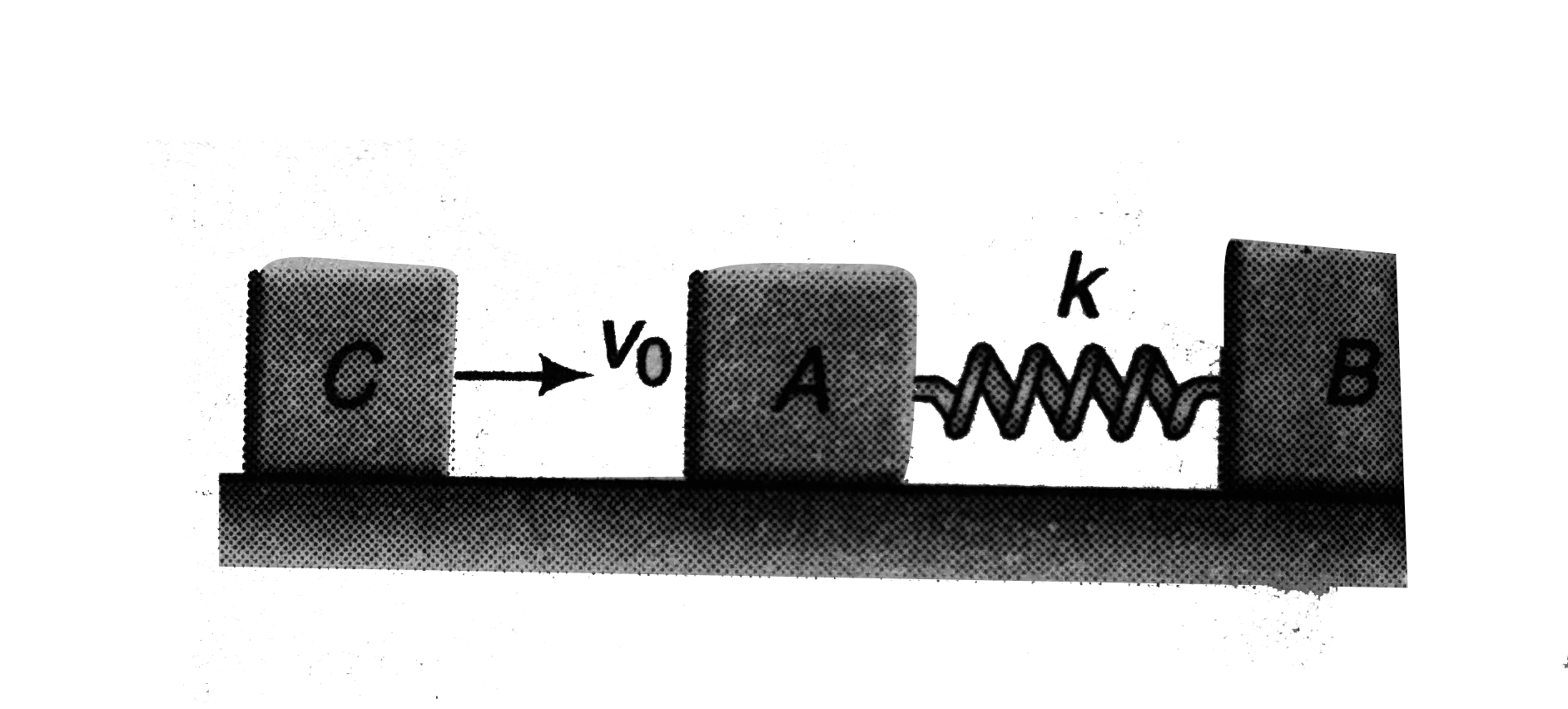Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
DC PANDEY|Exercise Exercise 14.1|5 VideosSIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
DC PANDEY|Exercise Intro. Exer.|1 VideosSIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
DC PANDEY|Exercise Level 2 Comprehension|2 VideosSEMICONDUCTORS AND ELECTRONIC DEVICES
DC PANDEY|Exercise More than One Option is Correct|3 VideosSOLVD PAPERS 2017 NEET, AIIMS & JIPMER
DC PANDEY|Exercise Solved paper 2018(JIPMER)|38 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY-SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION-Level 2 Subjective
- A 1kg block is executing simple harmonic motion of amplitude 0.1m on a...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles are in SHM along same line. Time period of each is T and...
Text Solution
|
- A particle that hangs from a spring oscillates with an angular frequen...
Text Solution
|
- A 2kg mass is attached to a spring of force constant 600 N//m and res...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 4kg hangs from a spring of force constant k = 400 N//m...
Text Solution
|
- A plank with a body of mass m placed on it starts moving straight up a...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m free to move in the x - y plane is subjected to a...
Text Solution
|
- Determine the natural frequency of vibration of the 100N disk. Assume ...
Text Solution
|
- The disk has a weight of 100 Nand rolls without slipping on the horizo...
Text Solution
|
- A solid uniform cylinder of mass m performs small oscillations due to ...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is attached to one end of a light inextensible strin...
Text Solution
|
- In the shown arrangement, both the spring are in their natural lengths...
Text Solution
|
- Two block A and B of masses m(1) = 3kg and m(2) = 6kg respectively are...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of length l and mass m, pivoted at one end, is held by a spring ...
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangement shown in figure, pulleys are light and spring are i...
Text Solution
|
- A light pulley is suspended at the lower end of a spring of constant k...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a solid uniform cylinder of radius R and mass M, which is...
Text Solution
|
- Find the natural frequency of the system shown in figure. The pulleys ...
Text Solution
|