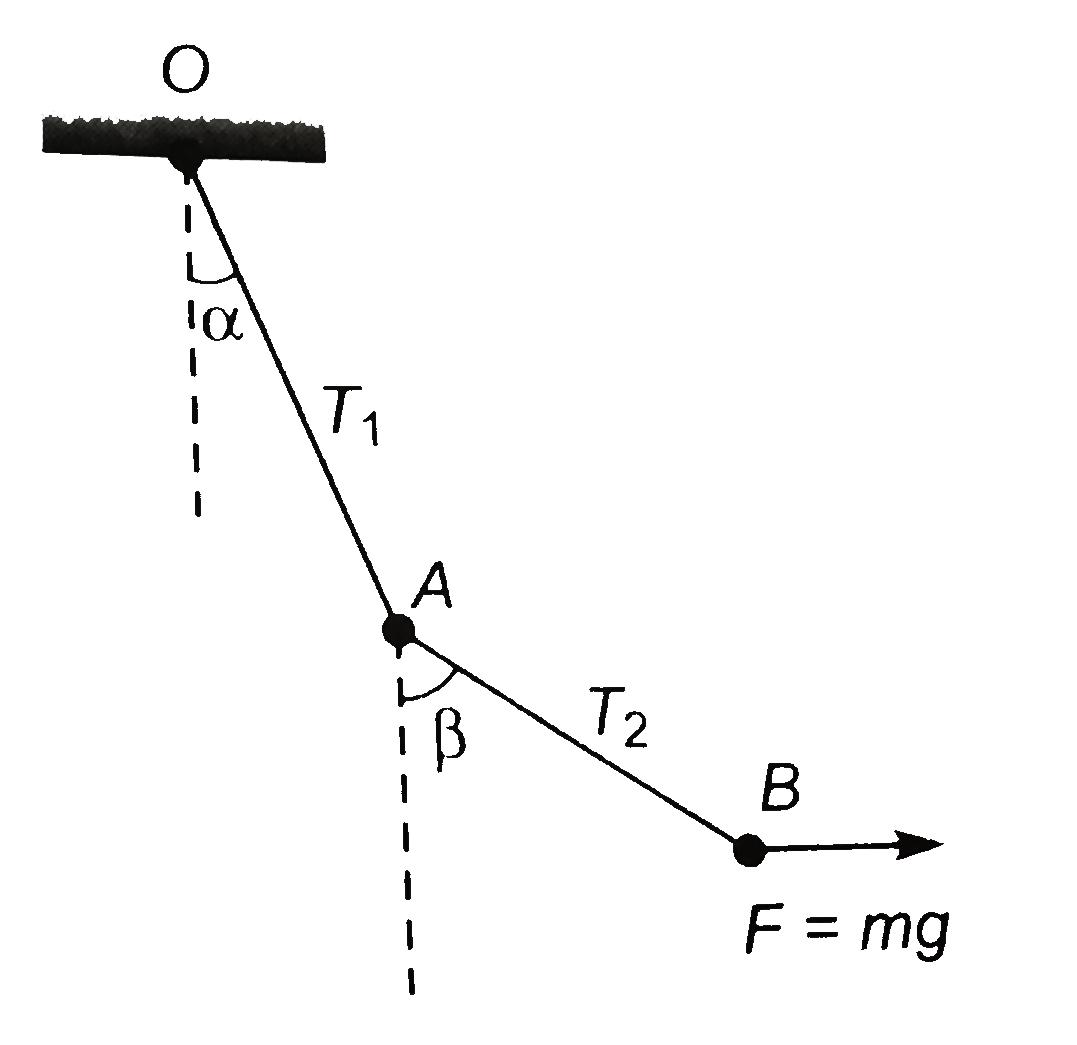
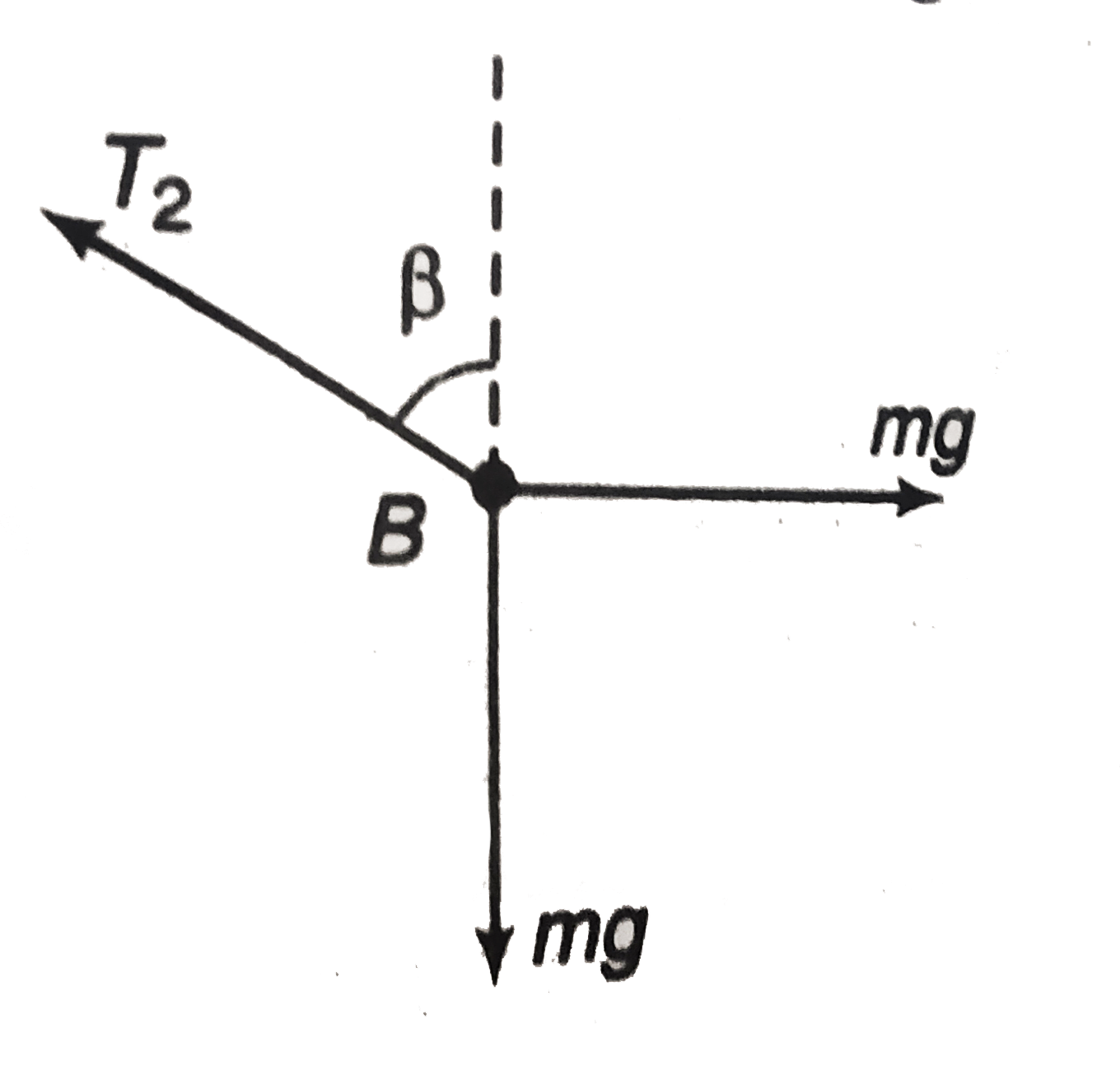
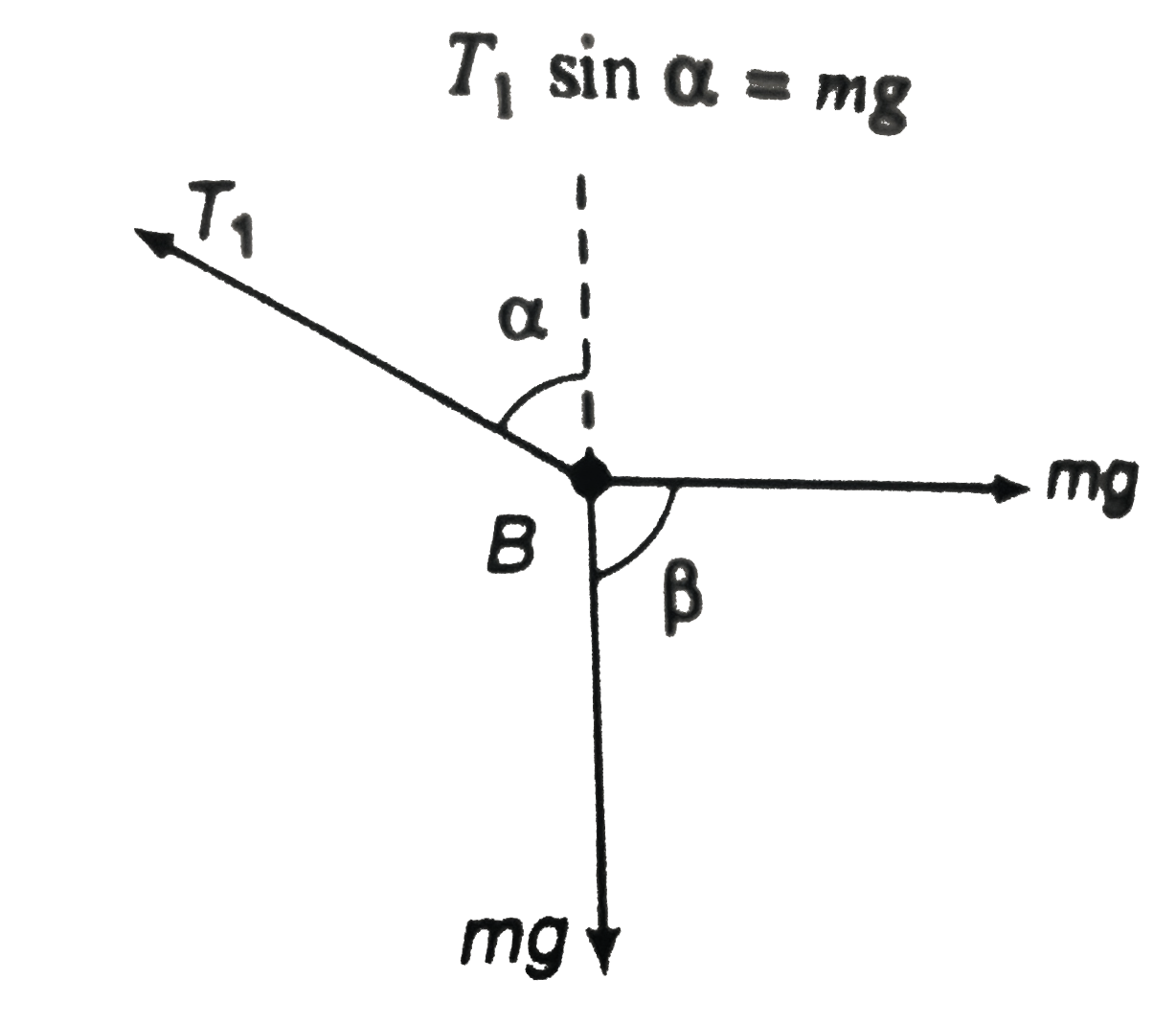
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY-LAWS OF MOTION-Objective Question
- Two blocks A and B each of mass m are placed on a smooth horizontal su...
Text Solution
|
- Two block A and Bmove along a semicircular wire frame as shown in figu...
Text Solution
|
- If the coefficient of friction between A and B is mu, the maximum acce...
Text Solution
|
- A livotad beam of negligible mass has mass suspended from one end and ...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m sides down an inclined right angled trough .If the c...
Text Solution
|
- If force F is increasing with time and at t=0, F = 0, where will slipp...
Text Solution
|
- A plank of mass 2 kg and length 1 m is placed on horizontal floor.A sm...
Text Solution
|
- The block each of mass 1 kg are placed as shown .They are connected by...
Text Solution
|
- Two particalA and B each of mass m are kept stationary by applying a h...
Text Solution
|
- The velocity- time graph of the figure shown the motion of a wooden bl...
Text Solution
|
- As shown in figure, A is a man of mass 60 kg standing on a block B of ...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown A and B are free to move . All the surface are smo...
Text Solution
|
- M(A) = 3 kg ,M(B) = 4 kg ,M(C) = 8 kg. Coefficient of friction between...
Text Solution
|
- A man pulls a block of mass equal to himself with a light string .The ...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 1 kg is at rest relative to a smooth wedge moving left...
Text Solution
|
- For the given situation shown in figure , choose the correct option (g...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown , all the string are massless and friction is abse...
Text Solution
|
- Force acting on a block versus time graph is as shown in figure Choose...
Text Solution
|
- For the situation shown in figure ,mark the correct options.
Text Solution
|
- For the situation shown in figure ,mark the correct options.
Text Solution
|