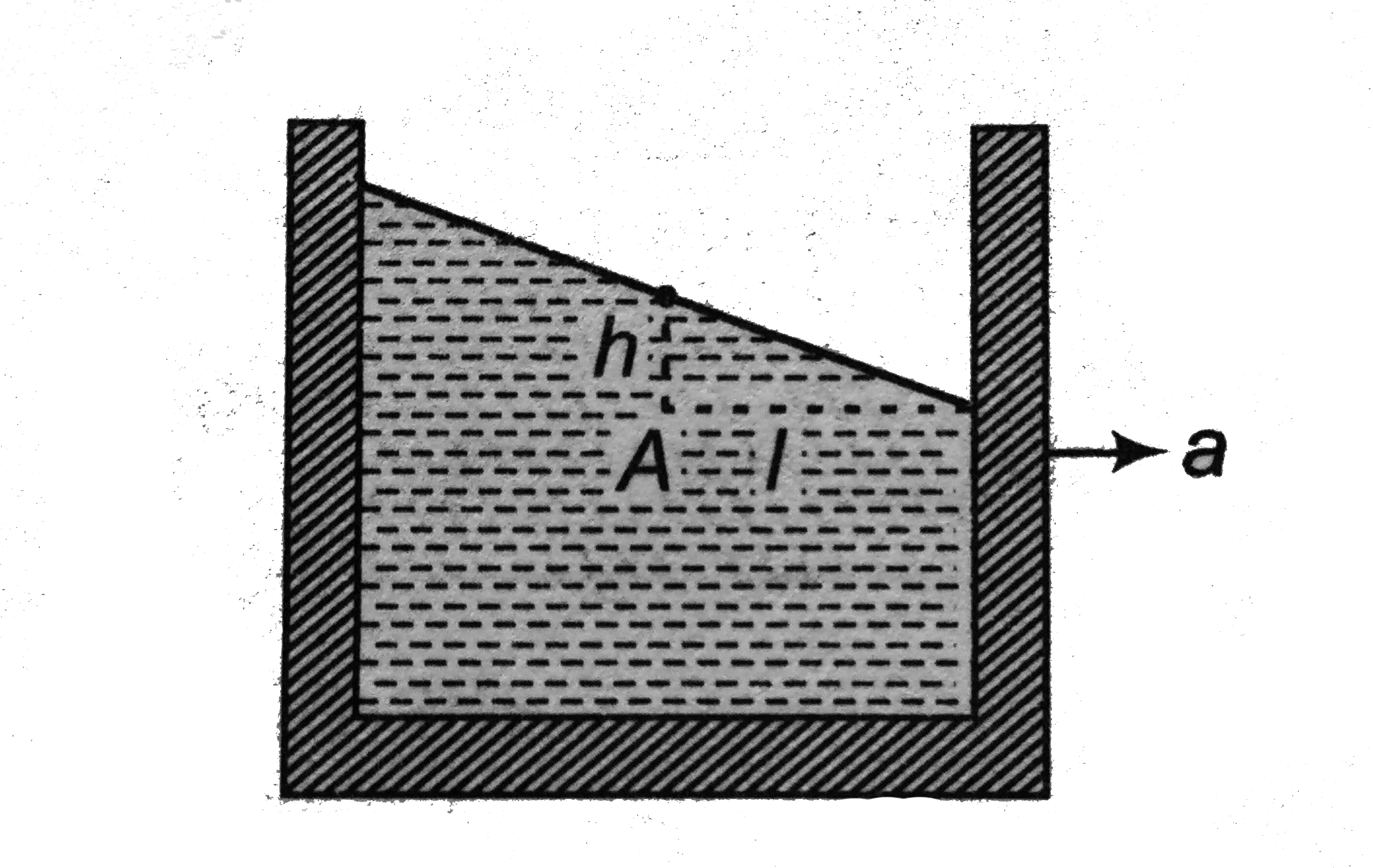
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
FLUID MECHANICS
DC PANDEY|Exercise Level 2 More Than One Correct|10 VideosFLUID MECHANICS
DC PANDEY|Exercise Level 2 Comprehension Based|7 VideosFLUID MECHANICS
DC PANDEY|Exercise Subjective Question|2 VideosEXPERIMENTS
DC PANDEY|Exercise Subjective|15 VideosGENERAL PHYSICS
DC PANDEY|Exercise INTEGER_TYPE|2 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY-FLUID MECHANICS-Level 2 Single Correct
- The figure shown a pipe of uniform cross-section inclined in a vertica...
Text Solution
|
- A horizontal tube of uniform cross-sectional area A is bent in the for...
Text Solution
|
- A rectangular container moves with an acceleration a along the positiv...
Text Solution
|
- A square gate of size 1mxx1m is hinged at its mid point. A fluid of de...
Text Solution
|
- A thin uniform circular tube is kept in a vertical plane. Equal volume...
Text Solution
|
- A plate moves normally with the speed v(1) towads a horizontal jet of ...
Text Solution
|
- A spherical ball of density rho and radius 0.003m is dropped into a tu...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown, the heavy cylinder (radius R) reasting on a smoot...
Text Solution
|
- A U-tube having horizontal arm of length 20 cm, has uniform cross-sect...
Text Solution
|
- A cubical block of side a and density rho slides over a fixed inclined...
Text Solution
|
- A spring balance reads 10kg when a bucket of water is suspened from it...
Text Solution
|
- Three points A,B,and C on a steady flow of a non-viscon and inconpress...
Text Solution
|
- A body of density rho is dropped from rest from height h (from the sur...
Text Solution
|
- A tank is filled up to a height 2H with a liquid and is placed on a pl...
Text Solution
|
- Two boats of base areas A(1) and A(2), connected by a string are being...
Text Solution
|
- A U-tube is partially filled with water. Oil which does not mix with w...
Text Solution
|
- There is a howizontal film of soap solution. On it a thread is placed ...
Text Solution
|
- A thin metal disc of radius r floats on water surface and bends the su...
Text Solution
|
- The radii of the two column is U-tube are r(1) and r(2)(gtr(1)). When ...
Text Solution
|
- Water rises to a height h in a capillary tube lowered vertically into ...
Text Solution
|