Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
D AND F- BLOCK ELEMENTS AND CO-ORDINATION COMPOUNDS
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)|Exercise LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS|23 VideosD AND F- BLOCK ELEMENTS AND CO-ORDINATION COMPOUNDS
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)|Exercise INTEXT QUESTIONS|33 VideosD AND F- BLOCK ELEMENTS AND CO-ORDINATION COMPOUNDS
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)|Exercise VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS|71 VideosCHEMISTRY IN EVERYDAY LIFE
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)|Exercise Intex questions|5 VideosELECTROCHEMISTRY & CHEMICAL KINETICS
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)|Exercise DAM SURE|18 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)-D AND F- BLOCK ELEMENTS AND CO-ORDINATION COMPOUNDS -SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
- Use Hund's rule to derive the electronic configuration of Ce^(3+) ion ...
Text Solution
|
- Write down the number of 3d electrons in each of the following ions : ...
Text Solution
|
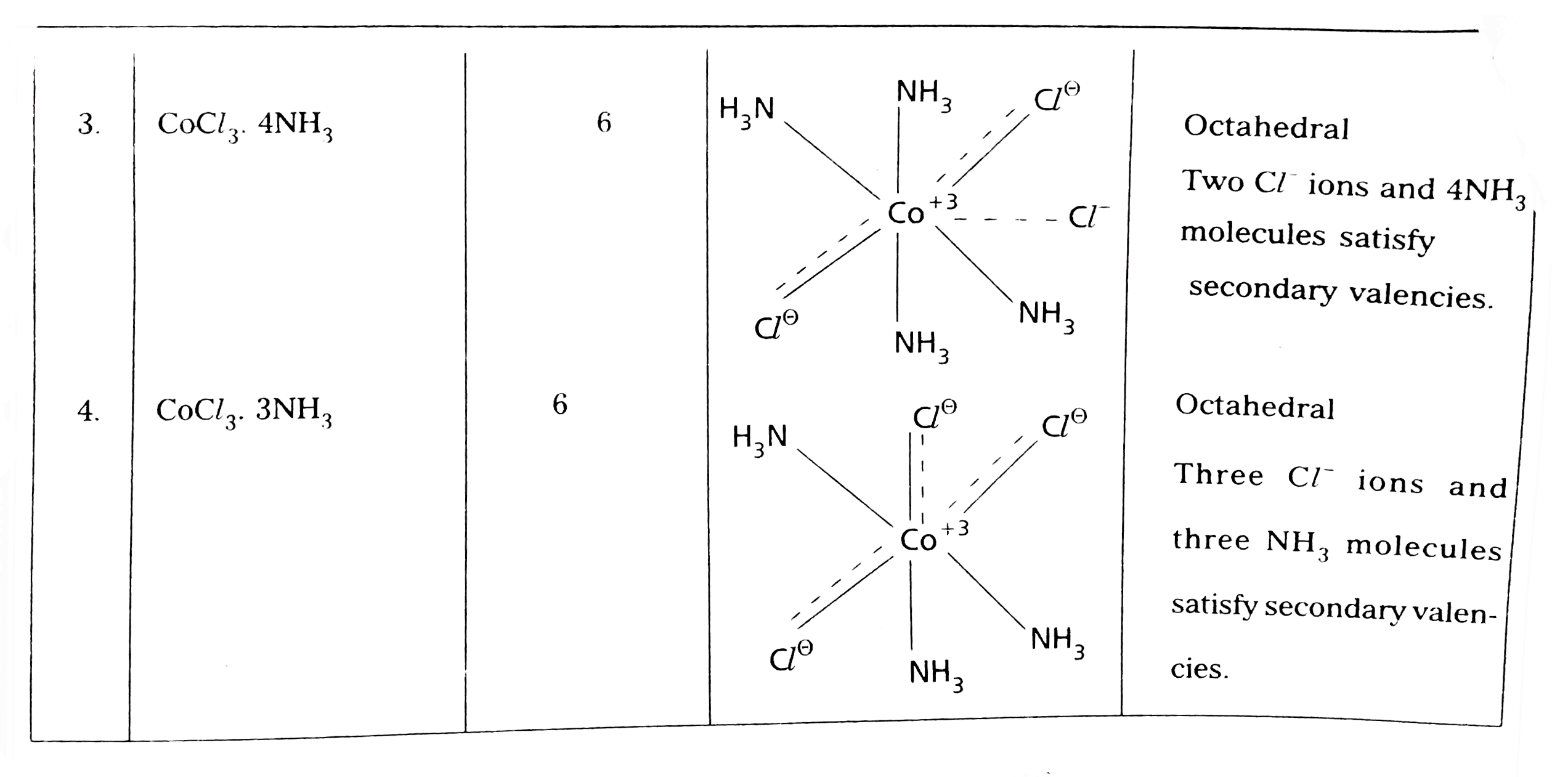
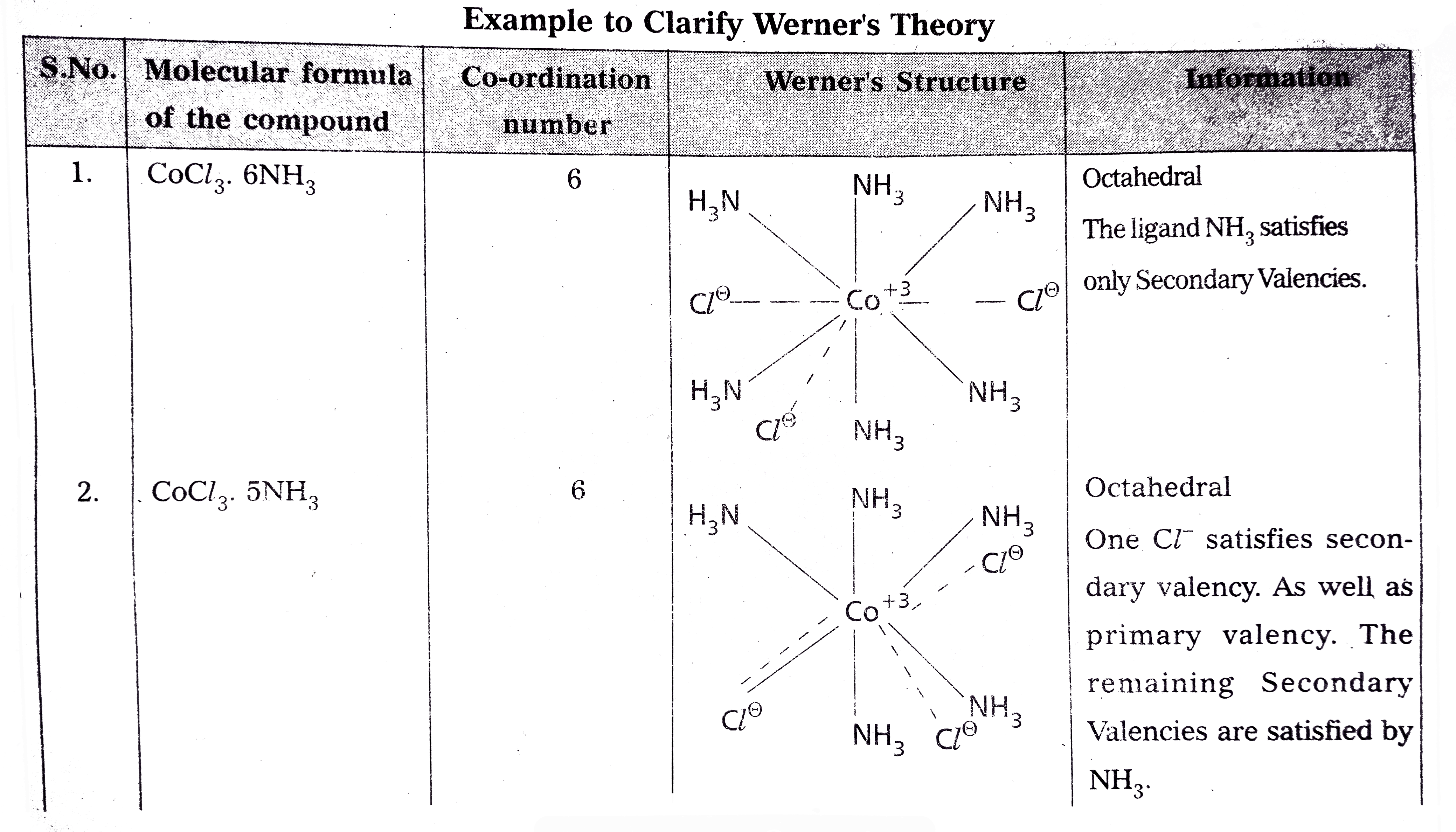
- Explain Werner's theory of coordination compounds with suitable exampl...
Text Solution
|
- Give the geometrical shapes of the following complex entities [Co(NH...
Text Solution
|
- Give the geometrical shapes of the following complex entities [Ni(CO...
Text Solution
|
- Give the geometrical shapes of the following complex entities [PtCl(...
Text Solution
|
- Give the geometrical shapes of the following complex entities [Fe(CN...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the terms Ligand
Text Solution
|
- Explain the terms Coordination number
Text Solution
|
- Explain the terms Coordination entity
Text Solution
|
- Explain the terms Central metal atom/ion.
Text Solution
|
- Explain the terms Unidentate ligand
Text Solution
|
- Explain the terms bidentate ligand
Text Solution
|
- Explain the terms polydentate ligand
Text Solution
|
- Explain the terms ambidentate ligand giving one example for each.
Text Solution
|
- What is meant by chelate effect ? Give example.
Text Solution
|
- Give the oxidation numbers of the central metal atoms in the following...
Text Solution
|
- Give the oxidation numbers of the central metal atoms in the following...
Text Solution
|
- Give the oxidation numbers of the central metal atoms in the following...
Text Solution
|
- Give the oxidation numbers of the central metal atoms in the following...
Text Solution
|