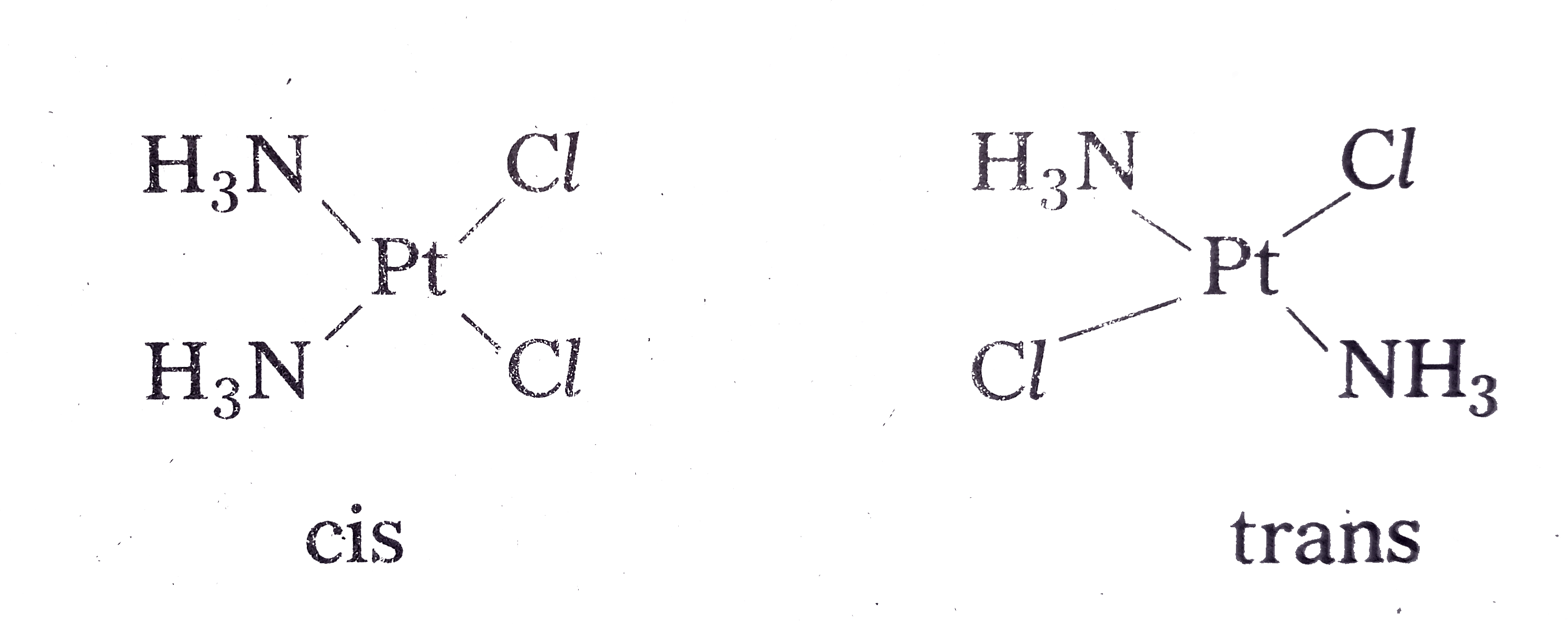Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
D AND F- BLOCK ELEMENTS AND CO-ORDINATION COMPOUNDS
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)|Exercise INTEXT QUESTIONS|33 VideosD AND F- BLOCK ELEMENTS AND CO-ORDINATION COMPOUNDS
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)|Exercise SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS|57 VideosCHEMISTRY IN EVERYDAY LIFE
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)|Exercise Intex questions|5 VideosELECTROCHEMISTRY & CHEMICAL KINETICS
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)|Exercise DAM SURE|18 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VIKRAM PUBLICATION ( ANDHRA PUBLICATION)-D AND F- BLOCK ELEMENTS AND CO-ORDINATION COMPOUNDS -LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
- Give two reactions in which transition metals or their compounds acts ...
Text Solution
|
- Describe the preparation of potassium permanganate. How does the acidi...
Text Solution
|
- Compare the chemistry of the actinoids with that of lanthanoids with r...
Text Solution
|
- How would you account for the of the d(4) species, Cr^(2+) is strongly...
Text Solution
|
- How would you account for the Cobalt (II) is stable in aqueous solutio...
Text Solution
|
- How would you account for the The d(1) configuration is very unstable ...
Text Solution
|
- Give examples and suggest reasons for the following features of the t...
Text Solution
|
- Give examples and suggest reasons for the following features of the t...
Text Solution
|
- Give examples and suggest reasons for the following features of the t...
Text Solution
|
- Compare the chemistry of the actinoids with that of lanthanoids with r...
Text Solution
|
- Explain IUPAC nomenclature of Co-ordination compounds with suitable ex...
Text Solution
|
- Explain different types of isomerism exhibited by Co-ordination compou...
Text Solution
|
- Discuss the nature of bonding and magnetic behaviour in the [Fe(CN)(6)...
Text Solution
|
- Discuss the nature of bonding and magnetic behaviour in the [FeF(6)]^(...
Text Solution
|
- Discuss the nature of bonding and magnetic behaviour in the [Co(C(2)O(...
Text Solution
|
- Discuss the nature of bonding and magnetic behaviour in the [CoF(6)]^(...
Text Solution
|
- Sketch the splitting of d orbitals in an octahedral crystal field,
Text Solution
|
- What is spectrochemical series ? Explain the difference between a weak...
Text Solution
|
- Discuss the nature of bonding in metal carbonyls.
Text Solution
|
- Explain the applications of Co-ordination compounds in different field...
Text Solution
|