A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
THERMODYNAMICS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises (Assertion-Reasoning)|23 VideosTHERMODYNAMICS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises (Interger)|10 VideosTHERMODYNAMICS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises (Multiple Correct)|50 VideosSTOICHIOMETRY
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Archives Subjective|33 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY-THERMODYNAMICS-Exercises (Single Correct)
- For an ideal gas Joule-Thomon coefficient is:
Text Solution
|
- Delta(f)H(H(2)O) =- 68 kcal mol^(-1) and DeltaH of neutralisation is -...
Text Solution
|
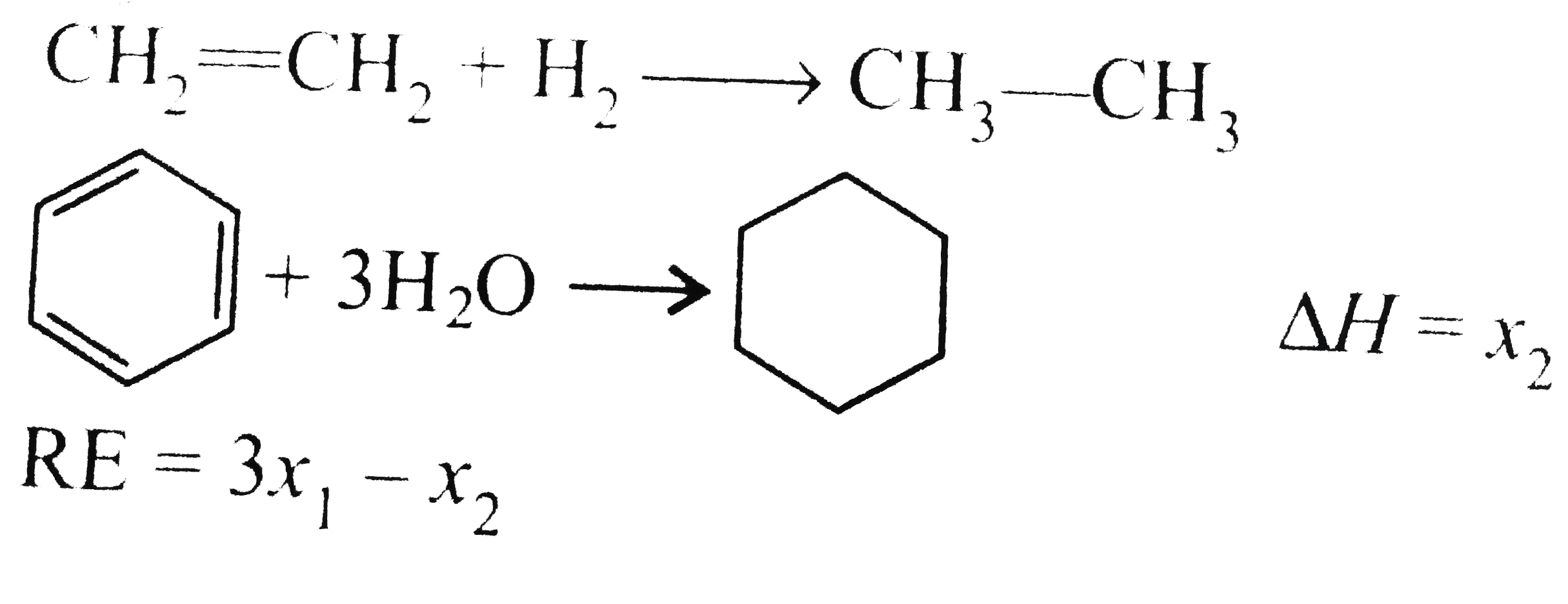
- Heat of hydrogenation of ethene is x(1) and that of benzene is x(2) . ...
Text Solution
|
- A (l) overset(1atn)hArr A(g), Delta(vap)H = 460.6 cal mol^(-1), boilin...
Text Solution
|
- H(2)(g) +(1)/(2)O(2)(g) rarr H(2)O(l) BE (H-H) = x(1), BE (O=O)=x(2)...
Text Solution
|
- If a certain mass of gas is made to undergo separately adiabatic and i...
Text Solution
|
- The dissolution of NH(4)CI in water is endothermic even though NH(4)CI...
Text Solution
|
- The enthalpy of formation of hypothetical MgCI is -125kJ mol^(-1) and ...
Text Solution
|
- The product of combustion of an aliphatic thiol (RSH) at 298K are :
Text Solution
|
- The enthalpy change for chemical reaction is denoted aas DeltaH^(Theta...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following equations corresponds to the enthalpy of combus...
Text Solution
|
- For the combustion reaction at 298K 2Ag(s)+1//2O(2)(g) rarr 2Ag(2)O(...
Text Solution
|
- For the equations C("diamond") +2H(2)(g) rarr CH(4)(g) DeltaH(1) C...
Text Solution
|
- The expression Delta("sub"1)H^(Theta) =Delta(fus)H^(Theta) +Delta(vap)...
Text Solution
|
- The word 'standard' in standard molar enthalpy change implies
Text Solution
|
- For which of the following equations, will DeltaH be equal to DeltaU?
Text Solution
|
- The enthalpy change for chemical reaction is denoted aas DeltaH^(Theta...
Text Solution
|
- Enthalpy chane of a reaction with be equal to
Text Solution
|
- The molar enthalpies of combustion of C(2)H(2)(g), C("graphite") and H...
Text Solution
|
- The relationship between enthalpy and internal energy change is
Text Solution
|