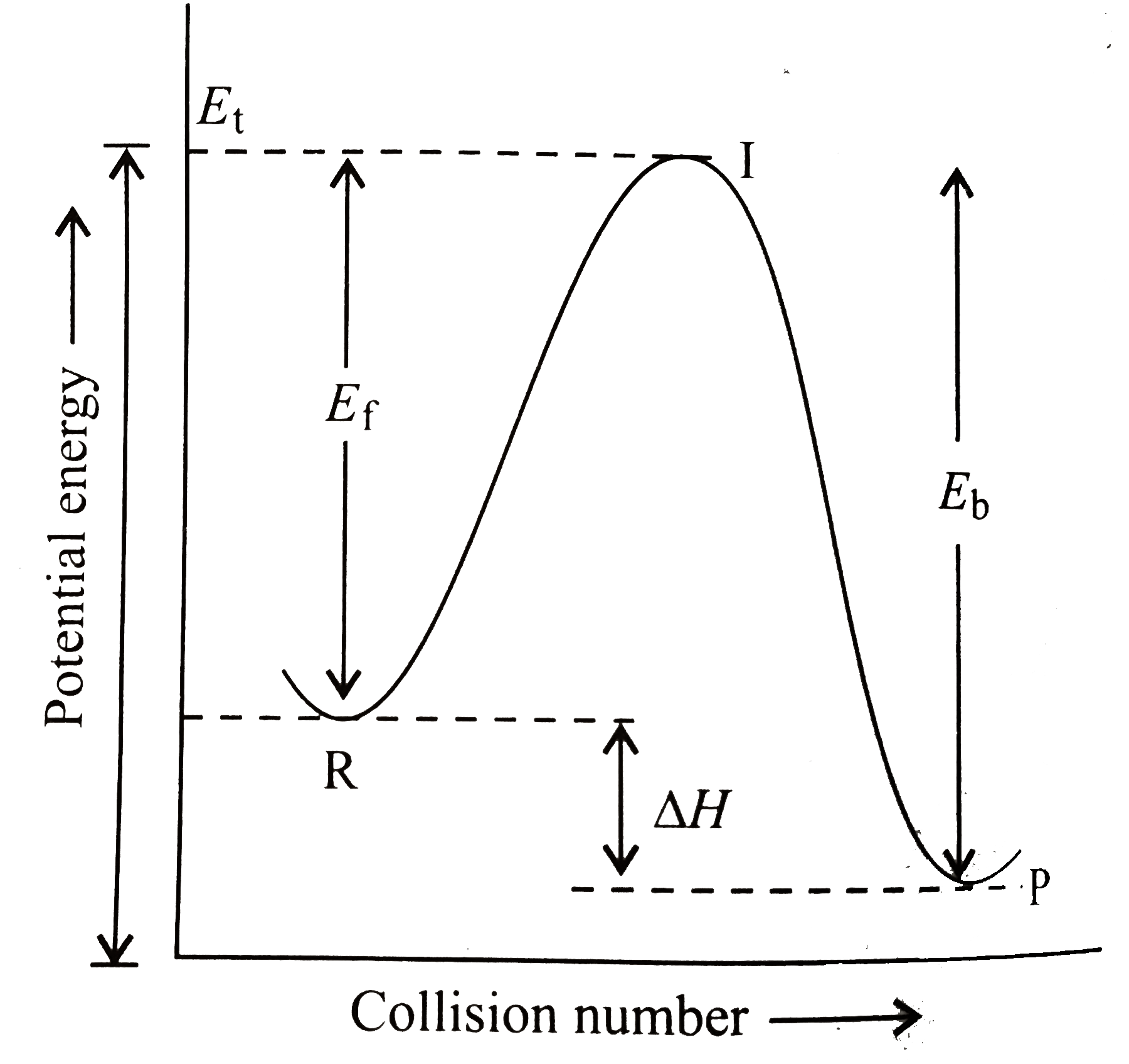
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CHEMICAL KINETICS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises Multiple Correct|34 VideosCHEMICAL KINETICS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises Single Correct|177 VideosCHEMICAL KINETICS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Ex4.4 Objective|10 VideosCARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVES
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Exercises Archives (Analytical And Descriptive)|34 VideosCOORDINATION COMPOUNDS
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY|Exercise Archives Subjective|18 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE CHEMISTRY-CHEMICAL KINETICS-Exercises Linked Comprehension
- A colliison between reactant molecules must occur with a certain minim...
Text Solution
|
- A colliison between reactant molecules must occur with a certain minim...
Text Solution
|
- A colliison between reactant molecules must occur with a certain minim...
Text Solution
|
- The order of reaction is an experimentally determined quanity. It may ...
Text Solution
|
- The order of reaction is an experimentally determined quanity. It may ...
Text Solution
|
- The order of reaction is an experimentally determined quanity. It may ...
Text Solution
|
- The order of reaction is an experimentally determined quanity. It may ...
Text Solution
|
- The order of reaction is an experimentally determined quanity. It may ...
Text Solution
|
- Conisder the following elementary reaction, 2A + B + C rarr Products...
Text Solution
|
- Conisder the following elementary reaction, 2A + B + C rarr Products...
Text Solution
|
- Conisder the following elementary reaction, 2A + B + C rarr Products...
Text Solution
|
- For the reaction: X(g) rarr Y(g)+Z(g), the following data were obtaine...
Text Solution
|
- For the reaction: X(g) rarr Y(g)+Z(g), the following data were obtaine...
Text Solution
|
- For the reaction: X(g) rarr Y(g)+Z(g), the following data were obtaine...
Text Solution
|
- The reaction 2AX(g)+2B(2)(g)rarr A(2)(g)+2B(2)X(g) has been studied ki...
Text Solution
|
- The reaction 2AX(g)+2B(2)(g)rarr A(2)(g)+2B(2)X(g) has been studied ki...
Text Solution
|
- The reaction 2AX(g)+2B(2)(g)rarr A(2)(g)+2B(2)X(g) has been studied ki...
Text Solution
|
- The rate law expresison is given for a typical reaction, n(1)A + n(2) ...
Text Solution
|
- The rate law expresison is given for a typical reaction, n(1)A + n(2) ...
Text Solution
|
- A secondary alkyl halide (A) hydrolyzes with alkali (B) in aqueous med...
Text Solution
|