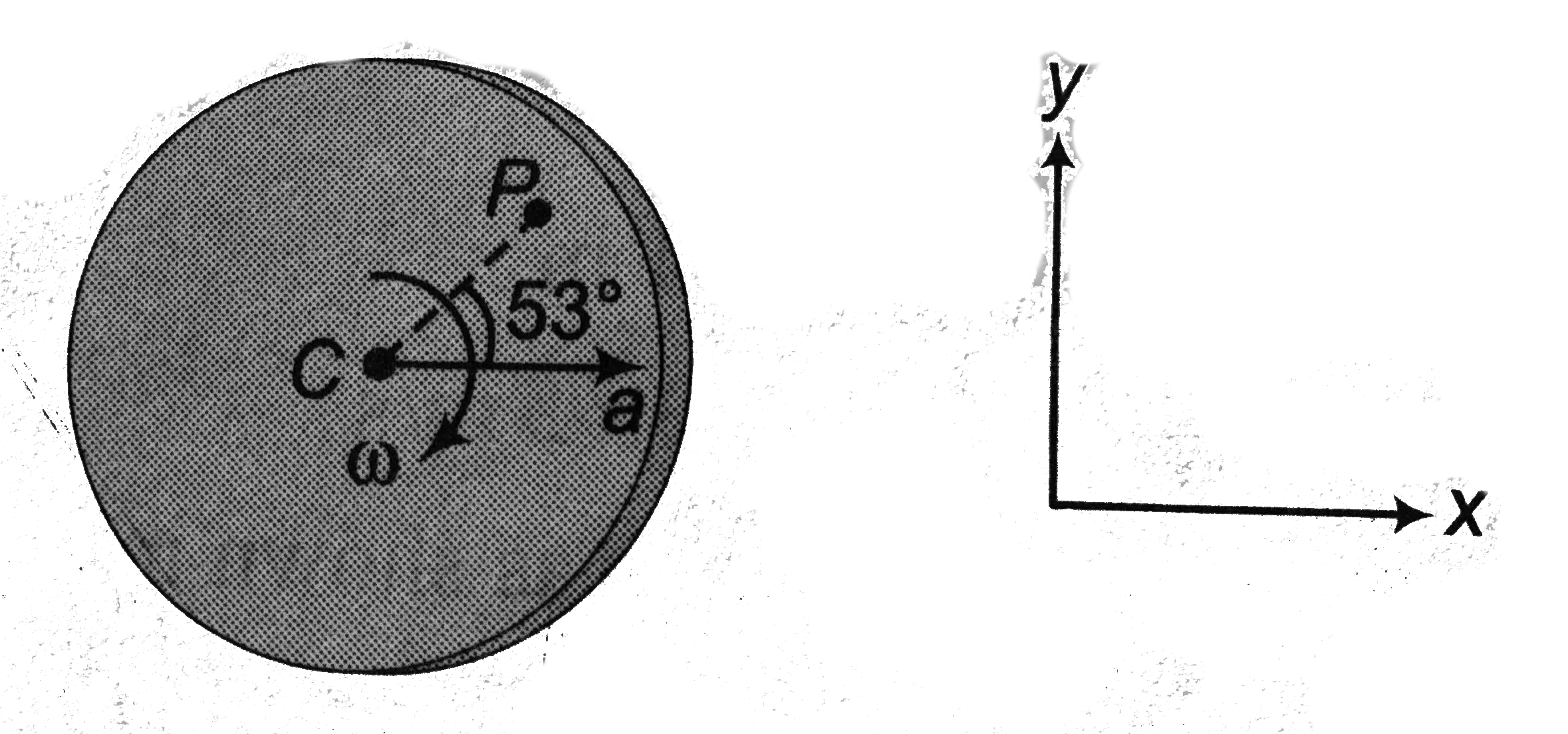
For particle at `P`
`r=CP=1m`
`impliesalpha=(domega)/(dt)=(d)/(dt)(2t)=2rad//s^(2)`
At `t=1` s
`omega=2rad//s`
`alpha=2rad//s^(2)`
`a_(t)=ralpha=2m//s^(2)`
`a_(r)=romega^(2)=4m//s^(2)`
and `a=2m//s^(2)`
Net acceleration of `P` is the vector sum of three terms a, `a_(r)` and `a_(t)` as shown in figure below.
`thereforea_(P)=2hati+(2cos37^(@)hati-2sin37^(@)hatj)+(-4sin37^(@)hati-2sin37^(@)hatj)-(-4sin37^(@)hati-4cos37^(@)hatj)`
`=2hati+1.6hati-1.2hatj-2.4hati-3.2hatj`
`=(1.2hati-4.4hatj)m//s^(2)`