Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
THERMOMETRY,THERMAL EXPANSION & KINETIC THEORY OF GASES
DC PANDEY|Exercise Exercise 20.1|5 VideosTHERMOMETRY,THERMAL EXPANSION & KINETIC THEORY OF GASES
DC PANDEY|Exercise Exercise 20.2|7 VideosTHERMOMETRY,THERMAL EXPANSION & KINETIC THEORY OF GASES
DC PANDEY|Exercise Example Type 3|2 VideosTHERMOMETRY THERMAL EXPANSION AND KINETIC THEORY OF GASES
DC PANDEY|Exercise Medical entrance gallary|30 VideosUNIT AND DIMENSIONS
DC PANDEY|Exercise Assertion And Reason|2 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY-THERMOMETRY,THERMAL EXPANSION & KINETIC THEORY OF GASES-Miscellaneous Example
- An ideal diatomic gas with CV = (5 R)/2 occupies a volume (V(i) at a p...
Text Solution
|
- Given, Avogadro's number N = 6.02 xx 10^23 and Boltzmann's constant k ...
Text Solution
|
- An air bubble starts rising from the bottom of a lake. Its diameter is...
Text Solution
|
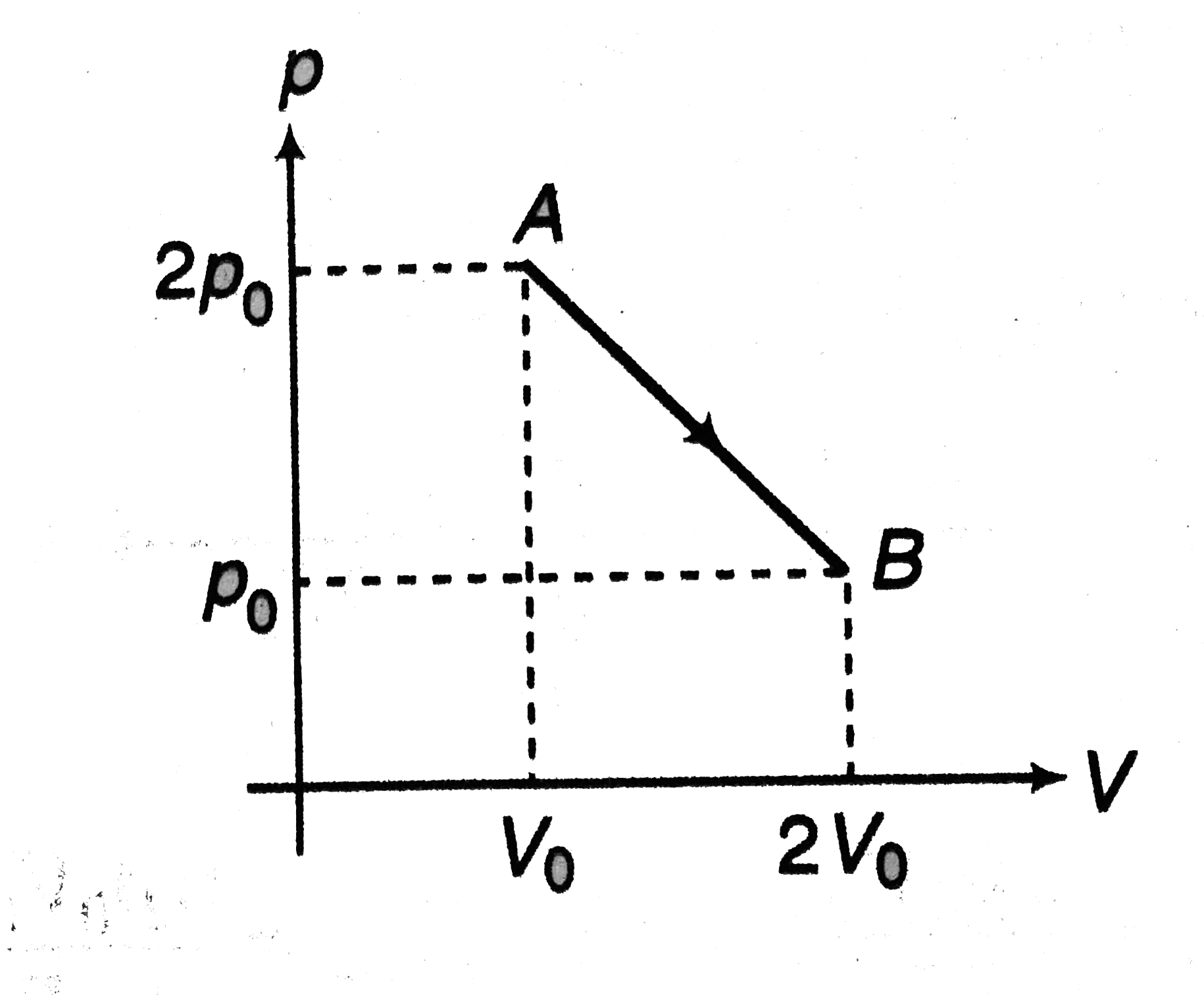
- (p - V) diagram of (n) moles of an ideal gas is as shown in figure. Fi...
Text Solution
|
- Plot (p - V),(V - T) and (rho - T) graph corresponding to the (p - T) ...
Text Solution
|
 .
.