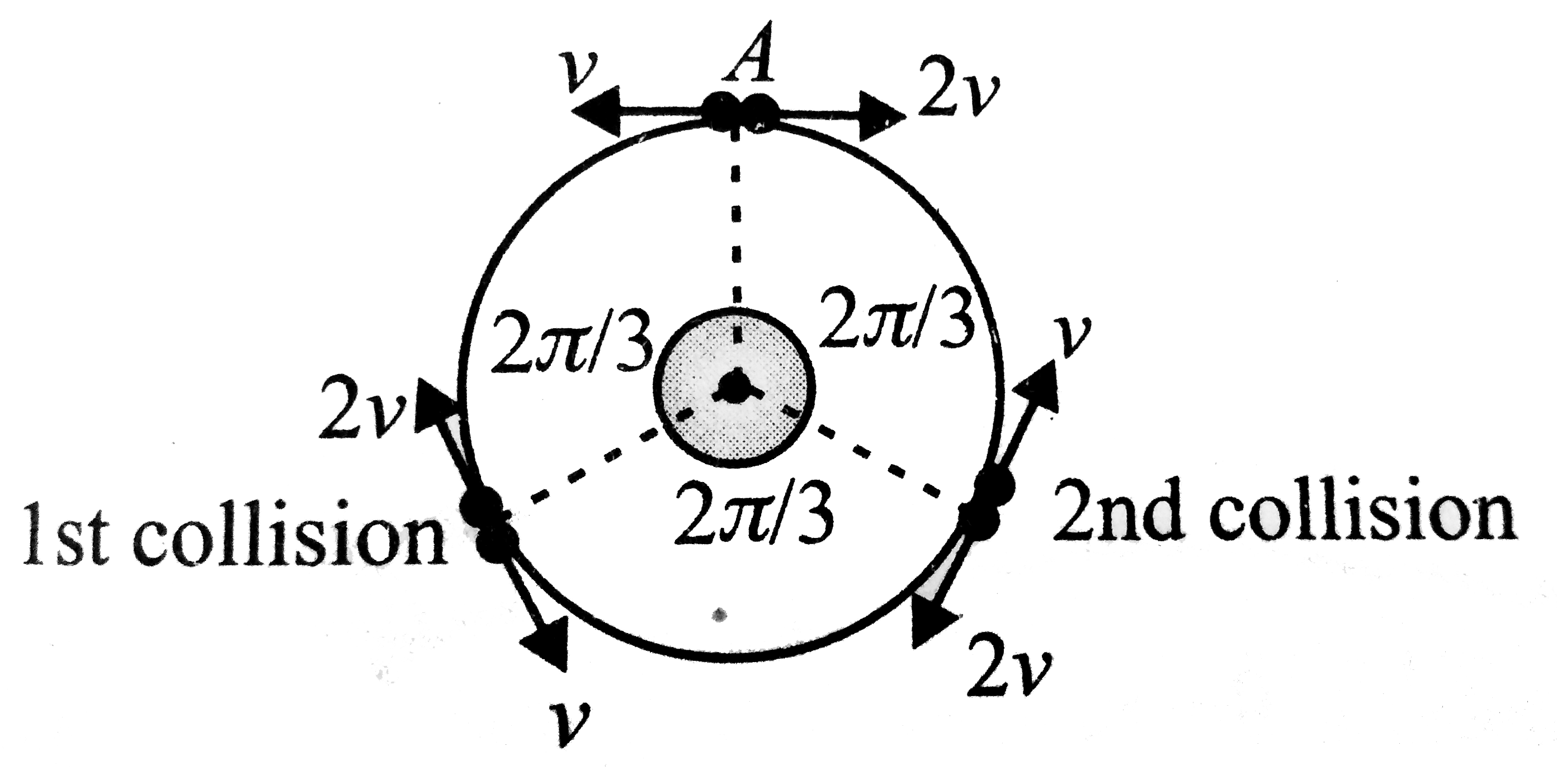
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CENTRE OF MASS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise MCQ_TYPE|4 VideosCENTRE OF MASS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise AR_TYPE|1 VideosCENTRE OF MASS
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Fill In The Blanks|2 VideosCALORIMETRY
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Solved Example|13 VideosDIMENSIONS & MEASUREMENT
CENGAGE PHYSICS|Exercise Integer|2 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-CENTRE OF MASS-SCQ_TYPE
- Two paricle A and B initially at rest, move towards each other under m...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform chain of length L and mass M is lying on a smooth table and ...
Text Solution
|
- A ball hits the floor and rebounds after an inelastic collision. In th...
Text Solution
|
- A shell is fired from a cannon with a velocity v (m//s) at an angle th...
Text Solution
|
- An isolated particle of mass m is moving in horizontal plane xy along ...
Text Solution
|
- Two particles of masses m(1) and m(2) in projectile motion have veloci...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of masses 10 kg and 4 kg are connected by a spring of negli...
Text Solution
|
- A particle moves in the xy plane under the influence of a force such t...
Text Solution
|
- Look at the drawing given in the figure which has been drawn with ink ...
Text Solution
|
- Two small particles of equal masses stant moving in opposite directio...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 2 kg is free to move along the x-axis. It at rest and ...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass 0.2 kg rests on a vertical post of height 5 m. A bullet...
Text Solution
|