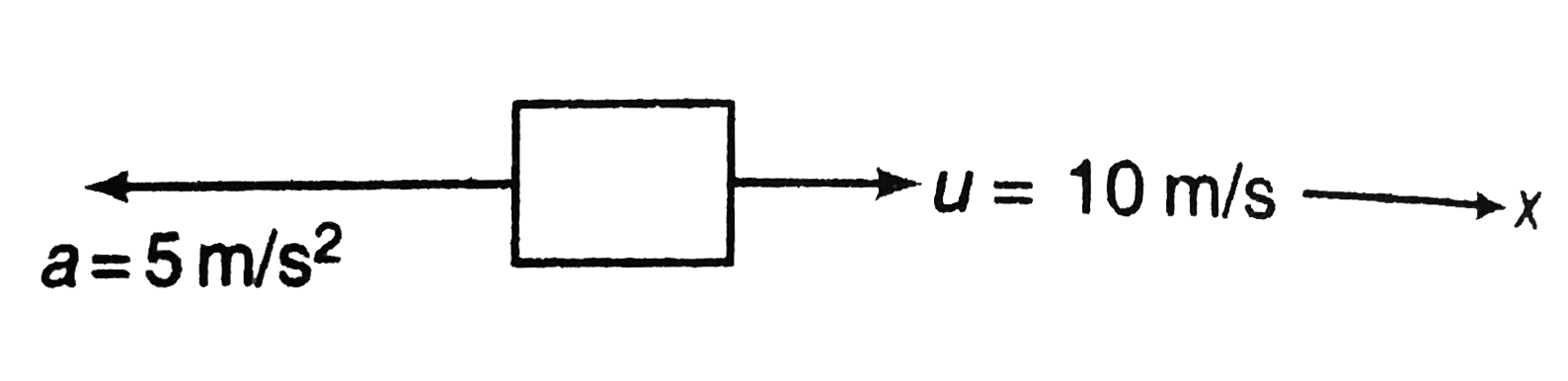
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY-LAWS OF MOTION-Single Correct
- In the adjoining figure a wedge is fixed to an elevator moving upwards...
Text Solution
|
- In figure m(1)= 1 kg and m(2)= 4 kg Find the mass m of the hanging blo...
Text Solution
|
- A 2 kg object is slide along the frictionless floor with intial voloci...
Text Solution
|
- A 2 kg object is slide along the frictionless floor with intial trans...
Text Solution
|
- A 2 kg object is slide along a rough floor (coefficient of sliding f...
Text Solution
|
- A block is placed on an inclined plane as shown in figure. What must b...
Text Solution
|
- A 6 kg block is kept on an inclined rough surface as shown in figure.F...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 200kg is set into motion on a frictionless , horizonta...
Text Solution
|
- A cube of mass 2 kg is help stationary against a rought wall by a forc...
Text Solution
|
- A 20 kg monkey has a firm hold on a light rope that passes over a fric...
Text Solution
|
- In the pulley-block arrangement shown in figure , find the relation be...
Text Solution
|
- In the pulley-block arrangement shown in figure , find the relation be...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown ,find :(g = 10 m//s^(2)) (a) acceleration of ...
Text Solution
|
- Find the acceleration of the A and B in the situation show in the figu...
Text Solution
|
- A conveyor belt is moving with constant speed of 6 m//s. A small block...
Text Solution
|
- Coefficient of friction between two block shown in figure ia mu = 0.4....
Text Solution
|
- A 2 kg block is present against a rough wall by a force F = 20 N as sh...
Text Solution
|
- A 2 kg block is kept over a ground with coefficient of friction mu = 0...
Text Solution
|
- A 6 kg block is kept over a rough surface with coefficient of friction...
Text Solution
|
- What is the largest mass of C in kg that can be suspended without movi...
Text Solution
|