Text Solution
Verified by Experts
DC PANDEY-REFRACTION OF LIGHT-Level 2 Subjective
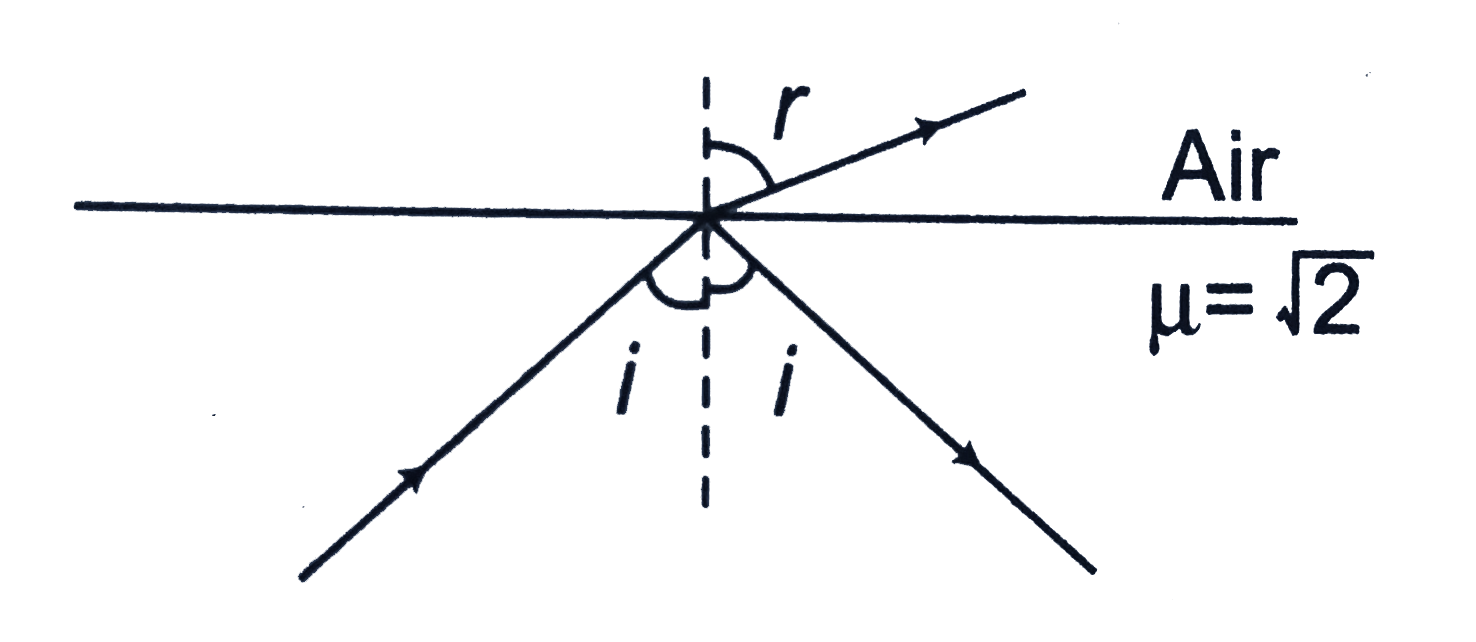
- Theory In the figure, i is increased from 0^@ "to" 90^@. But ray ...
Text Solution
|
- a. Figure (a) shows the optical axis of a lens, the point source of ...
Text Solution
|
- a. Figure (a) shows the optical axis of a lens, the point source of ...
Text Solution
|
- In Figure, a fish watcher watches a fish through a 3.0 cm thick glass ...
Text Solution
|
- A concave spherical mirror with a radius of curvature of 0.2 m is fill...
Text Solution
|
- A lens with a focal length of f=30 cm produces on a screen a sharp ima...
Text Solution
|
- One side of radius of curvature R2=120 cm of a convexo-convex lens of ...
Text Solution
|
- A small object is placed on the principal axis of concave spherical mi...
Text Solution
|
- A thin glass lens of refractive index mu2=1.5 behaves as an interface ...
Text Solution
|
- A glass hemisphere of radius 10 cm and mu=1.5 is silvered over its cur...
Text Solution
|
- A equilateral prism of flint glass (mug=3//2) is placed water (muw=4//...
Text Solution
|
- Rays of light fall on the plane surface of a half cylinder at an angle...
Text Solution
|
- The figure shows an arrangement of an equi-convex lens and a concave m...
Text Solution
|
- A convex lens is held 45 cm above the bottom of an empty tank. The ima...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel beam of light falls normally on the first face of a prism o...
Text Solution
|
- Two converging lenses of the same focal length f are separated by a di...
Text Solution
|
- A cubical vessel with non-transparent walls is so located that the eye...
Text Solution
|
- A spherical ball of transparent material has index of refractionmu. A ...
Text Solution
|
- A ray incident on the droplet of water at an angle of incidence i unde...
Text Solution
|
- A transparent solid sphere of radius 2 cm and density rho floats in a ...
Text Solution
|
- A hollow sphere of glass of inner and outer radii R and 2R respectivel...
Text Solution
|