Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY-LAWS OF MOTION-Medical entrances gallery
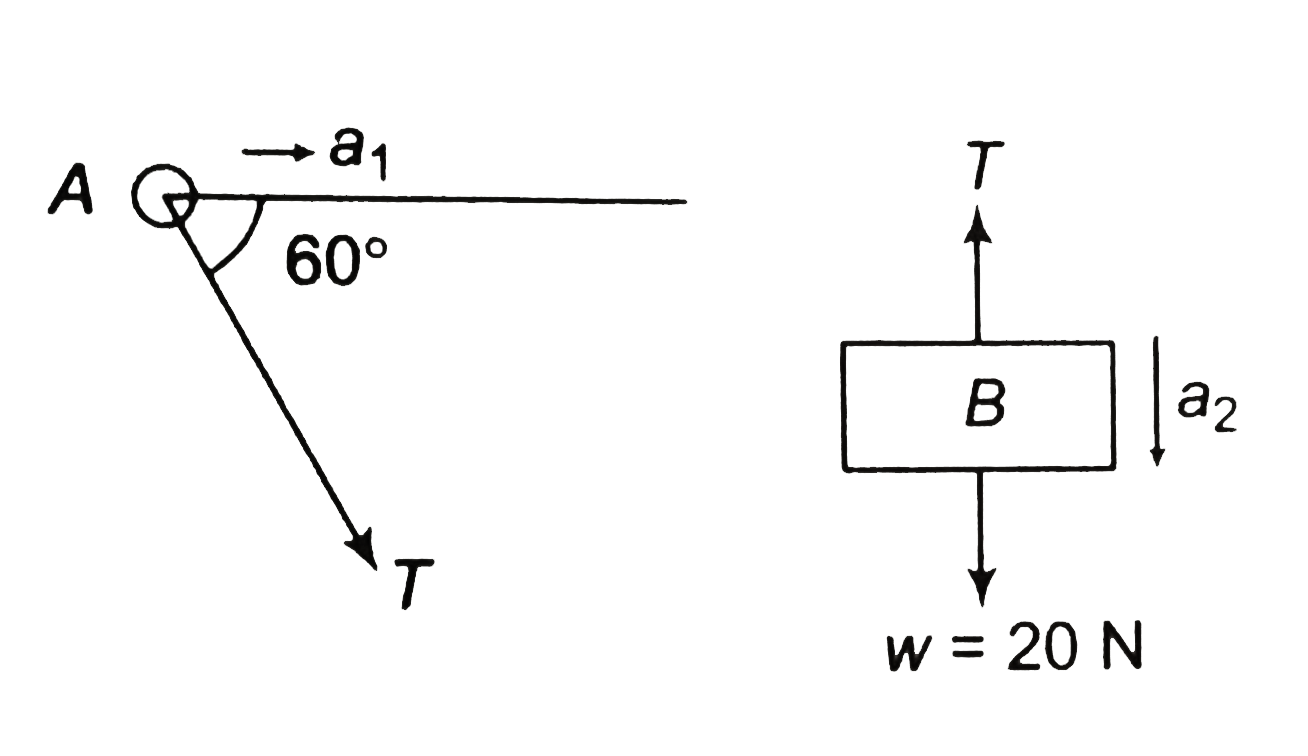
- In the abjoining figure, wire PQ is smooth, ring A has a mass 1kg and ...
Text Solution
|
- A rigid ball of mass m strikes a rigid wall at 60^(@) and gets reflect...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass 40kg resting on a rough horizontal surface is subjected...
Text Solution
|
- A balloon of mass 10 kf is raising up with an acceleration of 20 ms^(-...
Text Solution
|
- Block B lying on a table weighs w. The coefficient of static friction ...
Text Solution
|
- A stone of mass 0.05 kg is thrown vertically upwards. What is the dire...
Text Solution
|
- Three blocks A , B and C of masses 4kg , 2kg and 1kg respectively are ...
Text Solution
|
- A block A of mass m(1) rests on a horizontal table. A light string con...
Text Solution
|
- A balloon with mass m is descending down with an acceleration a (where...
Text Solution
|
- A bullet moving with a velocity of 30sqrt(2) ms^(-1) is fired into a f...
Text Solution
|
- A system consists of three masses m(1),m(2) " and " m(3) connected by ...
Text Solution
|
- A block B is pushed momentarily along a horizontal surface with an ini...
Text Solution
|
- Three identical blocks of masses m=2kg are drawn by a force 10.2 N on ...
Text Solution
|
- A wooden box of mass 8kg slides down an inclined plane of inclination ...
Text Solution
|
- To determine the coefficient of friction between a rough surface and a...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass m is placed on a rough surface with coefficient of fric...
Text Solution
|
- Three blocks with masses m , 2m and 3m are connected by strings, as sh...
Text Solution
|
- The upper half of an inclined plane with inclination phi is perfectly ...
Text Solution
|
- Newton's second law of motion is
Text Solution
|
- A balloon starting from rest ascends vertically with uniform accelerat...
Text Solution
|
- A 3 kg block is placed over a 10 kg block and both are palced on a smo...
Text Solution
|
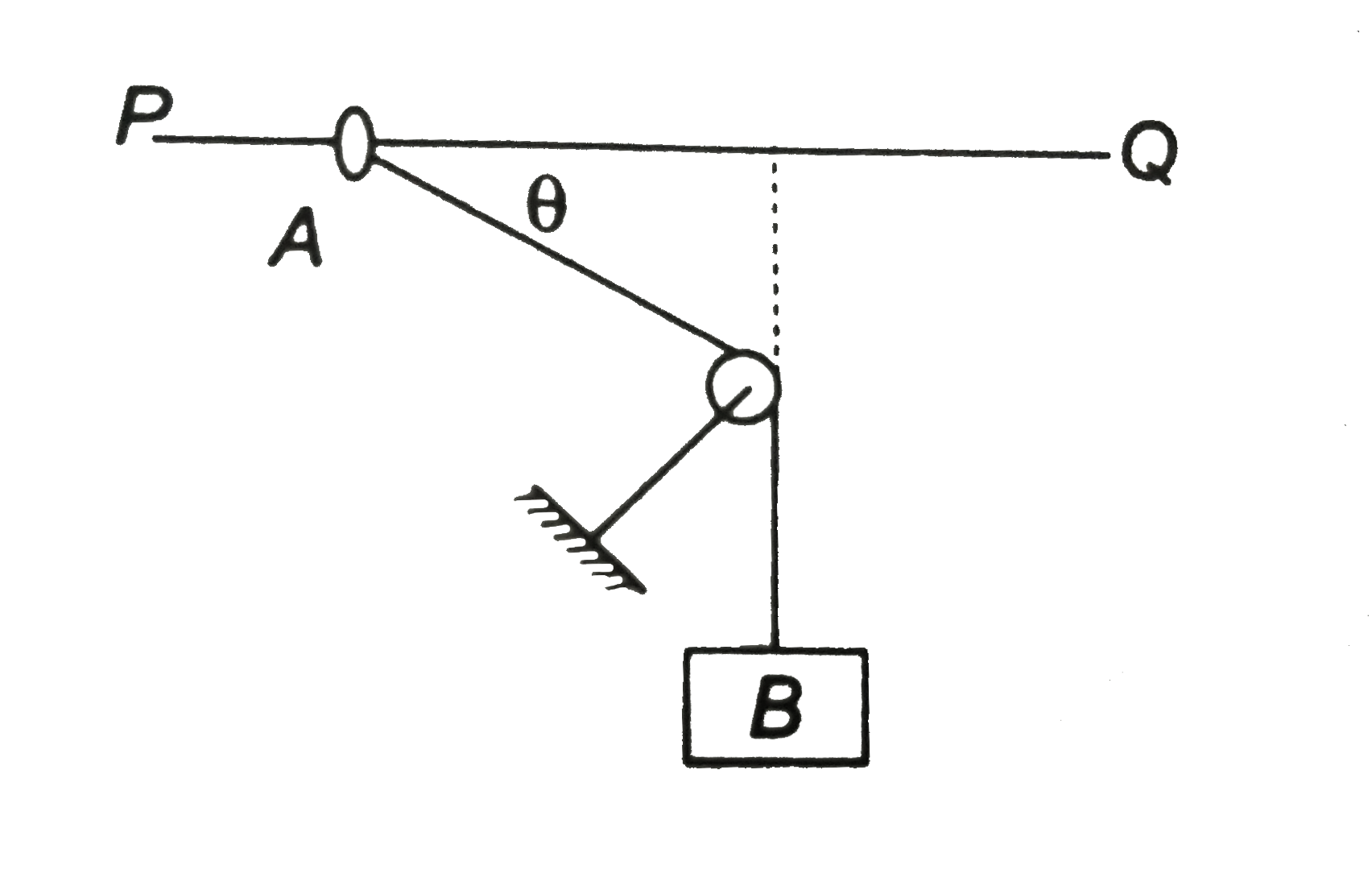
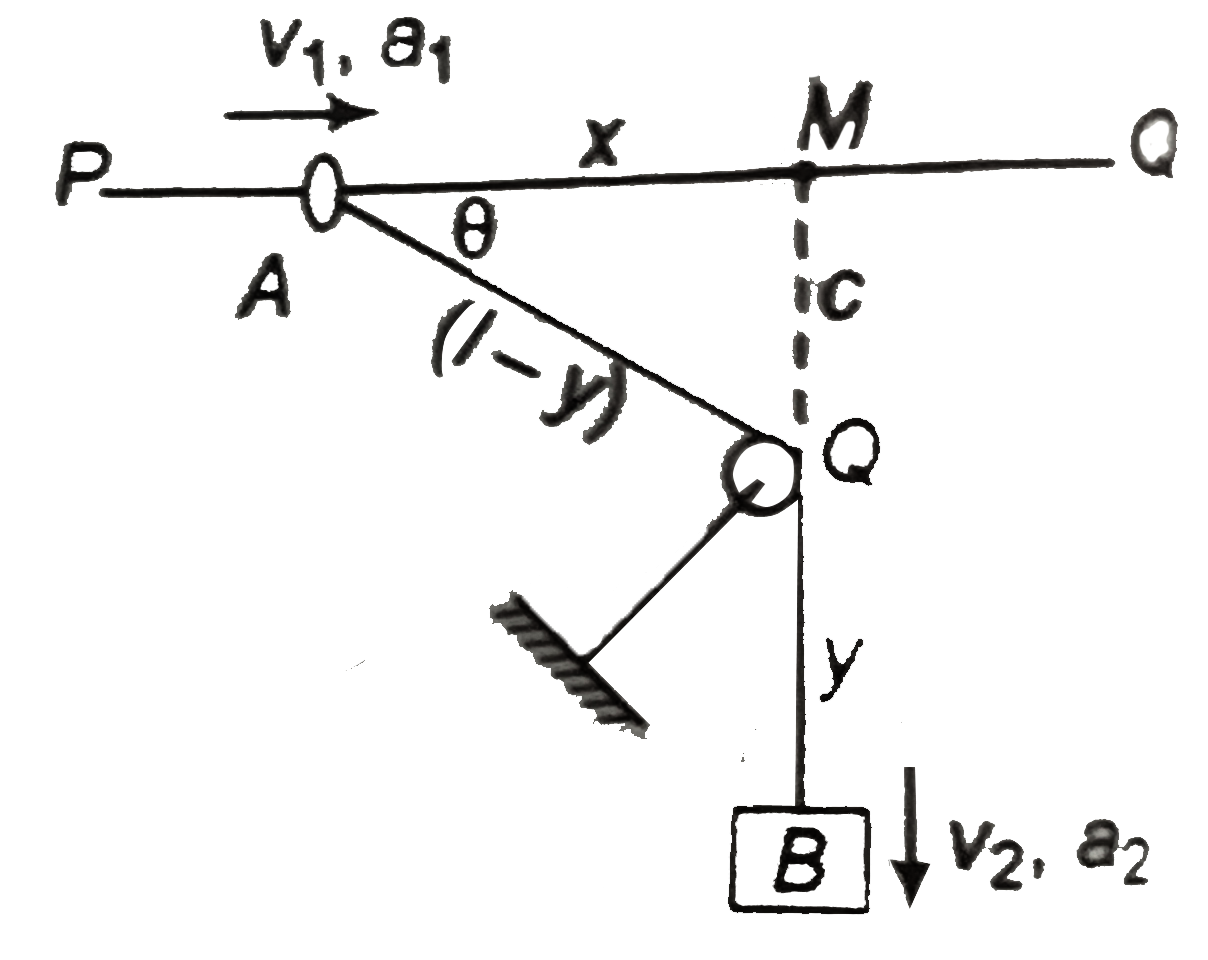 (a) In traingle `MQA, (l-y)^(2) =x^(2)+c^(2)`
(a) In traingle `MQA, (l-y)^(2) =x^(2)+c^(2)`