Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY-ELECTROSTATICS-Medical entrances gallery
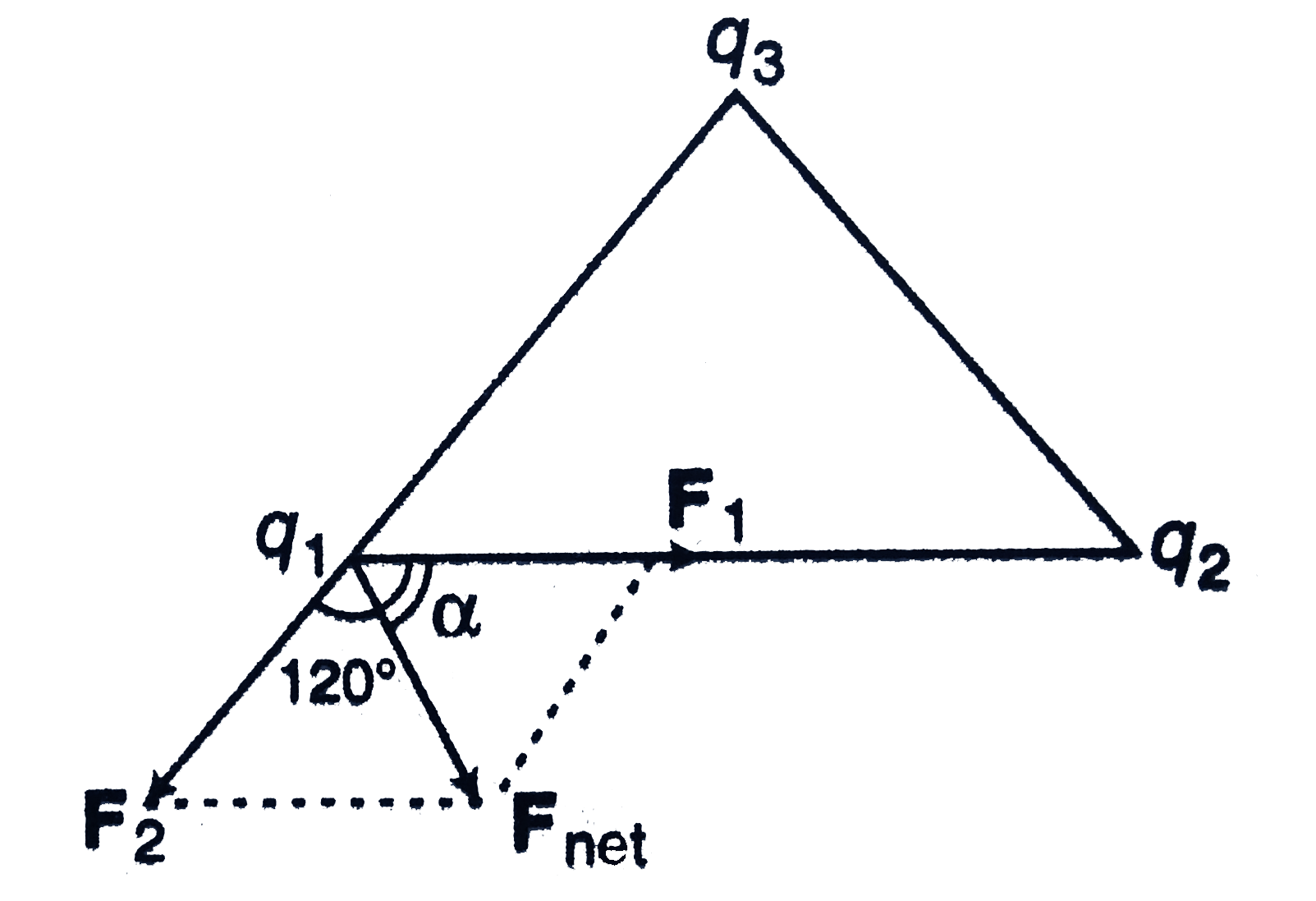
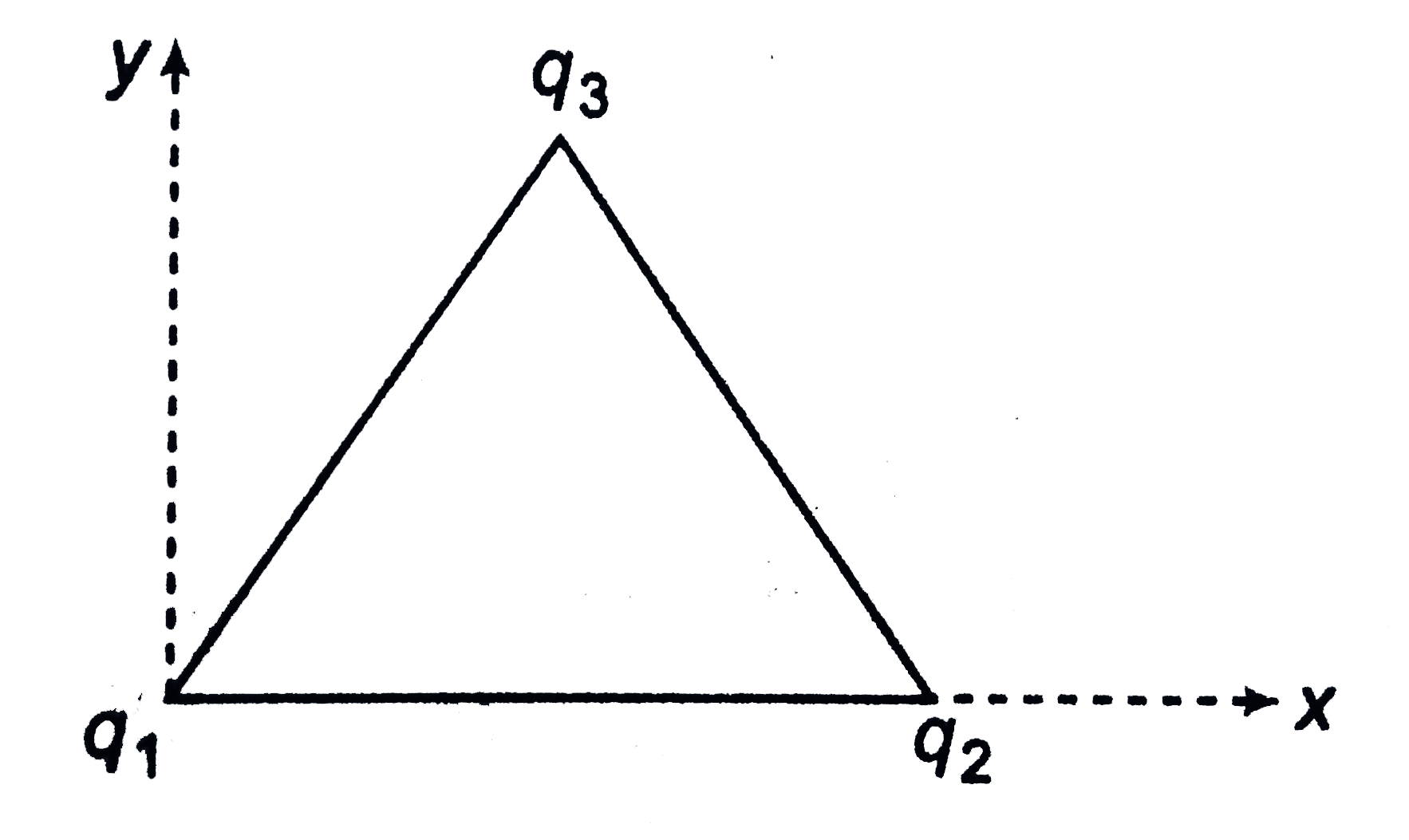
- Three charges q1=1muC, q2=2muC and q3=3muC are placed on the vertices ...
Text Solution
|
- An electric dipole is placed at an angle of 30^(@) with an electric fi...
Text Solution
|
- The electric field in a certain region is acting radially outwards and...
Text Solution
|
- A Gaussian surface in the cylinder of cross-section pia^(2) and length...
Text Solution
|
- A total charge of 5 muC is distributed uniformly on the surface of the...
Text Solution
|
- Two small spherical shells a and B are given positive charges of 9 C a...
Text Solution
|
- a point charge q is situated at a distance r from one end of a thin co...
Text Solution
|
- When 10^(19) electrons are removed from a neutral metal plate through ...
Text Solution
|
- A charge Q is uniformly distributed over a large plastic plate. The el...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform electric field E is created between two parallel ., charge...
Text Solution
|
- The line A A' is on charged infinite conducting plane which is perpend...
Text Solution
|
- The electric field at a point on equatorial of a dipole and direction ...
Text Solution
|
- Pick out the statement which is incorrect?
Text Solution
|
- An electron of mass m(e ) initially at rest moves through a certain di...
Text Solution
|
- Two charges 10 muC and - 10 muC are placed at points A. and B separate...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform electric field exists in space. Find the flux of this field...
Text Solution
|
- An inclined plane of length 5.60 m making an angle of 45^(@) with the ...
Text Solution
|
- Two charge spheres separated at a distance d exert a force F on each o...
Text Solution
|
- If a charge on the body is 1 nC, then how many electrons are present o...
Text Solution
|
- Electric field at a point of distance r from a uniformly charged wire ...
Text Solution
|
- Two equal and opposite charges of masses m(1) and m(2) are accelerated...
Text Solution
|
 `
`  `
`