A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
DC PANDEY|Exercise SUBJECTIVE TYPE|1 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
DC PANDEY|Exercise Level 2 Subjective|20 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
DC PANDEY|Exercise Level 2 More Than One Correct|10 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
DC PANDEY|Exercise Medical entrances gallery|97 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
DC PANDEY|Exercise Sec C|22 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DC PANDEY-ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION-Level 2 Comprehension Based
- A uniform but time varying magnetic field B=(2t^3+24t)T is present in ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform but time varying magnetic field B=(2t^3+24t)T is present in ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform but time varying magnetic field B=(2t^3+24t)T is present in ...
Text Solution
|
- A thin non conducting ring of mass m, radius a carrying a charge q can...
Text Solution
|
- A thin non conducting ring of mass m, radius a carrying a charge q can...
Text Solution
|
- A thin non conducting ring of mass m, radius a carrying a charge q can...
Text Solution
|
- A thin non conducting ring of mass m, radius a carrying a charge q can...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a conducting rod of negligible resistance that can slide ...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a conducting rod of negligible resistance that can slide ...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a conducting rod of negligible resistance that can slide ...
Text Solution
|
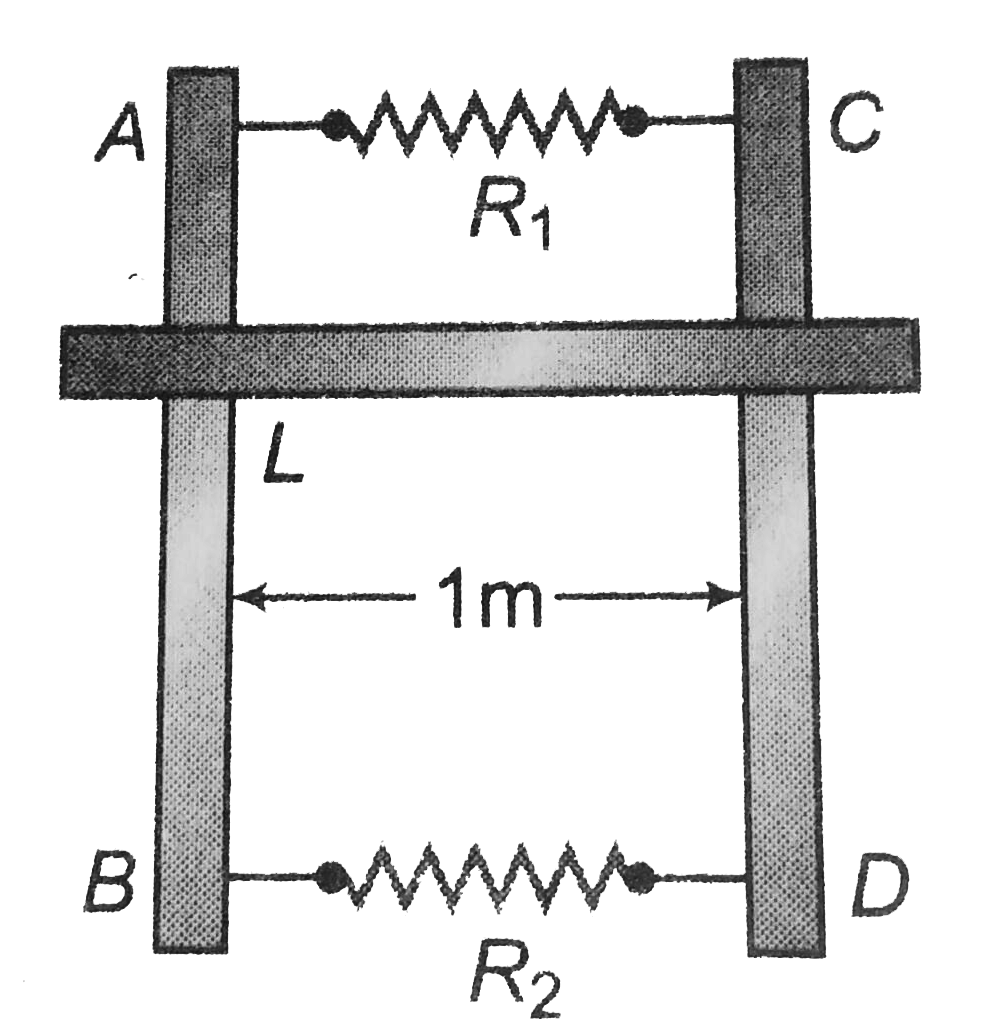
- Two parallel vertical metallic rails AB and CD are separated by 1m. Th...
Text Solution
|
- Two parallel vertical metallic rails AB and CD are separated by 1m. Th...
Text Solution
|
- Two parallel vertical metallic rails AB and CD are separated by 1m. Th...
Text Solution
|