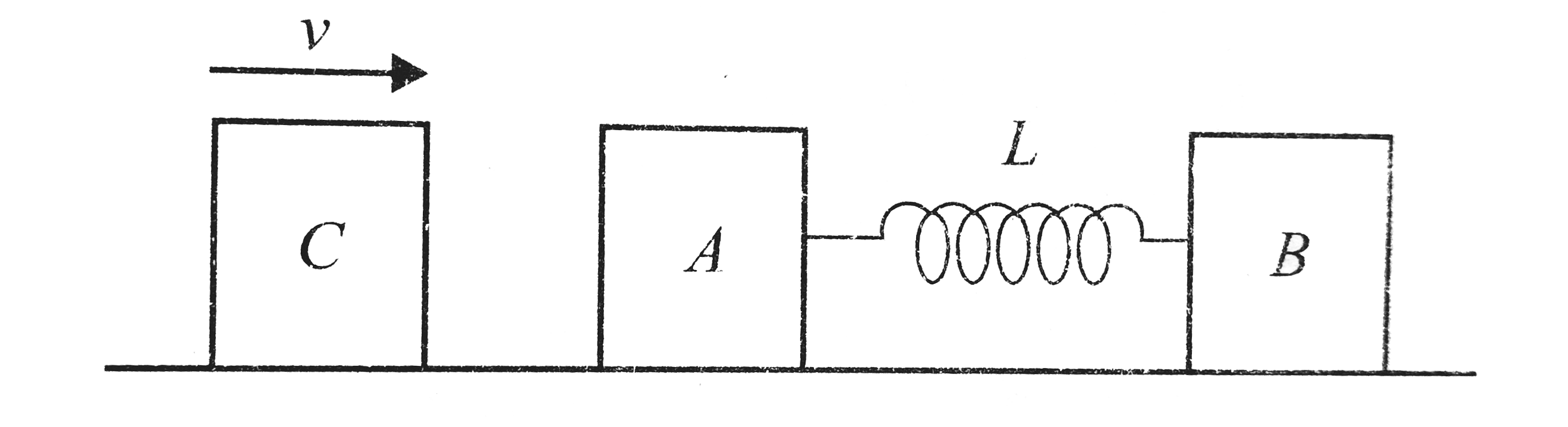
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE PHYSICS-CENTRE OF MASS-MCQ_TYPE
- A uniform bar of length 6a and mass 8m lies on a smooth horizontal tab...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks A and H. each of mass m, are connected by a massless spring...
Text Solution
|
- Two balls having linear momenta vecp(1)=phati and vecp(2)=-phati, und...
Text Solution
|
- A point mass of 1kg collides elastically with a stationary point mass ...
Text Solution
|