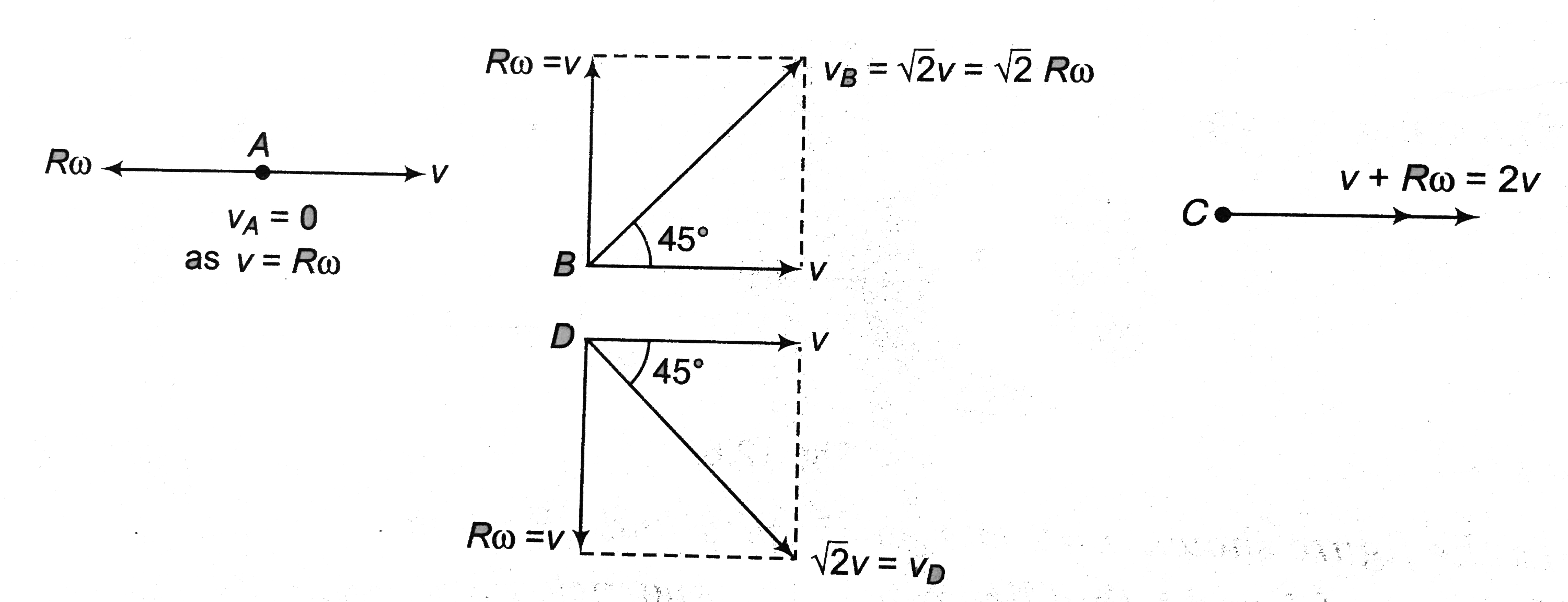

As stated in above article, velocity of ay point of the rigid body in rotation plus translationn is the vector sum of `v` (the velocity of centre of mass) and `romega`. Here, `r` is the distance of the point under consideration from the centre of mass of the body. direction of this `romega` is perpendicular to the line joining the point with centre of mass in the sense of rotation. Based on this, velocities of points A, B ,C and D are as shown below.
thus, `V_(A)` is zero, velocity of B and D is `sqrt(2v)` or `sqrt(2)Romega` and velocity of C is 2 v or `2Romega` in the direction shown in figure.