Balance the following equations:
a. `BaCrO_(4) + KI+HClrarrBaCl_(2)+I_(2)+KCl+CrCl_(3)+H_(2)O`
b. `SO_(2)+Na_(2)CrO_(4)+H_(2)SO_(4)rarrNa_(2)SO_(4)+Cr_(2)(SO_(4))_(3)+H_(2)O`
c. `C_(2)H_(5)OH+I_(2)+overset(ө)OHrarrCHI_(3)+HCO_(2)^(ө)+H_(2)O+I^(ө)` (Basic)
d. `As_(2)S_(3)+HNO_(3)rarrH_(3)AsO_(4)+H_(2)SO_(4)+NO`
e. `......+HC_(2)O_(4)^(ө)rarrCO_(3)^(2-)+Cl^(ө)` (Acidic)
f. `HgS+HCl+HNO_(3)rarrH_(2)NO_(3)rarrH_(2)HgCl_(4)+NO+S+H_(2)O`
g. `Mn_(2)O_(7)rarrMnO_(2)+O_(2)`
Balance the following equations:
a. `BaCrO_(4) + KI+HClrarrBaCl_(2)+I_(2)+KCl+CrCl_(3)+H_(2)O`
b. `SO_(2)+Na_(2)CrO_(4)+H_(2)SO_(4)rarrNa_(2)SO_(4)+Cr_(2)(SO_(4))_(3)+H_(2)O`
c. `C_(2)H_(5)OH+I_(2)+overset(ө)OHrarrCHI_(3)+HCO_(2)^(ө)+H_(2)O+I^(ө)` (Basic)
d. `As_(2)S_(3)+HNO_(3)rarrH_(3)AsO_(4)+H_(2)SO_(4)+NO`
e. `......+HC_(2)O_(4)^(ө)rarrCO_(3)^(2-)+Cl^(ө)` (Acidic)
f. `HgS+HCl+HNO_(3)rarrH_(2)NO_(3)rarrH_(2)HgCl_(4)+NO+S+H_(2)O`
g. `Mn_(2)O_(7)rarrMnO_(2)+O_(2)`
a. `BaCrO_(4) + KI+HClrarrBaCl_(2)+I_(2)+KCl+CrCl_(3)+H_(2)O`
b. `SO_(2)+Na_(2)CrO_(4)+H_(2)SO_(4)rarrNa_(2)SO_(4)+Cr_(2)(SO_(4))_(3)+H_(2)O`
c. `C_(2)H_(5)OH+I_(2)+overset(ө)OHrarrCHI_(3)+HCO_(2)^(ө)+H_(2)O+I^(ө)` (Basic)
d. `As_(2)S_(3)+HNO_(3)rarrH_(3)AsO_(4)+H_(2)SO_(4)+NO`
e. `......+HC_(2)O_(4)^(ө)rarrCO_(3)^(2-)+Cl^(ө)` (Acidic)
f. `HgS+HCl+HNO_(3)rarrH_(2)NO_(3)rarrH_(2)HgCl_(4)+NO+S+H_(2)O`
g. `Mn_(2)O_(7)rarrMnO_(2)+O_(2)`
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
a. First write the equation in ionic from as shown below.
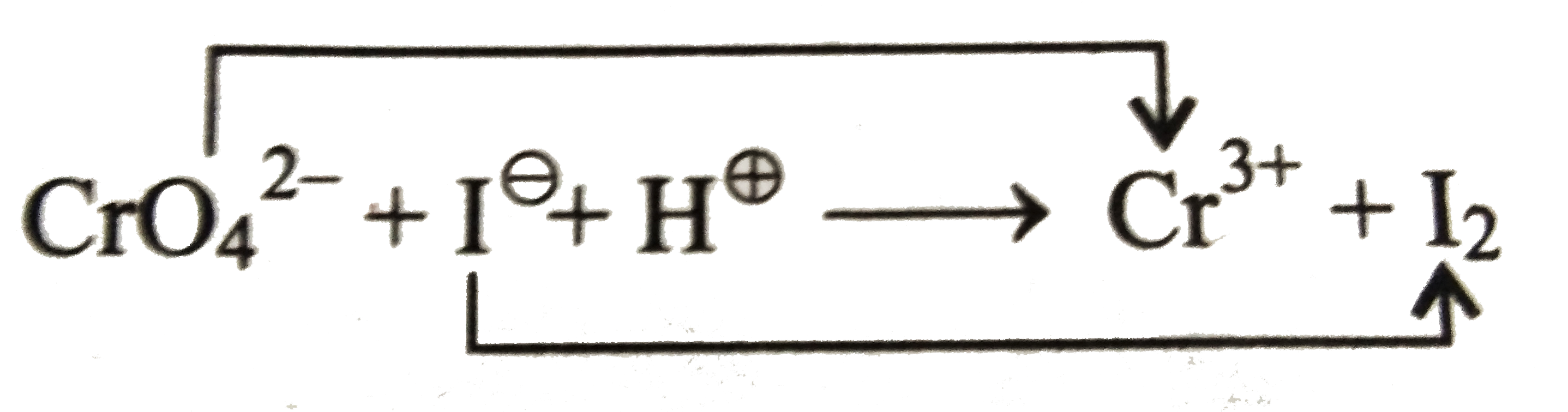
Ion electron method
i. `3e^(-)+CrO_(4)^(2-)rarrCr^(3+)`
`x-8 = -2, x=3`
ii. Balance `O` atom by adding `H_(2)O` to `RHS` and then balance `H` atom by adding `H^(o+)` ions ( acidic medium) to `LHS`.
`3e^(-)+8H^(o+)+CrO_(4)^(2-)rarrCr^(3+)+4H_(2)O`....(i)
Similarly, balance `I^(ө)` to `I_(2)`.
`2I^(ө)rarrI_(2)+2e^(-)`.....(ii)
iii. Multiply equation (i) by `2` and equation (ii) by `3`.
`cancel(6e^(-))+16H^(o+)+2CrO_(4)^(2-)rarr2Cr^(3+)+8H_(2)O`
`6I^(ө)rarr3I_(2)+cancel(6e^(-))`
`ulbar(16H^(o+)+2CrO_(4)^(2-)+6I^(ө)rarr2Cr^(3+)+8H_(2)O+3I_(2))`
Now add the other ions to both sides.
`LHS[[2Ba^(2+)],[6K^(+)],[16Cl^(ө)]]RHS[[2Ba^(2+)],[6K^(+)],[16Cl^(ө)]]`
Net equation is
`2BaCrO_(4)+6KI+16HClrarr2CrCl_(3)+3I_(2)+2BaCl_(2)+6KCl+8H_(2)O`
b. First write the equation in ionic form as shown below:
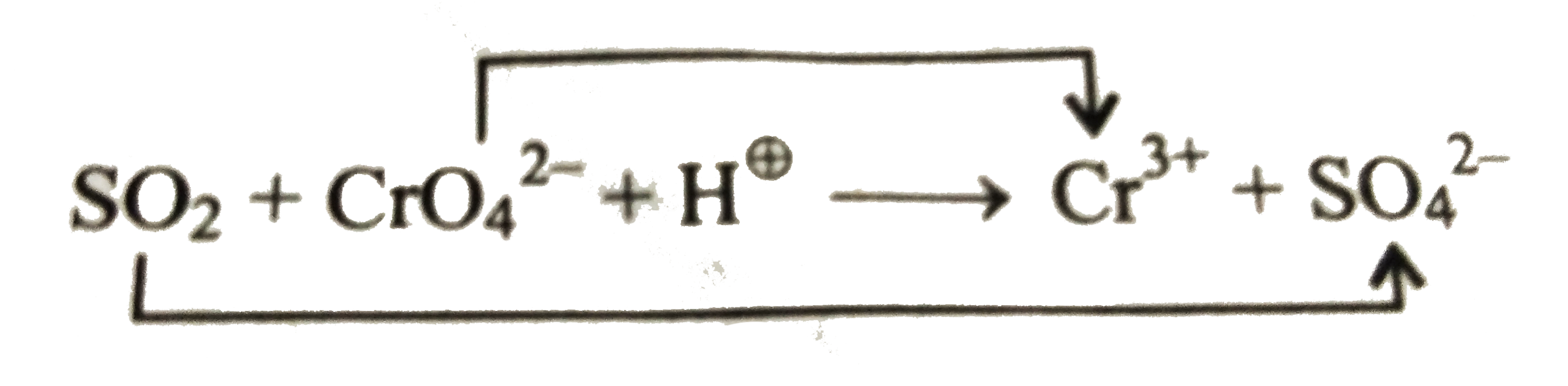
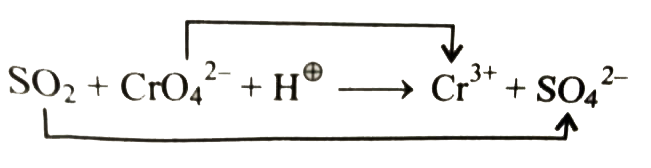
Ion electron method: (As in (a))
`16H^(o+)+6e^(-)+2CrO_(4)^(2-)rarr2Cr^(3+)+8H_(2)O`.....(i)
`SO_(2)+2H_(2)OrarrSO_(4)^(2-)+2e^(-)+4^(o+)`....(ii)
`x-4=0 x-8= -2`
`x=4 x=6`
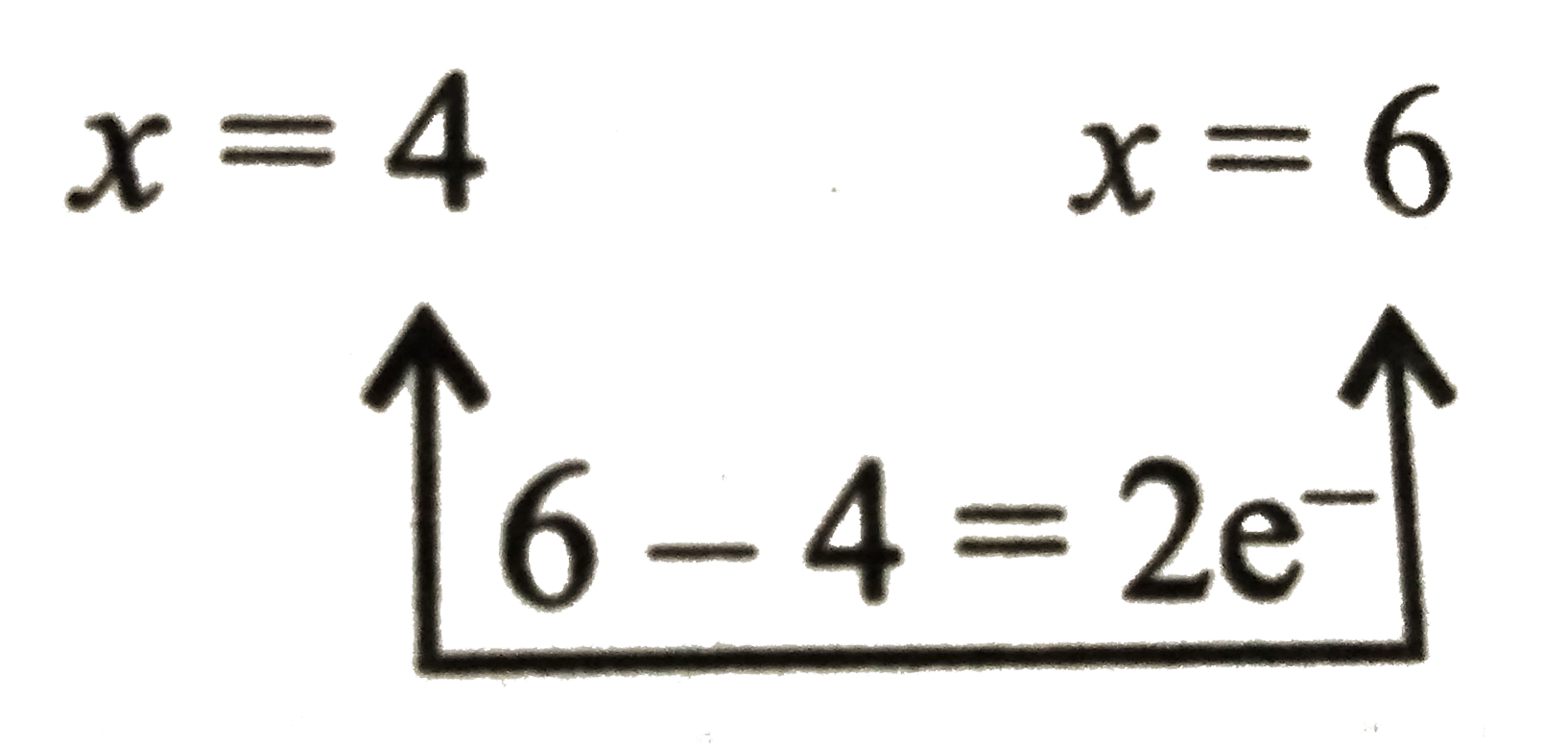
Multiply equation (ii) by `3` add eqations (i) and (ii)
`{:(16H^(o+)+cancel(6e^(-))+2Cr_(4)^(2-)rarr2Cr^(3+)+8H_(2)O),(3SO_(2)+6H_(2)Orarr3SO_(4)^(2-)+cancel(6e^(-))+12H^(o+)),(ulbar(4H^(o+)+3SO_(2)+2CrO_(4)^(2-)rarr2Cr^(3)+2SO_(4)^(2-)+2H_(2)O)):}`
It is a balanced redox equation
Now add others ions to both sides.
`LHS[[4Na^(o+)],[2SO_(4)^(2-)]],RHS[[4Na^(o+)],[2SO_(4)^(2-)]]`
Net equation is:
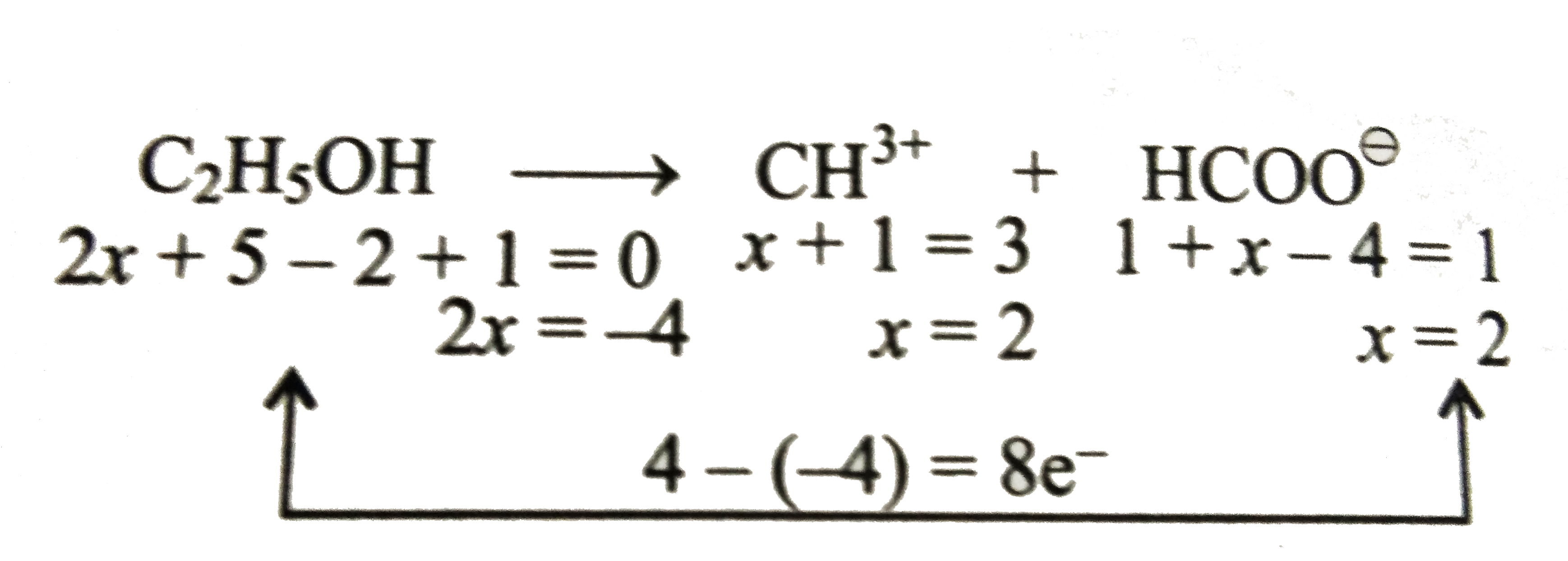
c. In this reaction, `C_(2)H_(5)OH` is changing to `CHI_(3)(i.e.,overset(+2+1)(CH)overset(-1xx3)(I_(3)))` and `HCOO^(ө)` ion.
`C_(2)H_(5)OHrarrCH^(3+)+HCOO^(ө)`
`2x+5-2+1=0 x+1=3 1+x-4=1`
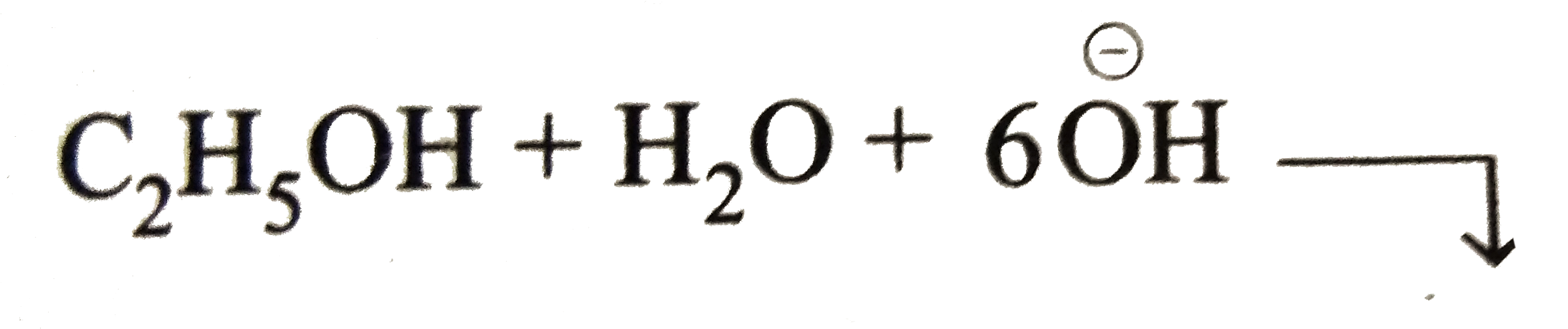
Balance `O` and `H` in basic medium.
Balancing of `O` atom by adding `H_(2)O` to `LHS C_(2)H_(5)OH+H_(2)OrarrCH^(3+)+HCOO^(ө)+8e^(-)`
Balancing of `H` atom by adding `6H_(2)O` to `RHS` and simulatneously add `6overset(ө)OH` to `LHS`
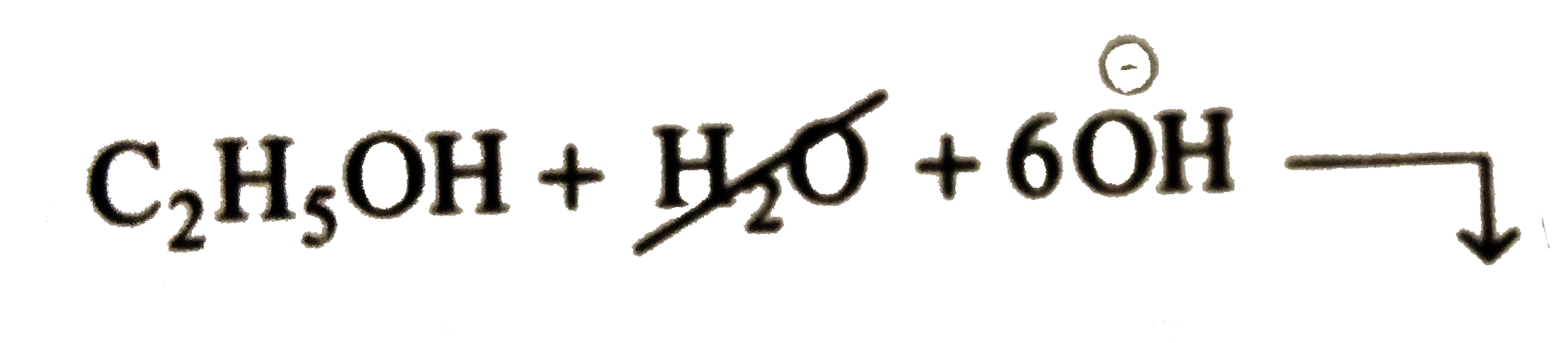
It is a balanced equation. Similarly, balance the reduction reaction.
`2e^(-)+I_(2)rarr2I^(ө)`....(ii)
Multiply equation (ii) by `4` and add equation (i) and (ii)
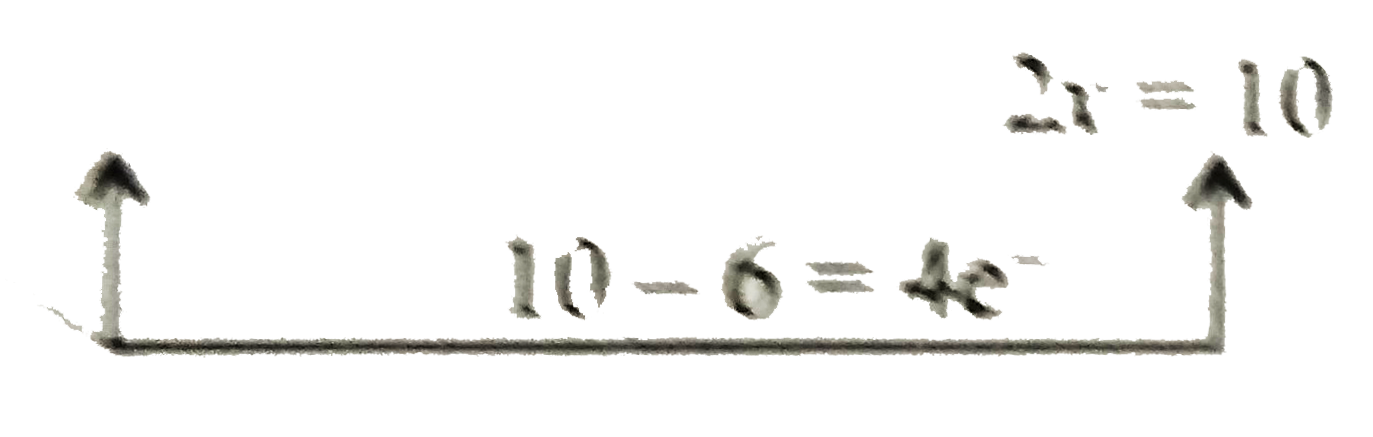
`{:(8e^(ө)+4I_(2)rarr8I^(ө))" "(ulbar(C_(2)H_(5)OH+6overset(ө)OHrarrCH^(3+)+HCOO^(ө)5H_(2)+8I^(ө))):}`
`CH^(3+)` is combined with `3I^(ө)` to form `CHI_(3)`.
So net balanced equation is:
`ulbar(C_(2)H_(5)OH+6overset(ө)OHrarrCHI_(3)+HICOO^(ө)+5I^(ө)+5H_(2)O)`
d. Here, `As_(2)S_(3)` (i.e, `overset(+3xx2`) `(As_(2))overset(-2xx3)S)` is split into two parts `As_(2)^(6+)` and `S_(3)^(6-)` in which `As_(2)^(6+)` (i.e., `H_(2)SO_(4)`)
`As_(2)^(6+)impliesH_(3)AsO_(4)`
i. Balanced As atom by multiplying `RHS` by `2` and then add proper number of electrons.

ii. Balance `O` and `H` atoms.
`8H_(2)O+As_(2)^(6+)rarr2H_(3)AsO_(4)+4e^(-)+10H^(o+)`....(i)
iii. Similarly, balance `S_(3)^(6-)` to `H_(2)SO_(4)`.

iv. Add equation (i) and (ii)
`20H_(2)O+As_(2)S_(3)rarr2H_(3)AsO_(4)+3H_(2)SO_(4)+28H^(o+)+28e^(-)`.....(iii)
v. Now balance reduction reaction of `HNO_(3)` to `NO`.

vi. Multiply equation (iii) by `3` and equation (iv) by `28` and then add both the equation.
`{:(60H_(2)O+3As_(2)S_(3)rarr 6H_(3)AsO_(4)+9H_(2)SO_(4)),(" "+cancel(84H^(o+))+cancel(84e^(-))....(v)):}`
`ulbar(cancel(84H^(o+))+cancel(84e^(-))+27HNO_(3) rarr 28NO +56H_(2)O....(vi)`
`4H_(2)O+3As_(2)S_(3)+28HNO_(3)rarr6H_(3)AsO_(4)+(H_(2)SO_(4)+9H_(2)SO_(4)+28NO`
It is a balanced redox equation.
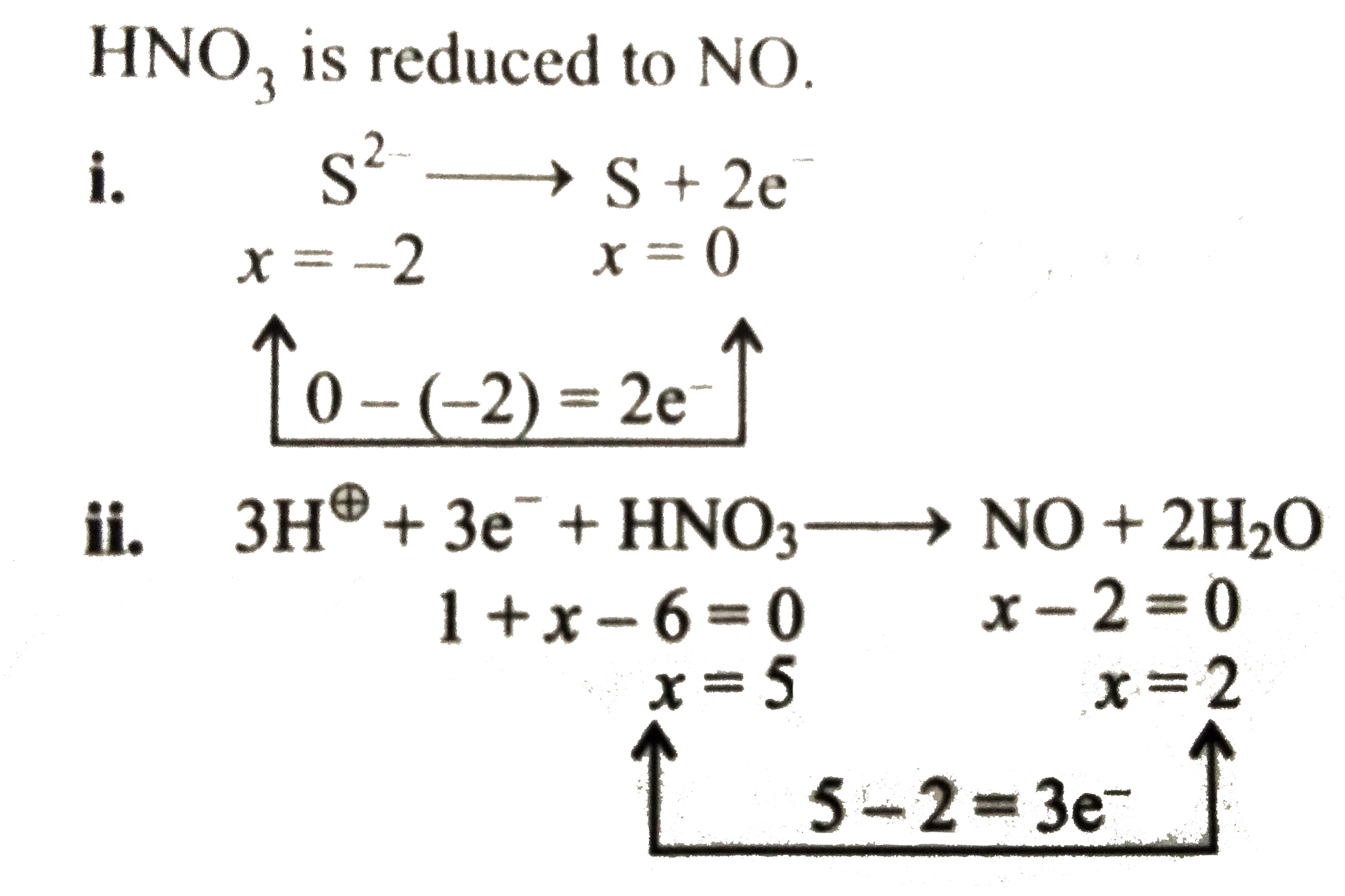
In the blank space on `LHS`, put `Cl_(2)`, since `HC_(2)O_(4)^(ө)` is oxidised, therefore `Cl_(2)` is reduced.
i. `2e^(-)+CI_(2)rarr2Cl^(ө)`.....(i)
ii.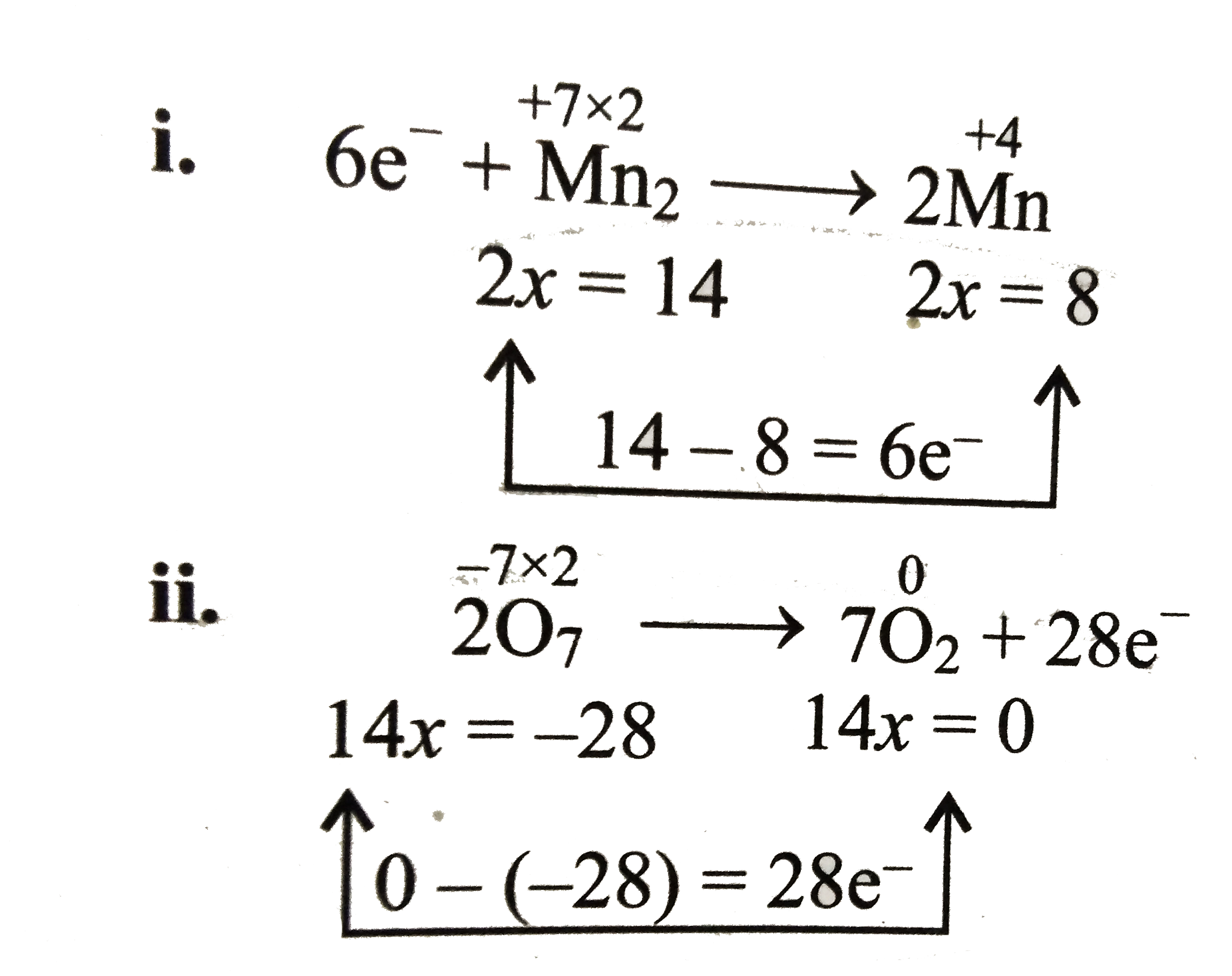
Add eqution (i) and (ii)
`{:(cancel(2e^(-))+Cl_(2)rarr2Cl^(ө)),(2H_(2)O+HC_(2)O_(4)^(ө)rarr2CO_(3)^(2-)+cancel(2e^(-))+5H^(o+)),(ulbar(Cl_(2)+HC_(2)O^(ө)+2H_(2)Orarr2H_(2)Orarr2Cl^(ө)+2CO_(3)^(2-)+5H^(o+))):}`
It is a balanced equation.
f. Here, `HgS` (i.e., `Hg^(2+)S^(2-)`) is split into two parts `Hg^(2+)` and `S^(2-)` in which only `S^(2-)` (sulphide ion) is oxidised to `S`, whereas `Hg^(2+)` is uncharged in `(overset(+1xx2)(H_(2))overset(+2)(Hg)overset(-1xx4)(Cl_(4)))`
`HNO_(3)` is reduced to `NO`.
iii. Multiply equation (i) by `3` and equation (ii) by `2` and then add both the equation.
`{:(3S^(2-)rarr3S+cancel(6e^(-))),(6H^(o+)+cancel(6e^(-))+2HNO_(3)rarr2NO+4H_(2)O),(ulbar(6H^(o+)+3S^(2-)+2HNO_(3)rarr3S+2NO+4H_(2))):}`
It is balanced equation.
iv. Now add other ions to both sides.
`LHS {:[(3Hg^(2+),,,,,),(6H^(oplus),,,,) (12Cl^(ө),,,,)]:}" " RHS{:[(3Hg^(2+),,,,,),(6H^(oplus),,,,),(12Cl^(ө),,,,)]:}`
Net equation is
`12HCl+3HgS+2HNO_(3)rarr3H_(2)HgCl_(4)+3S+2NO+4H_(2)O`
g. `overset(+7xx2)(Mn_(2))overset(-2xx7)(O_(7))rarroverset(+4)(Mn)overset(-2xx2)(O_(2))+overset(0)(O_(2))`
`Mn_(2)O_(7)` is splitted into two parts `(overset(+7xx2)(Mn_(2))` and `overset(-2xx7)(O_(7)))`
iii. Multiply equation (i) by `28` and equation (ii) by `6` and add them.
`{:(cancel(28xx6e^(-))+28Mn_(2)^(7+)rarr56Mn^(4+)),(12O_(7)^(2-)rarr42O_(2)+cancel(28xx6e^(-))),(ulbar(28Mn_(2)^(7+)+12O_(7)^(2-)rarr56Mn^(4+)+42O_(2))):}`
or `28Mn_(2)O_(7)+12Mn_(2)O_(7)rarr56MnO_(2)+42O_(2)`
iv. Balance `Mn` atom except `H` and `O`.
`40Mn_(2)O_(7)rarr56MnO_(2)+24MnO_(2)+42O_(2)`
v. Balance `O` atom
`40Mn_(2)O_(7)rarr 80MnO_(2)+42O_(2)+18O_(2)`
or
`2Mn_(2)O_(7)rarr4MnO_(2)+3O_(2)`.
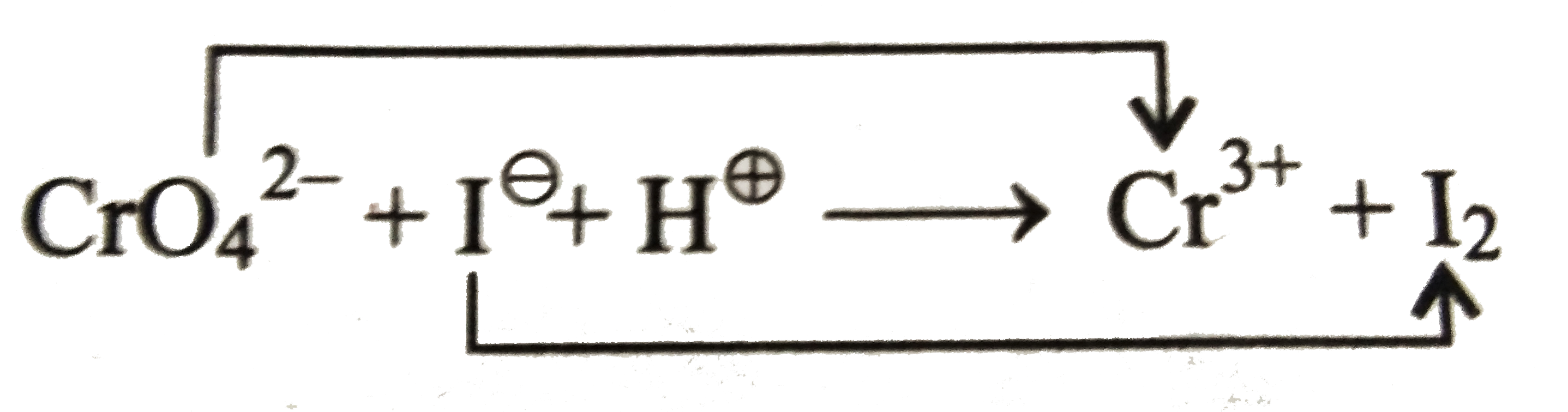
Ion electron method
i. `3e^(-)+CrO_(4)^(2-)rarrCr^(3+)`
`x-8 = -2, x=3`

ii. Balance `O` atom by adding `H_(2)O` to `RHS` and then balance `H` atom by adding `H^(o+)` ions ( acidic medium) to `LHS`.
`3e^(-)+8H^(o+)+CrO_(4)^(2-)rarrCr^(3+)+4H_(2)O`....(i)
Similarly, balance `I^(ө)` to `I_(2)`.
`2I^(ө)rarrI_(2)+2e^(-)`.....(ii)
iii. Multiply equation (i) by `2` and equation (ii) by `3`.
`cancel(6e^(-))+16H^(o+)+2CrO_(4)^(2-)rarr2Cr^(3+)+8H_(2)O`
`6I^(ө)rarr3I_(2)+cancel(6e^(-))`
`ulbar(16H^(o+)+2CrO_(4)^(2-)+6I^(ө)rarr2Cr^(3+)+8H_(2)O+3I_(2))`
Now add the other ions to both sides.
`LHS[[2Ba^(2+)],[6K^(+)],[16Cl^(ө)]]RHS[[2Ba^(2+)],[6K^(+)],[16Cl^(ө)]]`
Net equation is
`2BaCrO_(4)+6KI+16HClrarr2CrCl_(3)+3I_(2)+2BaCl_(2)+6KCl+8H_(2)O`
b. First write the equation in ionic form as shown below:

Ion electron method: (As in (a))
`16H^(o+)+6e^(-)+2CrO_(4)^(2-)rarr2Cr^(3+)+8H_(2)O`.....(i)
`SO_(2)+2H_(2)OrarrSO_(4)^(2-)+2e^(-)+4^(o+)`....(ii)
`x-4=0 x-8= -2`
`x=4 x=6`
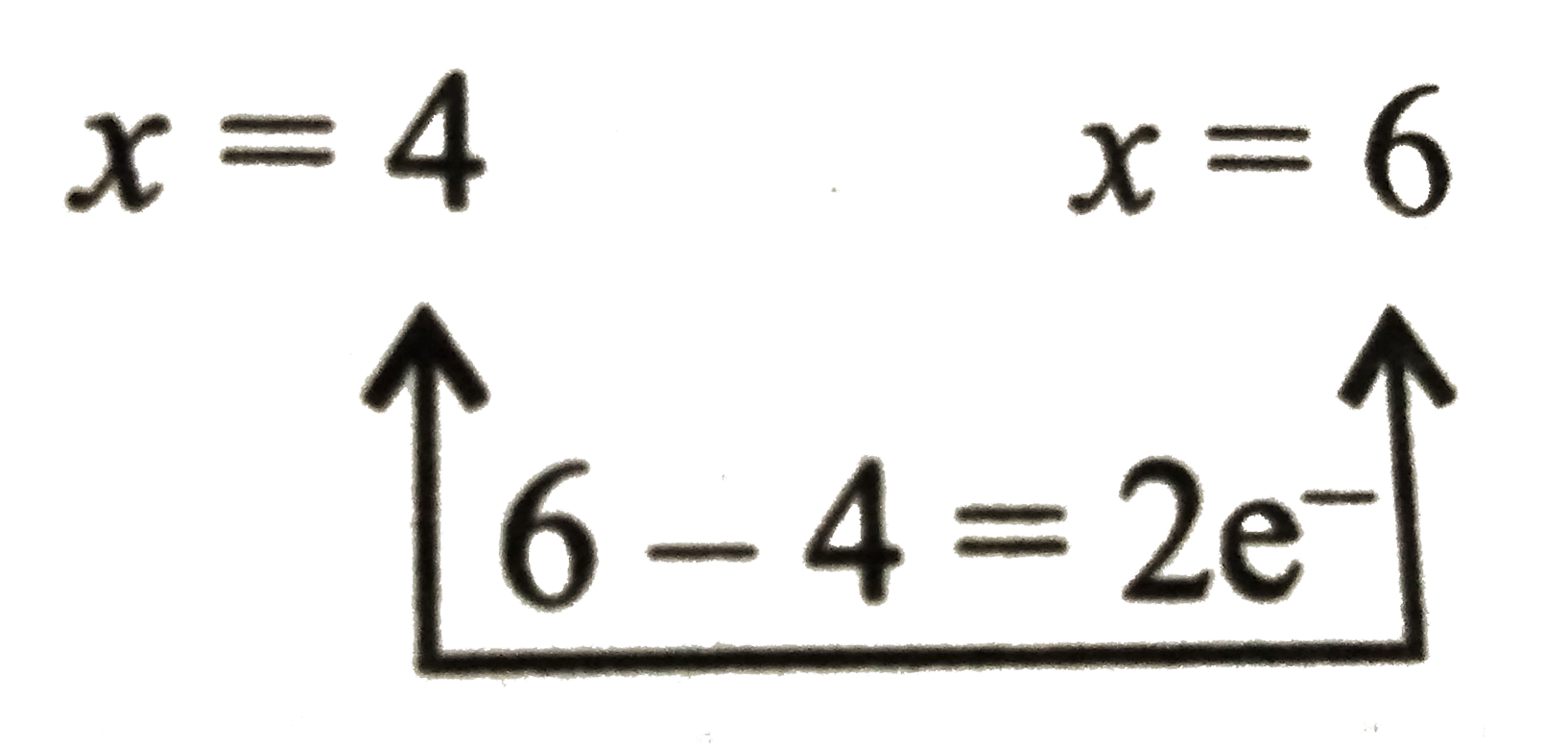
Multiply equation (ii) by `3` add eqations (i) and (ii)
`{:(16H^(o+)+cancel(6e^(-))+2Cr_(4)^(2-)rarr2Cr^(3+)+8H_(2)O),(3SO_(2)+6H_(2)Orarr3SO_(4)^(2-)+cancel(6e^(-))+12H^(o+)),(ulbar(4H^(o+)+3SO_(2)+2CrO_(4)^(2-)rarr2Cr^(3)+2SO_(4)^(2-)+2H_(2)O)):}`
It is a balanced redox equation
Now add others ions to both sides.
`LHS[[4Na^(o+)],[2SO_(4)^(2-)]],RHS[[4Na^(o+)],[2SO_(4)^(2-)]]`
Net equation is:
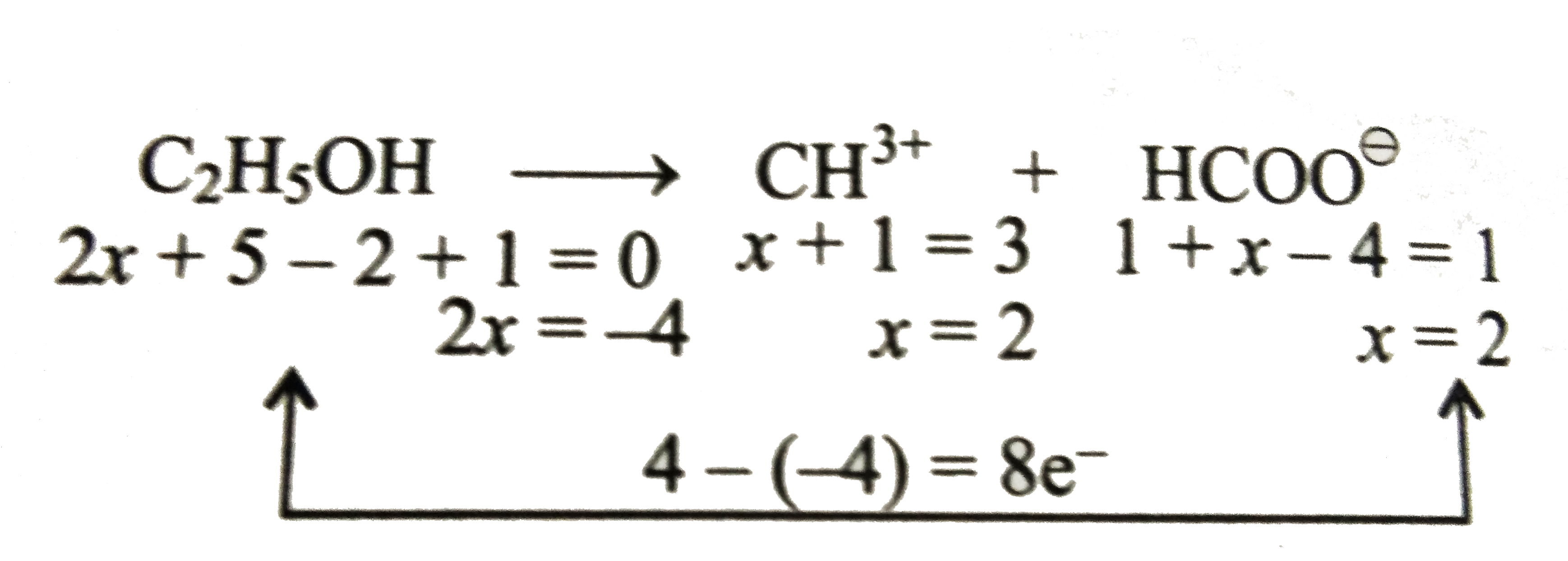
c. In this reaction, `C_(2)H_(5)OH` is changing to `CHI_(3)(i.e.,overset(+2+1)(CH)overset(-1xx3)(I_(3)))` and `HCOO^(ө)` ion.
`C_(2)H_(5)OHrarrCH^(3+)+HCOO^(ө)`
`2x+5-2+1=0 x+1=3 1+x-4=1`
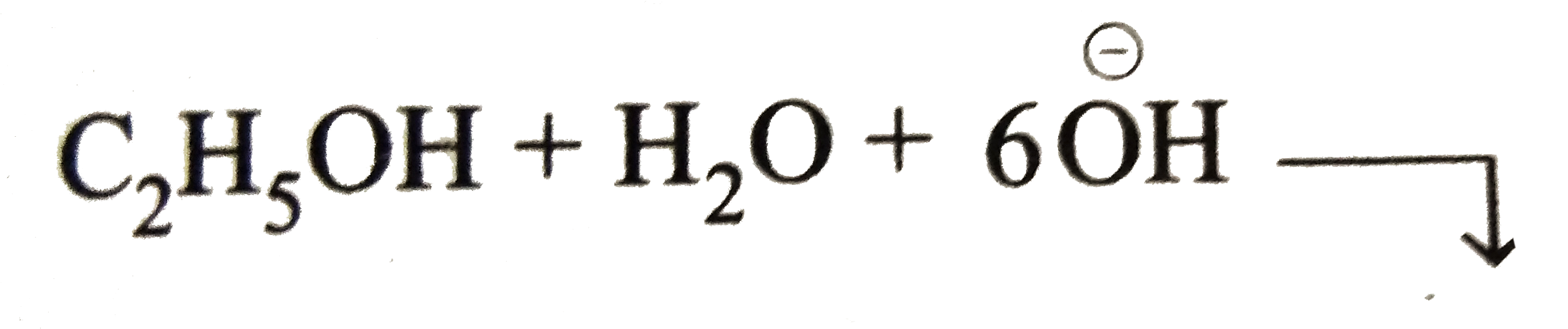
Balance `O` and `H` in basic medium.
Balancing of `O` atom by adding `H_(2)O` to `LHS C_(2)H_(5)OH+H_(2)OrarrCH^(3+)+HCOO^(ө)+8e^(-)`
Balancing of `H` atom by adding `6H_(2)O` to `RHS` and simulatneously add `6overset(ө)OH` to `LHS`
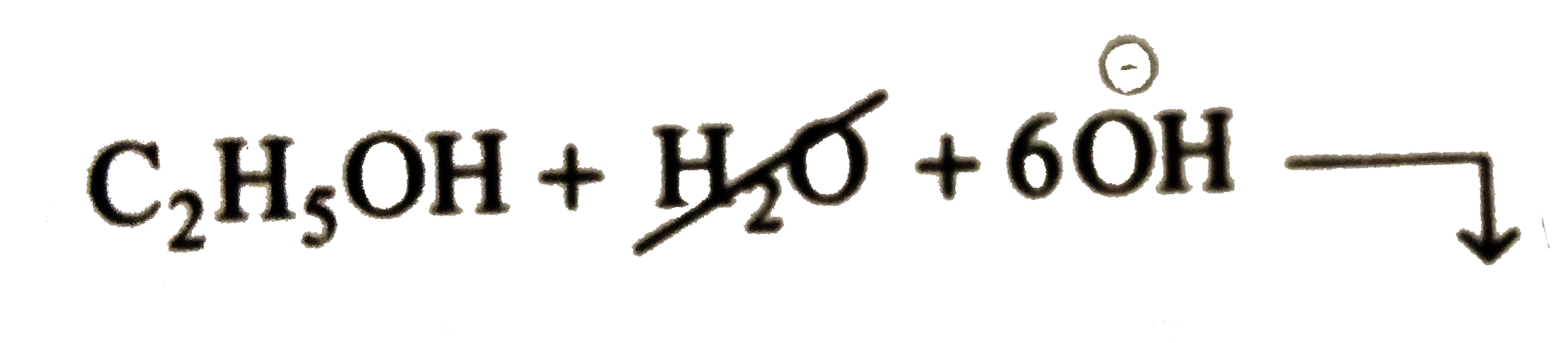
It is a balanced equation. Similarly, balance the reduction reaction.
`2e^(-)+I_(2)rarr2I^(ө)`....(ii)
Multiply equation (ii) by `4` and add equation (i) and (ii)
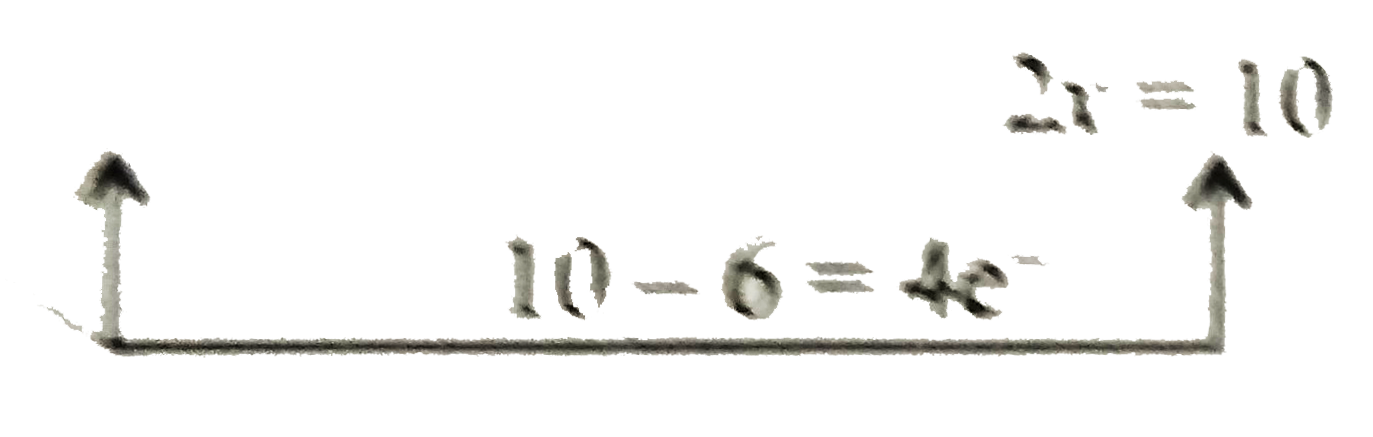
`{:(8e^(ө)+4I_(2)rarr8I^(ө))" "(ulbar(C_(2)H_(5)OH+6overset(ө)OHrarrCH^(3+)+HCOO^(ө)5H_(2)+8I^(ө))):}`
`CH^(3+)` is combined with `3I^(ө)` to form `CHI_(3)`.
So net balanced equation is:
`ulbar(C_(2)H_(5)OH+6overset(ө)OHrarrCHI_(3)+HICOO^(ө)+5I^(ө)+5H_(2)O)`
d. Here, `As_(2)S_(3)` (i.e, `overset(+3xx2`) `(As_(2))overset(-2xx3)S)` is split into two parts `As_(2)^(6+)` and `S_(3)^(6-)` in which `As_(2)^(6+)` (i.e., `H_(2)SO_(4)`)
`As_(2)^(6+)impliesH_(3)AsO_(4)`
i. Balanced As atom by multiplying `RHS` by `2` and then add proper number of electrons.

ii. Balance `O` and `H` atoms.
`8H_(2)O+As_(2)^(6+)rarr2H_(3)AsO_(4)+4e^(-)+10H^(o+)`....(i)
iii. Similarly, balance `S_(3)^(6-)` to `H_(2)SO_(4)`.

iv. Add equation (i) and (ii)
`20H_(2)O+As_(2)S_(3)rarr2H_(3)AsO_(4)+3H_(2)SO_(4)+28H^(o+)+28e^(-)`.....(iii)
v. Now balance reduction reaction of `HNO_(3)` to `NO`.

vi. Multiply equation (iii) by `3` and equation (iv) by `28` and then add both the equation.
`{:(60H_(2)O+3As_(2)S_(3)rarr 6H_(3)AsO_(4)+9H_(2)SO_(4)),(" "+cancel(84H^(o+))+cancel(84e^(-))....(v)):}`
`ulbar(cancel(84H^(o+))+cancel(84e^(-))+27HNO_(3) rarr 28NO +56H_(2)O....(vi)`
`4H_(2)O+3As_(2)S_(3)+28HNO_(3)rarr6H_(3)AsO_(4)+(H_(2)SO_(4)+9H_(2)SO_(4)+28NO`
It is a balanced redox equation.
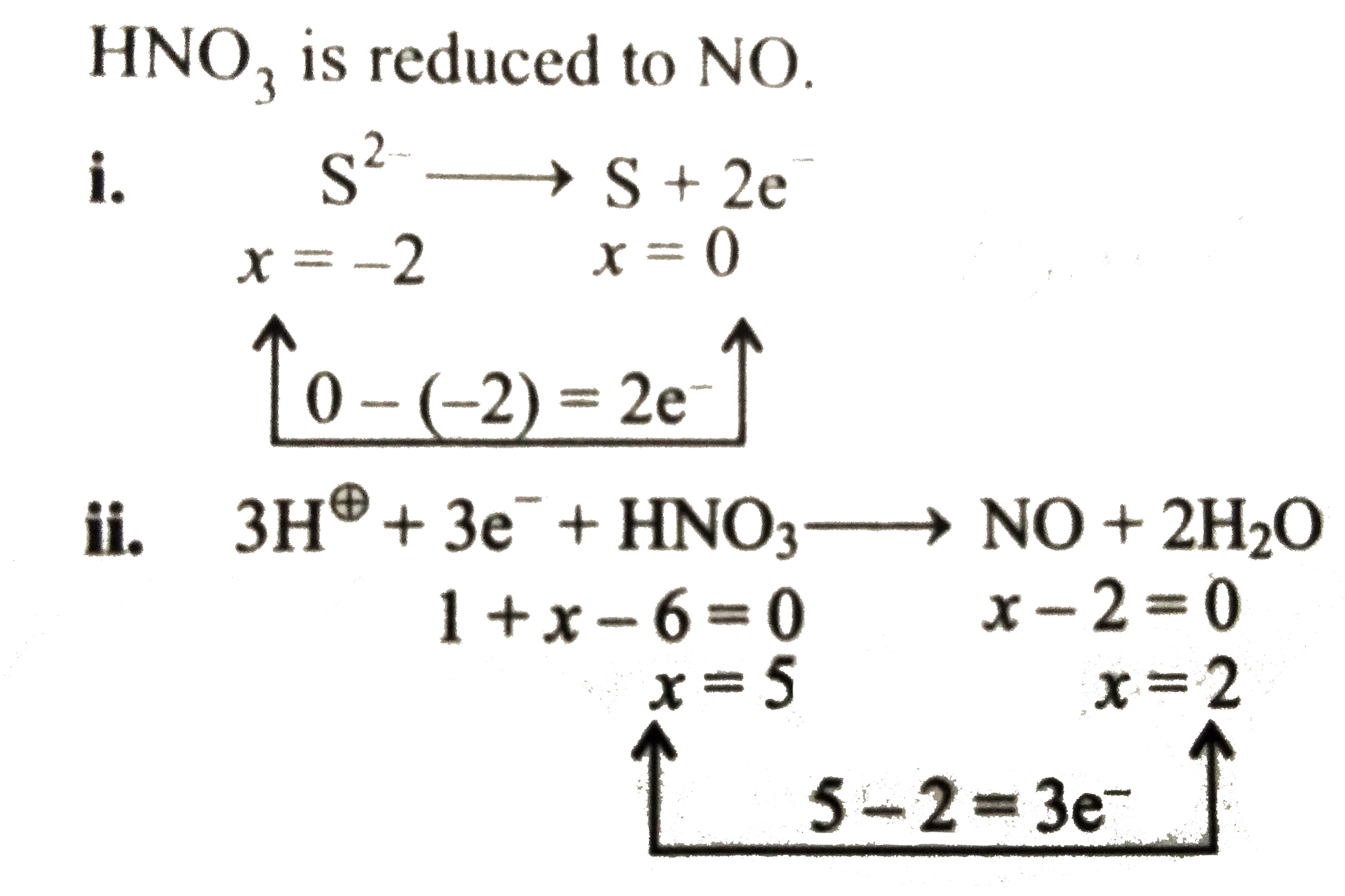
In the blank space on `LHS`, put `Cl_(2)`, since `HC_(2)O_(4)^(ө)` is oxidised, therefore `Cl_(2)` is reduced.
i. `2e^(-)+CI_(2)rarr2Cl^(ө)`.....(i)
ii.
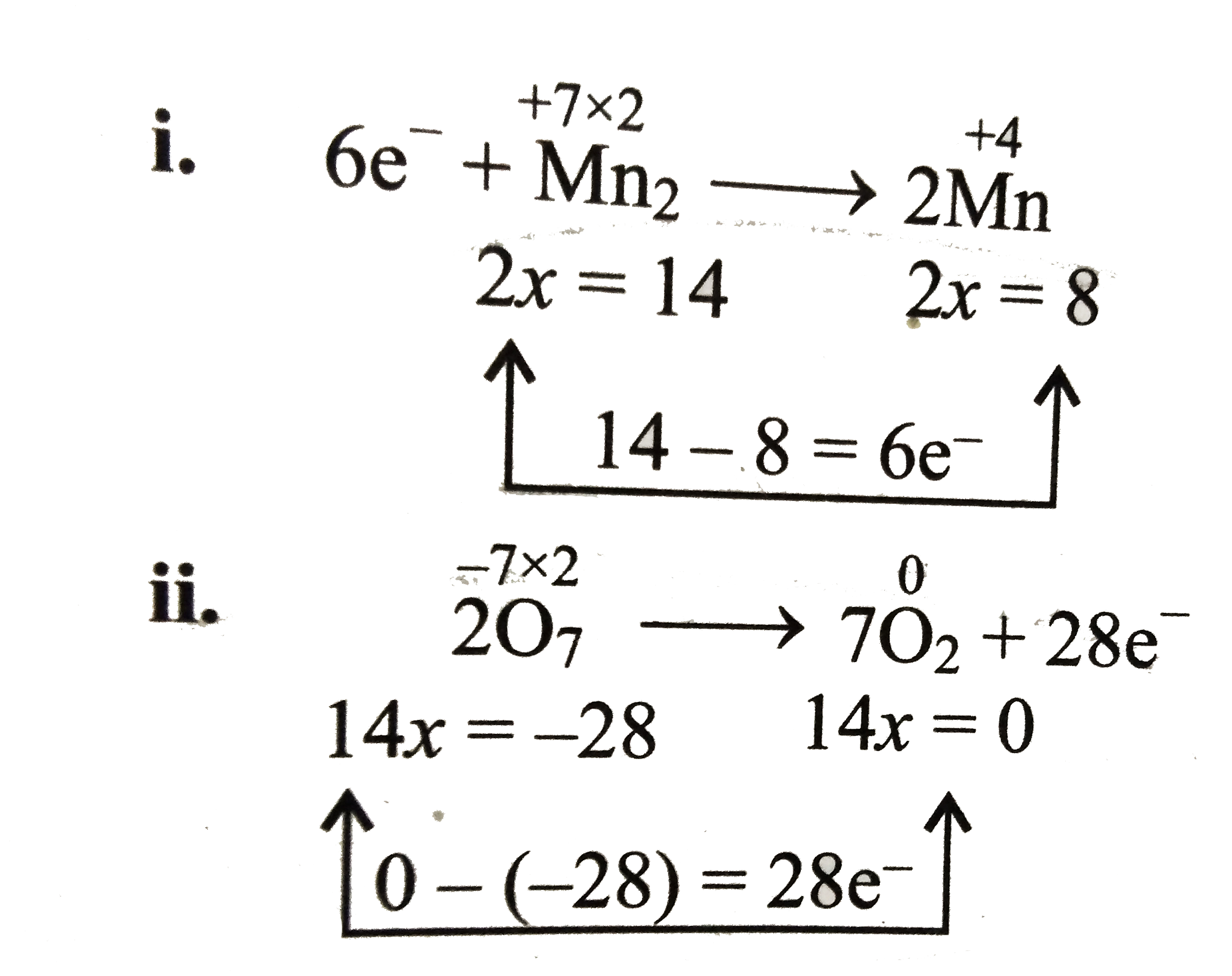
Add eqution (i) and (ii)
`{:(cancel(2e^(-))+Cl_(2)rarr2Cl^(ө)),(2H_(2)O+HC_(2)O_(4)^(ө)rarr2CO_(3)^(2-)+cancel(2e^(-))+5H^(o+)),(ulbar(Cl_(2)+HC_(2)O^(ө)+2H_(2)Orarr2H_(2)Orarr2Cl^(ө)+2CO_(3)^(2-)+5H^(o+))):}`
It is a balanced equation.
f. Here, `HgS` (i.e., `Hg^(2+)S^(2-)`) is split into two parts `Hg^(2+)` and `S^(2-)` in which only `S^(2-)` (sulphide ion) is oxidised to `S`, whereas `Hg^(2+)` is uncharged in `(overset(+1xx2)(H_(2))overset(+2)(Hg)overset(-1xx4)(Cl_(4)))`
`HNO_(3)` is reduced to `NO`.
iii. Multiply equation (i) by `3` and equation (ii) by `2` and then add both the equation.
`{:(3S^(2-)rarr3S+cancel(6e^(-))),(6H^(o+)+cancel(6e^(-))+2HNO_(3)rarr2NO+4H_(2)O),(ulbar(6H^(o+)+3S^(2-)+2HNO_(3)rarr3S+2NO+4H_(2))):}`
It is balanced equation.
iv. Now add other ions to both sides.
`LHS {:[(3Hg^(2+),,,,,),(6H^(oplus),,,,) (12Cl^(ө),,,,)]:}" " RHS{:[(3Hg^(2+),,,,,),(6H^(oplus),,,,),(12Cl^(ө),,,,)]:}`
Net equation is
`12HCl+3HgS+2HNO_(3)rarr3H_(2)HgCl_(4)+3S+2NO+4H_(2)O`
g. `overset(+7xx2)(Mn_(2))overset(-2xx7)(O_(7))rarroverset(+4)(Mn)overset(-2xx2)(O_(2))+overset(0)(O_(2))`
`Mn_(2)O_(7)` is splitted into two parts `(overset(+7xx2)(Mn_(2))` and `overset(-2xx7)(O_(7)))`
iii. Multiply equation (i) by `28` and equation (ii) by `6` and add them.
`{:(cancel(28xx6e^(-))+28Mn_(2)^(7+)rarr56Mn^(4+)),(12O_(7)^(2-)rarr42O_(2)+cancel(28xx6e^(-))),(ulbar(28Mn_(2)^(7+)+12O_(7)^(2-)rarr56Mn^(4+)+42O_(2))):}`
or `28Mn_(2)O_(7)+12Mn_(2)O_(7)rarr56MnO_(2)+42O_(2)`
iv. Balance `Mn` atom except `H` and `O`.
`40Mn_(2)O_(7)rarr56MnO_(2)+24MnO_(2)+42O_(2)`
v. Balance `O` atom
`40Mn_(2)O_(7)rarr 80MnO_(2)+42O_(2)+18O_(2)`
or
`2Mn_(2)O_(7)rarr4MnO_(2)+3O_(2)`.
Topper's Solved these Questions
REDOX REACTIONS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Ex 2.1|10 VideosREDOX REACTIONS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Ex 2.2|18 VideosPURIFICATION OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS AND QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Assertion Reasoning Type|5 VideosS-BLOCK GROUP 1 - ALKALI METALS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Archives Subjective|8 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Na_(2)CrO_(4)+HCl to H_(2)Cr_(2)O_(7)+Na_(2)SO_(4)
Na_(2)SO_(3)+H_(2)O_(2) rarr Na_(2)SO_(4) +H_(2)O , in reaction
{:(2NaOH+H_(2)SO_(4)rarrNa_(2)SO_(4)+2H_(2)O),("Base Acid"):}