Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-KINEMATICS-2-Exercise Integer
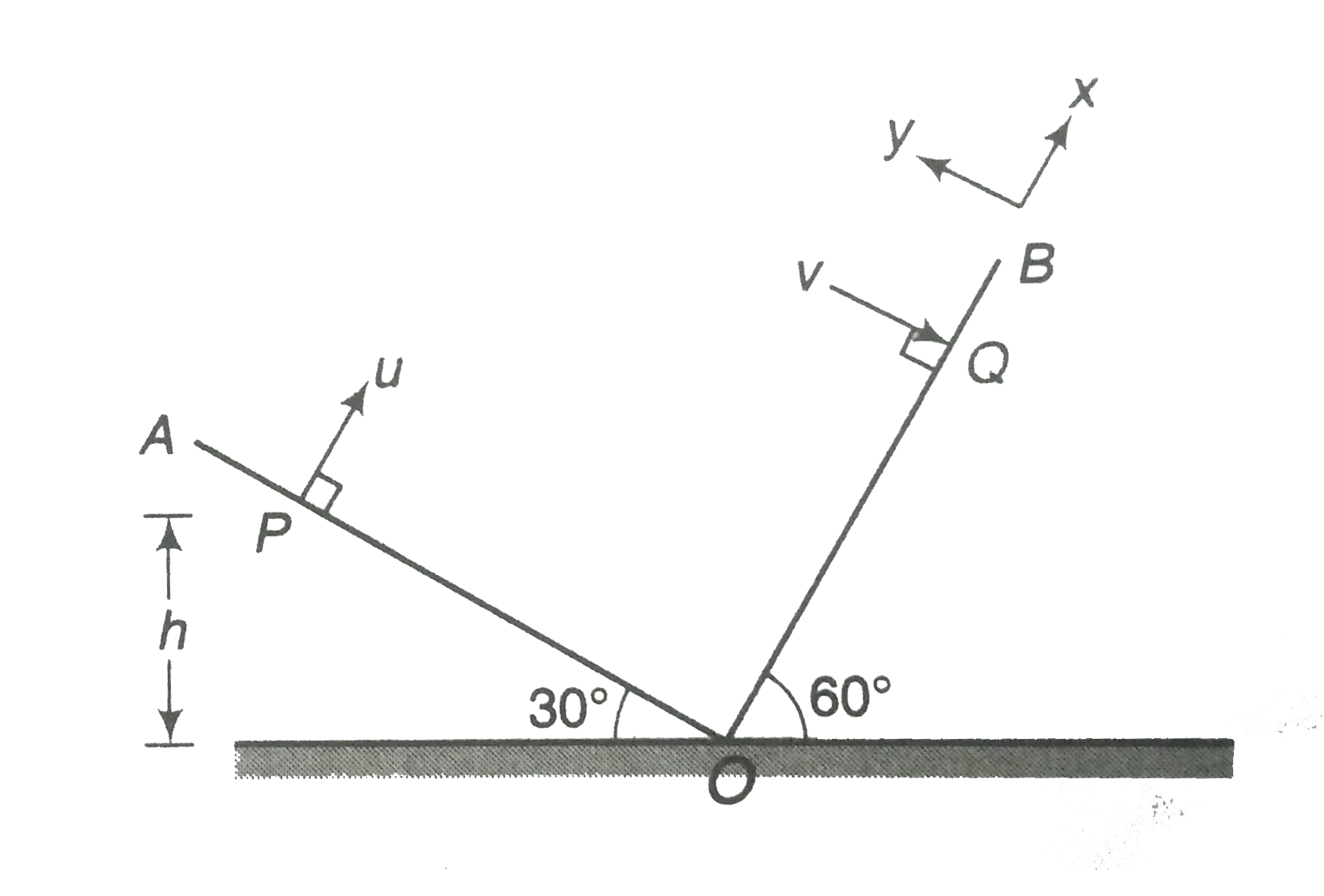
- Two inclined planes OA and OB having inclinations 30^@ and 60^@ with t...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is projected with velocity u at angle theta with horizontal...
Text Solution
|
- From the top of tower of height 80 m, two stones are projected horizon...
Text Solution
|
- A bead is free to slide down on a smooth wire rightly stretched betwee...
Text Solution
|
- A golfer standing on the ground hits a ball with a velocity of 52 m//s...
Text Solution
|
- A body is thrown with the velocity v0 at an angle of theta to the hori...
Text Solution
|
- A boy standing on a long railroad car throws a ball straight upwards. ...
Text Solution
|
- A staircase contains three steps each 10 cm high and 20 cm wide figure...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is projected up an inclined plane of inclination beta at an...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is moving in a circle of radius R with constant speed. The ...
Text Solution
|