a continuous fun...
Text Solution
|
- Solve the differential equation (dy)/(dx)=(y+sqrt(x^(2)+y^(2)))/(x).
Text Solution
|
- Given X ~ B(n,p) If n= 20,, E(x)= 10 , Find p, Car(X) and S.D (X)
Text Solution
|
- A bakerman sells 5 types of cakes. Profit due to the sale of each type...
Text Solution
|
- Varify Lagrange's mean value theorem for the function f(x)=x+(1)/(x)...
Text Solution
|
- int(a)^(b)f(x)dx=int(a)^(b)f(a+b-x)dx. Hence evaluate : int(a)^(b)(f(x...
Text Solution
|